Abstract
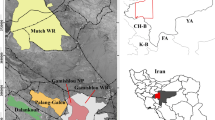
The structure and function of network is a central issue in landscape ecology. Road networks with hierarchical structure are crucial for understanding landscape dynamics. In this study, we compared the distribution of national road, provincial road, county road and rural road in the Three Parallel Rivers Region (TPRR) in Yunnan Province of China, and estimated the effect of roads (and other factors) on the spatial patterns of land use and land cover with logistic regression. In addition, we analyzed the land use and land cover change (LUCC) and landscape fragmentation in 1989–2005 along a buffer zone of the primary traffic corridor, national road G214. The results showed that, county and rural roads had much higher percentage of length extending into more natural habitats at higher elevation and steeper slope, compared with the higher level roads in this region. While the distributions of natural land cover types were dominated by environmental factors, human land use types i.e., building land and farmland types were significantly related with roads, linking more closely with lower level roads. The LUCC dynamics (1989–2005) of the G214 buffer zone showed a general trend of land transformation from conifer forests and valley arid shrubs to building land and farmland, and from ice and snow to alpine shrubs and forests. With the length of G214 unchanged during the time, the overall landscape pattern changed little in the buffer zone, but habitat fragmentation and area decrease had occurred for the natural vegetation types, in contrast to patch mergence and expansion of human land use types, and landscape fragmentation was intensified above 2500 m a.s.l. but declined below the elevation. The results indicated the dynamics of landscape composition and patch type level distribution in spite of the stability of the overall landscape pattern, and implied the potential role of roads, especially the low level roads on landscape changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askins R A, 1994. Open corridors in a heavily forested landscape: Impact on shrubland and forest-interior birds. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 22(2): 339–347.
Benítez-López A, Rob A, Pita A V et al., 2010. The impacts of roads and other infrastructure on mammal and bird populations: A meta-analysis. Biological Conservation, 143(6): 1307–1316. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2010.02.009
Boer E P J, Beurs K M, Hartkamp A D, 2001. Kriging and thin plate splines for mapping climate variables. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 3(2): 146–154. doi: 10.1016/S0303-2434(01)85006-6
Campbell J E, Gibson D J, 2001. The effect of seeds of exotic species transported via horse dung on vegetation along trail corridors. Plant Ecology, 157(1): 23–35. doi: 10.1023/A: 1013751615636
Chen Jiang, Cao Likun, Chen Yang, 2004. Value of world natural heritage’ Three Parallel Rivers’—Scene diversity. World Natural Heritage, 22(5): 22–26. (in Chinese)
Chen Xueping, Guan Lei, Wang Xinjun et al., 2013. The impacts of road network on the habitats of animals and plants in the Three Parallel Rivers region. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development (Technical Application Edition), 12: 333–336. (in Chinese)
Coffin A W, 2007. From roadkill to road ecology: A review of the ecological effects of roads. Journal of Transport Geography, 15(5): 396–406. doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2006.11.006
Forman R T T, 1998. Road ecology: A solution for the giant embracing us. Landscape Ecology, 13(4): 3–5. doi: 10.1023/A:1008036602639
Forman R T T, Sperling D, Bissonette J A et al., 2003. Road Ecology: Science and Solutions. Washington, D.C.: Island Press, 481.
