Abstract
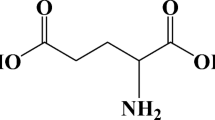
In this work, we report on synergistic effect of chloride ion and albumin on the corrosion of pure magnesium through corrosion tests. We show that the adsorption of albumin mainly affects the anodic polarization behavior of pure magnesium in NaCl solution. Low concentration of albumin enhances the reaction reactivity of pure magnesium and the initial evolvement of hydrogen at the initial immersion time. Addition of 1 g/L albumin provides limited corrosion control for pure magnesium in NaCl solution. In comparison with low concentration albumin, addition of 10 g/L albumin can effectively inhibit the further dissolution of pure magnesium in test solutions with NaCl concentration of 0.2–0.8 wt.%, but this effect lowers gradually with increasing the concentration of chloride ion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamamoto A, Hiromoto S. Effect of inorganic salts amino acids and proteins on the degradation of pure magnesium in vitro. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2009, 29(5): 1559–1568
Witte F, Hort N, Vogt C, et al. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2008, 12(5–6): 63–72
Xin Y, Hu T, Chu P K. In vitro studies of biomedical magnesium alloys in a simulated physiological environment: a review. Acta Biomaterialia, 2011, 7(4): 1452–1459
Virtanen S. Biodegradable Mg and Mg alloys: Corrosion and biocompatibility. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2011, 176(20): 1600–1608
Witte F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: a review. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6(5): 1680–1692
Balamurugan A, Rajeswari S, Balossier G, et al. Corrosion aspects of metallic implants — An overview. Materials and Corrosion, 2008, 59(11): 855–869
Vogt C, Bechstein K, Gruhl S, et al. Investigation of the degradation of biodegradable Mg implant alloys in vitro and in vivo by analytical methods. In: Kainer K U, Weimar D G M, eds. Proceeding of the 8th International Conference on Magnesium Alloys and Their Applications. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2010, 1162–1174
Mueller W-D, de Mele MF L, Nascimento ML, et al. Degradation of magnesium and its alloys: dependence on the composition of the synthetic biological media. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2009, 90(2): 487–495
Liu C, Xin Y, Tian X, et al. Degradation susceptibility of surgical magnesium alloy in artificial biological fluid containing albumin. Journal of Materials Research, 2007, 22(7): 1806–1814
Liu C L, Wang Y J, Zeng R C, et al. In vitro corrosion degradation behaviour of Mg-Ca alloy in the presence of albumin. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(10): 3341–3347
Gu X N, Zheng Y F, Chen L J. Influence of artificial biological fluid composition on the biocorrosion of potential orthopedic Mg- Ca, AZ31, AZ91 alloys. Biomedical Materials, 2009, 4(6): 065011
Rettig R, Virtanen S. Time-dependent electrochemical characterization of the corrosion of a magnesium rare-earth alloy in simulated body fluids. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2008, 85(1): 167–175
Hornberger H, Witte F, Hort N, et al. Effect of fetal calf serum on the corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloys. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2011, 176(20): 1746–1755
Xin Y C, Hu T, Chu P K. Influence of test solutions on in vitro studies of biomedical magnesium alloys. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(7): C238–C243
Xin Y, Huo K, Tao H, et al. Influence of aggressive ions on the degradation behavior of biomedical magnesium alloy in physiological environment. Acta Biomaterialia, 2008, 4(6): 2008–2015
Cheng X, Roscoe S G. Corrosion behavior of titanium in the presence of calcium phosphate and serum proteins. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(35): 7350–7356
Hara N, Kobayashi Y, Kagaya D, et al. Formation and breakdown of surface films on magnesium and its alloys in aqueous solutions. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(1): 166–175
Song G L, Atrens A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys. Advanced Engineering Materials, 1999, 1(1): 11–33
Roach P, Eglin D, Rohde K, et al. Modern biomaterials: a review — bulk properties and implications of surface modifications. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2007, 18(7): 1263–1277
Klinger A, Steinberg D, Kohavi D, et al. Mechanism of adsorption of human albumin to titanium in vitro. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1997, 36(3): 387–392
Ouerd A, Alemany-Dumont C, Berthomé G, et al. Reactivity of titanium in physiological medium I. Electrochemical characterization of the metal/protein interface. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2007, 154(10): C593–C601
Padilla N, Bronson A. Electrochemical characterization of albumin protein on Ti-6Al-4V alloy immersed in a simulated plasma solution. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2007, 81(3): 531–543
Song S G, Atrens A, Wu X L, et al. Corrosion behaviour of AZ21, AZ501 and AZ91 in sodium chloride. Corrosion Science, 1998, 40(10): 1769–1791
Wang L, Shinohara T, Zhang B P. Influence of chloride, sulfate and bicarbonate anions on the corrosion behavior of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 496(1–2): 500–507
Qu Q, Ma J, Wang L, et al. Corrosion behaviour of AZ31B magnesium alloy in NaCl solutions saturated with CO2. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(4): 1186–1193
Cohavi O, Corni S, De Rienzo F, et al. Protein-surface interactions: challenging experiments and computations. Journal of Molecular Recognition, 2010, 23(3): 259–262
Song G L, Bowles A L, StJohn D H. Corrosion resistance of aged die cast magnesium alloy AZ91D. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 366(1): 74–86
Song YW, Shan D Y, Chen R S, et al. Biodegradable behaviors of AZ31 magnesium alloy in simulated body fluid. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2009, 29(3): 1039–1045
Zhang Y J, Yan CW, Wang F H, et al. Electrochemical behavior of anodized Mg alloy AZ91D in chloride containing aqueous solution. Corrosion Science, 2005, 47(11): 2816–2831
Contu F, Elsener B, Böhni H. Characterization of implant materials in fetal bovine serum and sodium sulfate by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. I. Mechanically polished samples. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2002, 62(3): 412–421
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, CL., Zhang, Y., Zhang, CY. et al. Synergistic effect of chloride ion and albumin on the corrosion of pure magnesium. Front. Mater. Sci. 8, 244–255 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-014-0251-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-014-0251-y