Abstract
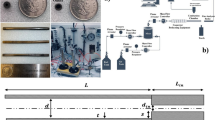
Laminar flame speeds of hydrogen/natural gas/air mixtures have been measured over a full range of fuel compositions (0–100% volumetric fraction of H2) and a wide range of equivalence ratio using Bunsen burner. High sensitivity scientific CCD camera is use to capture the image of laminar flame. The reaction zone area is employed to calculate the laminar flame speed. The initial temperature and pressure of fuel air mixtures are 293 K and 1 atm. The laminar flame speeds of hydrogen/air mixture and natural gas/air mixture reach their maximum values 2.933 and 0.374 m/s when equivalence ratios equal to 1.7 and 1.1, respectively. The laminar flame speeds of hydrogen/natural gas/air mixtures rise with the increase of volumetric fraction of hydrogen. Moreover, the increase in laminar flame speed as the volumetric fraction of hydrogen increases presents an exponential increasing trend versus volumetric fraction of hydrogen. Empirical formulas to calculate the laminar flame speeds of hydrogen, natural gas, and hydrogen/natural gas mixtures are also given. Using these formulas, the laminar flame speed at different hydrogen fractions and equivalence ratios can be calculated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zaporowski B, Szczerbowski R. Energy analysis of technological systems of natural gas fired combined heat-and-power plants. Applied Energy, 2003, 75(1–2): 43–50
Rousseau S, Lemoult B, Tazerout M. Combustion characteristics of natural gas in a lean burn spark-ignition engine. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Part D, Journal of Automobile Engineering, 1999, 213(5): 481–489
Blarigan P V, Keller J O. A hydrogen fueled internal combustion engine designed for single speed/power operation. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 1998, 23(7): 603–609
Akansu S O, Dulger Z, Kahraman N, Veziroglu T N. Internal combustion engines fuelled by natural gas-hydrogen mixtures. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2004, 29(14): 1527–1539
Scholte T G, Vaags P B. Burning velocities of mixtures of hydrogen, carbon monoxide and methane with air. Combustion and Flame, 1959, 3: 511–524
Liu Y, Lenze B, Leuckel W. Investigation on the laminar and turbulent burning velocities of premixed lean and rich flames of methane-hydrogen-air mixtures. Prog Astronaut Aeronaut, 1991, 131: 259–274
Milton B E, Keck J C. Laminar burning velocities in stoichiometric hydrogen and hydrogen-hydrocarbon gas mixtures. Combustion and Flame, 1984, 58(1): 13–22
Yu G, Law C K, Wu C K. Laminar flame speed of hydrocarbon + air mixtures with hydrogen addition. Combustion and Flame, 1986, 63(3): 339–347
Ren J Y, Qin W, Egolfopoulos F N, Tsotsis T T. Strain-rate effects on hydrogen-enhanced lean premixed combustion. Combustion and Flame, 2001, 124(4): 717–720
Ren J Y, Qin W, Egolfopoulos F N, Mak H, Tsotsis T T. Methane reforming and its potential effect on the efficiency and pollutant emissions of lean methane-air combustion. Chemical Engineering Science, 2001, 56(4): 1541–1549
Halter F, Chauveau C, Djebaïli-Chaumeix N, Gökalp I. DjebaIli-Chaumeix N, Gokalp I. Characterization of the effects of pressure and hydrogen concentration on laminar burning velocities of methane-hydrogen-air mixtures. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2005, 30(1): 201–208
Law C K, Kwon O C. Effects of hydrocarbon substitution on atmospheric hydrogen-air flame propagation. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2004, 29(8): 867–879
Miller D R, Evers R L, Skinner G B. Effects of various inhibitors on hydrogen-air flame speeds. Combustion and Flame, 1963, 7: 137–142
Huang Z H, Zhang Y, Zeng K, Liu B, Wang Q, Jiang D M. Measurements of laminar burning velocities for natural gas-hydrogen-air mixtures. Combustion and Flame, 2006, 146(1-2): 302–311
Law C K, Sung C J. Structure, aerodynamics, and geometry of premixed flamelets. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2000, 26(4–6): 459–505
Natarajan J, Lieuwen T, Seitzman J. Laminar flame speeds of H2/CO mixtures: effect of CO2 dilution, preheat temperature, and pressure. Combustion and Flame, 2007, 151(1–2): 104–119
Liu D D S, Macfarlane R. Laminar burning velocities of hydrogen-air and hydrogen-air-steam flames. Combustion and Flame, 1983, 49(1–3): 59–71
Ilbas M, Crayford A P, Yilmaz I, Bowen P J, Syred N. Laminar burning velocities of hydrogen-air and hydrogen-methane-air mixtures: an experimental study. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2006, 31(12): 1768–1779
Takahashi F, Mizomoto M, Ikai S. Laminar burning velocities of hydrogen/oxygen/inert gas mixtures. Alternative Energy Sources. III. Nuclear Energy/Synthetic Fuels, 1983, 5: 447
Dowdy D R, Smith D B, Taylor S C, Williams A. The use of expanding spherical flames to determine burning velocities and stretch effects in hydrogen-air mixtures. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 1990, 23: 325–332
Aung K T, Hassan M I, Faeth G M. Flame stretch interactions of laminar premixed hydrogen/air flames at normal temperature and pressure. Combustion and Flame, 1997, 109(1–2): 1–24
Lamoureux N, Djebaili-Chaumeix N, Paillard C E. Laminar flame velocity determination for H2-air-He-CO2 mixtures using the spherical bomb method. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2003, 27(4): 385–393
Huang Z H, Zhang Y, Zeng K, Liu B, Wang Q, Jiang D M. Measurements of laminar burning velocities for natural gas-hydrogen-air mixtures. Combustion and Flame, 2006, 146(1–2): 302–311
Vagelopoulos C M, Egolfopoulos F N. Laminar flame speeds and extinction strain rates of mixtures of carbon monoxide with hydrogen, methane, and air. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 1994, 25(1): 1317–1323
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, C., Zhou, Q., Zhang, X. et al. Experimental study on the laminar flame speed of hydrogen/natural gas/air mixtures. Front. Chem. Eng. China 4, 417–422 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-010-0515-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-010-0515-8