Friedl M A, McIver D K, Hodges J C F et al., 2002. Global land cover mapping from MODIS: Algorithms and early results. Remote Sensing of Environment, 83(1–2): 287–302. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00078-0
Fu W, Liu S, Dong S, 2010. Landscape pattern changes under the disturbance of road networks. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2: 859–867. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.097
Grant E H C, Lowe W H, Fagan W F, 2007. Living in the branches: Population dynamics and ecological processes in dendritic networks. Ecology Letters, 10(2): 165–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.01007.x
Hawbaker T J, Radeloff V C, Clayton M K et al., 2006. Road development, housing growth, and landscape fragmentation in northern Wisconsin: 1937–1999. Ecological Applications, 16(3): 1222–1237. doi:10.1890/1051-0761(2006)016[1222:RDHGAL]2.0.CO;2
Jin Zhenzhou, 2002. Floristic Features of Dry-hot and Dry-warm Valleys, Yunnan and Sichuan. Kunming: Yunnan Science & Technology Press, 226. (in Chinese)
Kenworthy J R, 2006. The eco-city: Ten key transport and planning dimensions for sustainable city development. Environment and Urbanization, 18(1): 67–85. doi: 10.1177/0956247806063947
Lámmer S, Gehlsen B, Helbing D, 2006. Scaling laws in the spatial structure of urban road networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 363(1): 89–95. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2006.01.051
Li Bingyuan, 1989. Geomorphologic regionalization of the Hengduan Mountains region. Mountain Research, 7(1): 13–20. (in Chinese)
Li Chuantong, Zhang Guangxian, 2013. The farm household’s behavior behind agricultural non-point source pollution: A panel analysis on Changle County in Shandong Province. Areal Research and Development, 32(1): 158–164. (in Chinese)
Li H, Wu J, 2004. Use and misuse of landscape indices. Landscape Ecology, 19(4): 389–399. doi: 10.1023/B:LAND.0000030441.15628.d6
Li Junsheng, Zhang Xiaolan, Wu Xiaopu et al., 2009. Ecological Impacts from Road Traffic: A Review. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 18(3): 1169–1175. (in Chinese)
Li Yuehui, Hu Yuanman, Li Xiuzhen et al., 2003. Research progress of road ecology. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14(3): 447–452. (in Chinese)
Liang Jun, 2010. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Land Use/Cover and Landscape Fragmentation of the Three Parallel Rivers Region in Northwestern Yunnan Province. Beijing: Peking University. (in Chinese)
Lin Zhiguang, Zhang Jiacheng, 1985. The Climate in China. Xi’an: Shaanxi People’s Publishing House. (in Chinese)
Liu Shiliang, Guo Xudong, Fu Bojie et al., 2006. Effects of road networks on land ecological security: A case study in a transitional area of the Loess Plateau. Arid Zone Research, 23(1): 127–132. (in Chinese)
Liu Shiliang, Wen Minxia, Cui Baoshan et al., 2008. Ecological effect of road based on network analysis: A case study in Lancang River Valley. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(4): 1672–1680. (in Chinese)
Liu Shiliang, Yang Zhifeng, Cui Baoshan et al., 2005. Effects of road on landscape and its ecological risk assessment: A case study of Lancangjiang River valley. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 24(8): 897–901. (in Chinese)
Lu Dadao, 2002. Formation and dynamics of the ‘Pole-Axis’ spatial system. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 22(1): 1–6. (in Chinese)
Luo Renfu, Zhang Linxiu, Zhao Qiran et al., 2011. Trends on public infrastructure and public investment priority in rural China. Chinese Soft Science Magazine, 9: 30–39. (in Chinese)
McGarigal K, Cushman S A, Neel M C et al., 2002. Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps. Amherst, Massachusetts, USA: University of Massachusetts.
Monz C A, Cole D N, Leung Y F et al., 2010. Sustaining visitor use in protected areas: Future opportunities in recreation ecology research based on the USA experience. Environmental Management, 45(3): 551–562. doi: 10.1007/s00267-009-9406-5
National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2006. Chinese Statistics Yearbook 2005. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese)
Nega T, Smith C, Bethune J et al., 2012. An analysis of landscape penetration by road infrastructure and traffic noise. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 36(3): 245–256. doi: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2011.09.001
Nepal S K, 2003. Trail impacts in Sagarmantha (Mt. Everest) National Park, Nepal: A logistic regression analysis. Environmental Management, 32(3): 312–321. doi: 10.1007/s00267-003-0049-7
Olive N D, Marion J L, 2009. The influence of use-related, environmental, and managerial factors on soil loss from recreational trails. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(3): 1483–1493. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.10.004
Peeters P, Szimba E, Duijnisveld M, 2007. Major environmental impacts of European tourist transport. Journal of Transport Geography, 15(2): 83–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2006.12.007
Pickering C M, Hill W, 2007. Impacts of recreation and tourism on plant biodiversity and vegetation in protected areas in Australia. Journal of Environmental Management, 85(4): 791–800. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.11.021
Pickering C, Castley J G, Hill W et al., 2010b. Environmental, safety and management issues of unauthorised trail technical features for mountain bicycling. Landscape and Urban Planning, 97(1): 58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.04.012
Pickering C, Hill W, Newsome D et al., 2010a. Comparing hiking, mountain biking and horse riding impacts on vegetation and soils in Australia and the United States of America. Journal of Environmental Management, 91(3): 551–562. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.09.025
Prestemon J P, Pye J M, Butry D T et al., 2002. Understanding broadscale wildfire risks in a human-dominated landscape. Forest Science, 48(4): 685–693.
