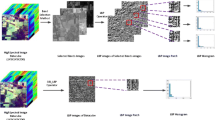
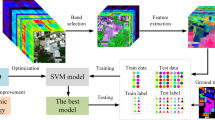
Abstract
A novel approach using volumetric texture and reduced-spectral features is presented for hyperspectral image classification. Using this approach, the volumetric textural features were extracted by volumetric gray-level co-occurrence matrices (VGLCM). The spectral features were extracted by minimum estimated abundance covariance (MEAC) and linear prediction (LP)-based band selection, and a semi-supervised k-means (SKM) clustering method with deleting the worst cluster (SKMd) bandclustering algorithms. Moreover, four feature combination schemes were designed for hyperspectral image classification by using spectral and textural features. It has been proven that the proposed method using VGLCM outperforms the gray-level co-occurrence matrices (GLCM) method, and the experimental results indicate that the combination of spectral information with volumetric textural features leads to an improved classification performance in hyperspectral imagery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelo N P, Haertel V (2003). On the application of Gabor filtering in supervised image classification. Int J Remote Sens, 24(10): 2167–2189
Benediktsson J A, Palmason J A, Sveinsson J R (2005). Classification of hyperspectral data from urban areas based on extended morphological profiles. IEEE Trans Geosci Rem Sens, 43(3): 480–491
Bernabe S, Marpu P R, Plaza A, Mura M D, Benediktsson J A (2014). Spectral-spatial classification of multispectral images using kernel feature space representation. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett, 11(1): 288–292
Chang C I (2003). Hyperspectral Imaging: Techniques for Spectral Detection and Classification. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, 13–15
Chang C I (2013). Hyperspectral Data Processing: Algorithm Design and Analysis. New Jersey: Wiley-Interscience, 1–5
Chen C, Li W, Tramel E W, Cui M, Prasad S, Fowler J E (2014a). Spectral-spatial preprocessing using multihypothesis prediction for noise-robust hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 7(4): 1047–1059
Chen C, Li W, Tramel E W, Fowler J E (2014b). Reconstruction of hyperspectral imagery from random projections using multihypothesis prediction. IEEE Trans Geosci Rem Sens, 52(1): 365–374
Gamba P, Dell’ Acqua F, Lisini G, Trianni G (2007). Improved VHR urban area mapping exploiting object boundaries. IEEE Trans Geosci Rem Sens, 45(8): 2676–2682
Haralick R M, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I H (1973). Texture features for image classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern, 3(6): 610–621
Huang X, Zhang L, Gong W (2011). Information fusion of aerial images and LIDAR data in urban areas: vector stacking, re-classification, and post-processing approaches. Int J Remote Sens, 32(1): 69–84
Jackson Q, Landgrebe D (2002). Adaptive bayesian contextual classification based on markov random fields. IEEE Trans Geosci Rem Sens, 40(11): 2454–2463
Li J, Bioucas-Dias J, Plaza A (2012). Spectral-spatial hyperspectral image segmentation using subspace multinomial logistic regression and markov random fields. IEEE Trans Geosci Rem Sens, 50(3): 809–823
Liu K, Du Q, Yang H, Ma B (2010). Optical flow and principle component analysis-based motion detection in outdoor videos. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process, 2010: 680623
Liu K, Ma B, Du Q, Chen G (2012). Fast motion detection from airborne videos using graphics processing units. J Appl Remote Sens, 6(1): 061505
Marceau D J, Howarth P J, Dubois J M, Gratton D J (1990). Evaluation of the grey-level co-occurrence matrix method, for land-cover classification using SPOT imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Rem Sens, 28(4): 513–519
Mokji M M, Bakar S A R A (2007). Adaptive thresholding based on cooccurrence matrix edge information. Journal of Computers, 2(8): 44–52
Mura M D, Villa A, Benediktsson J A, Chanussot J, Bruzzone L (2011). Classification of hyperspectral images by using extended morphological attribute profiles and independent component analysis. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett, 8(3): 541–545
Nyoungui A N, Tonye E, Akono A (2002). Evaluation of speckle filtering and texture analysis methods for land cover classification from SAR images. Int J Remote Sens, 23(9): 1895–1925
Plaza J, Plaza A, Barra C (2009). Multi-channel morphological profiles for classification of hyperspectral image data using support vector machines. Sensors (Basel Switzerland), 9(1): 196–218
Rahman A F, Gamon J A, Sims D A, Schmidts M (2003). Optimum pixel size for hyperspectral studies of ecosystem function in southern California chaparral and grassland. Remote Sens Environ, 84(2): 192–207
Rajadell O, Garcia-Sevilla P, Pla F (2013). Spectral-spatial pixel characterization using gabor filters for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett, 10(4): 860–864
Su H, Du Q (2012). Hyperspectral band clustering and band selection for urban land cover classification. Geocarto Int, 27(5): 395–411
Su H, Sheng Y, Du P, Liu K (2012). Adaptive affinity propagation with spectral angle mapper for semi-supervised hyperspectral band selection. Appl Opt, 51(14): 2656–2663
Su H, Yang H, Du Q, Sheng Y (2011). Semi-supervised band clustering for dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett, 8(6): 1135–1139
Tsai F, Chang C K, Rau J Y, Lin T H, Liu G R (2007). 3D computation of gray level co-occurrence in hyperspectral image cubes. Lect Notes Comput Sci, 4679: 429–440
Yang H, Du Q, Su H, Sheng Y (2011). An efficient method for supervised hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett, 8(1): 138–142
Yang H, Ma B, Du Q, Yang C (2010). Improving urban land use and land cover classification from high-spatial-resolution hyperspectral imagery using contextual information. J Appl Remote Sens, 4(1): 041890
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Sheng, Y., Du, P. et al. Hyperspectral image classification based on volumetric texture and dimensionality reduction. Front. Earth Sci. 9, 225–236 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-014-0473-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-014-0473-4