Qiu Qingan, Lin Boxiong, 2004. Estimate the spatial distribution of temperature and precipitation in Taiwan from the station data. Atmospheric Science, 32(4): 329–350. (in Chinese)
Sherman R, Mullen R, Li H M et al., 2008. Spatial patterns of plant diversity and communities in Alpine ecosystems of the Hengduan Mountains, Northwest Yunnan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 1(2): 117–136. doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtn012
Stevens V M, Polus E, Wesselingh R A et al., 2004. Quantifying functional connectivity: Experimental evidence for patch-specific resistance in the Natterjack toad (Bufo calamita). Landscape Ecology, 19(8): 829–842. doi: 10.1007/s10980-005-0166-1
Strahler A N, 1952. Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography. Geological Society American Bulletin, 63(11): 1117–1142. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1952)63[1117:HAAOET]2.0.CO;2
van der Ree R, Jaeger J A G, van der Grift E A et al., 2011. Effects of roads and traffic on wildlife populations and landscape function: Road ecology is moving towards larger scales. Ecology and Society, 16(1): 48.
Wang Jinliang, Jiang Lianfang, Ma Jian, 2000. An analysis on driving force of land use change in nationality community of ‘Three Rivers’ in northwest Yunnan Province. Areal Research and Development, 19(4): 62–64. (in Chinese)
Wang Juan, Cui Baoshan, Liu Shiliang et al., 2007. The effects of road network on the ecosystem services in the paralleled ridge-villey region. Chinese Sciences Bulletin, 52(Supp. II): 154–165. (in Chinese)
Wang Juan, Cui Baoshan, Liu Shiliang et al., 2008. Effects of different leve1 road networks on landscape structure health in the Longitudina1 Range-Gorge Region. Acta Scientiae Cireumstantiae, 28(2): 26l–268. (in Chinese)
Xie Weijia, Li Zhaoguang, Li Yan et al., 2005. A preliminary report on the resources of wild genus Cypripedium in the Three Parallel Rivers Region. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 24(2): 28–30. (in Chinese)
Xu J, Wilkes A, 2004. Biodiversity impact analysis in Northwest Yunnan, Southwest China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13(5): 959–983. doi: 10.1023/B:BIOC.0000014464.80847.02
Yang Qinye, Shen Kangda. 1984. On vertical zonation of northwestern Yunnan. Acta Geographica Sinica, 39(2): 141–147. (in Chinese)
Yao Zukang, 1993. Road Design Handbook—Road Surface. Beijing: China Communications Press. (in Chinese)
Ying Lingxiao, Shen Zehao, Chen Jiding et al., 2014. Spatio-temporal patterns of road network and road development priority in Three Parallel Rivers Region in Yunnan, China: An evaluation based on modified kernel distance estimate. Chinese Geographical Science, 24(1): 39–49. doi: 10.1007/s11769-014-0654-9 (in press)
Yu Rongrong, Wang Kelin, Yue Yuemin, 2010. Farmland changes and its driving forces analysis based on logistic regression model in Hechi, northwestern Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 19(2): 186–191. (in Chinese)
Zhang Yiguang, 1998. Several issues concerning vertical climate of the Hengduan Mountains. Resources Science, 20(3): 12–19. (in Chinese)
Zhao Jun, 2006. Landform Pattern of Land Use/Cover Change and Its Effects on Soil Erosion, in Xiangxi River Drainage Area. Beijing: Peking University. (in Chinese)
Zheng Yu, Li Xiaowen, Cui Baoshan et al., 2009. The multi-scale effect of road network on the ecosystem in Longitudinal Range-Gorge region of Yunnan Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(8): 4267–4277. (in Chinese)
Zhou Qigang, Zhou Wancun, Zhang Baolei et al., 2006. Study on land use and land cover pattern in Three Rivers Parallel Area based on RS and GIS. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(6): 156–162. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41371190, 31021001), Scientific and Technical Projects of Western China Transportation Construction, Ministry of Transport of China (No. 2008-318-799-17)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, J., Liu, Y., Ying, L. et al. Road impacts on spatial patterns of land use and landscape fragmentation in three parallel rivers region, Yunnan Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 24, 15–27 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-014-0652-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-014-0652-y