Abstract
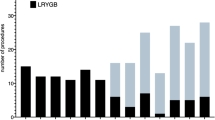
Robotic Roux en Y gastric bypass (R-RYGB) is becoming more common due to the shifting trend toward robotic gastrointestinal surgery. The goal of this study is to determine if R-RYGB can be safely implemented at a robotic bariatric surgery program in a community hospital with similar results to laparoscopic RYGB (L-RYGB) in a cost-effective manner. A total of 50 R-RYGB procedures were performed with the Xi and the X da Vinci systems and compared with 50 L-RYGB cases by a single surgeon from October 2018 to January 2020 at an acute-care community hospital in a rural setting with a high-volume MBSAQIP-accredited program. A retrospective chart review was conducted with IRB approval and statistical analysis of 30-day morbidity, mortality, re-interventions, and resolution of co-morbidities, with financial analysis of cost reduction. Both groups were similar in age, gender, ASA class, co-morbidities, and body mass index (BMI). There was no mortality or anastomotic leak. The 30-day morbidity for R-RYGB was 10.0% with a re-operation rate of 4.0%. There were no conversions to open, and the mean hospital length of stay was 2.22 ± 1.19 days. There were no statistically significant differences between R-RYGB and L-RYGB with respect to any measured outcome, including intraoperative time (121.94 vs. 113.52, respectively; p = 0.1495). However, when incidences and percentages were used, R-RYGB had improved performance for most of the outcomes measuring safety. There was an average cost reduction of $816.90 per case (total saving of $40,845.00 for 50 cases) in the R-RYGB by transitioning from a hybrid approach to a totally robotic approach. R-RYGB appears to be as safe as L-RYGB and can be performed in a rural community hospital while maintaining a low complication rate, achieving a high co-morbidity resolution rate, and saving costs with a totally robotic approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colquitt JL, Pickett K, Loveman E, Frampton GK (2014) Surgery for weight loss in adults (Review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 8:1–184
Chang SH et al (2014) Bariatric surgery: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Surg 149(3):275–287. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2013.3654
Cirocchi R et al (2013) Current status of robotic bariatric surgery: a systematic review. BMC Surg 13: 53. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2482/13/53
Thorell A et al (2016) Guidelines for perioperative care in bariatric surgery: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Society recommendations. World J Surg 40:2065–2083. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-016-3492-3
Acquafresca PA, Palermo M, Rogula T, Duza GE, Serra E (2015) Most common robotic bariatric procedures: review and technical aspects. Ann Surg Innov Res 9:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13022-015-0019-9
Avgousti S et al (2016) Medical telerobotic systems: current status and future trends. Biomed Eng Online 15:96. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-016-0217-7
Shah J, Vyas A, Vyas D (2014) The history of robotics in surgical specialties. Am J Robot Surg 1(1):12–20. https://doi.org/10.1166/ajrs.2014.1006
Lanfranco AR, Castellanos AE, Desai JP, Meyers WC (2004) Robotic surgery: a current perspective. Ann Surg 239(1):14–21. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000103020.19595.7d
Antoniou SA, Antoniou GA, Antoniou AI, Granderath FA (2015) Past, present and future of minimally invasive abdominal surgery. JSLS 19(3):e2015.0052. https://doi.org/10.4293/JSLS.2015.00052
Bindal V et al (2015) Review of contemporary role of robotics in bariatric surgery. J Minim Access Surg 11(1):16–21. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-9941.147673
Fourman MM, Saber AA (2012) Robotic bariatric surgery: a systematic review. Surg Obes Relat Dis 8(4):438–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2012.02.012
Bhatia P et al (2014) Robot-assisted sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese versus super obese patients. JSLS 18(3):e2014.00099. https://doi.org/10.4293/JSLS.2014.00099
Bailey GJ, Hayden JA, Davis PJ, Liu RY, Haardt D, Ellsmere J (2014) Robotic versus laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) in obese adults ages 18 to 65 years: a systematic review and economic analysis. Surg Endosc 28(2):414–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3217-8
Buchs NC et al (2013) Robot-assisted Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for super obese patients: a comparative study. Obes Surg 23(3):353–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0824-8
Stefanidis D, Bailey SB, Kuwada T, Simms C, Gersin K (2018) Robotic gastric bypass may lead to fewer complications compared to laparoscopy. Surg Endosc 32(2):610–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5710-y
Mohr CJ, Nadzam GS, Curet MJ (2005) Totally robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Arch Surg 140(8):779–786
Benizri E et al (2013) Perioperative outcomes after totally robotic gastric bypass: a prospective nonrandomized controlled study. Am J Surg 206(2):145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2012.07.049
Buchs NC, Pugin F, Azagury DE, Huber O, Chassot G, Morel P (2014) Robotic revisional bariatric surgery: a comparative study with laparoscopic and open surgery. Int J Med Robot 10(2):213–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.1549
Bindal V, Gonzalez-Heredia R, Elli EF (2015) Outcomes of robotic-assisted Roux-en-Y gastric bypass as a reoperative bariatric procedure. Obes Surg 25(10):1810–1815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-015-1632-8
Acevedo E, Mazzei M, Zhao H, Lu X, Soans R, Edwards MA (2019) Outcomes in conventional laparoscopy versus robotic-assisted primary bariatric surgery: a retrospective, case-controlled study of the MBSAQIP database. Surg Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06915-7
Li K, Zou J, Tang J, Di J, Han X, Zhang P (2016) Robotic versus laparoscopic bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg 26:3031–3044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-016-2408-5
Sanchez BR, Mohr CJ, Morton JM, Safadi BY, Alami RS, Curet MJ (2005) Comparison of totally robotic laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and traditional laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis 1(6):549–554
Moon RC, Gutierrez JC, Royall NA, Teixeira AF, Jawad MA (2016) Robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is it safer than laparoscopic bypass? Obes Surg 26:1016–1020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-015-1884-3
Smeenk RM, van’t Hof G, Elsten E, Feskens PG (2016) The results of 100 robotic versus 100 laparoscopic gastric bypass procedures: a single high volume centre experience. Obes Surg 26(6):1266–1273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-015-1933-y
Renaud M et al (2013) Multifactorial analysis of the learning curve for totally robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Obes Surg 23(11):1753–1760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-013-1020-1
Chitwood WR et al (2001) Robotic surgical training in an academic institution. Ann Surg 234(4):475–486
Yu SC, Clapp BL, Lee MJ, Albrecht WC, Scarborough TK, Wilson EB (2006) Robotic assistance provides excellent outcomes during the learning curve for laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: results from 100 robotic-assisted gastric bypasses. Am J Surg 192:746–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2006.08.038
Oviedo RJ, Robertson JC, Alrajhi S (2016) First 101 robotic general surgery cases in a community hospital. JSLS 20(3):e2016.00056. https://doi.org/10.4293/JSLS.2016.00056
Oviedo RJ, Brownstein NC, Smith SL, Robertson JC, Nair-Collins S (2018) First 200 robotic general surgery cases in a community hospital: a retrospective cohort study. World J Surg Surgical Res 1:1034
Ahmad A, Carleton JD, Ahmad ZF, Agarwala A (2016) Laparoscopic versus robotic-assisted Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a retrospective, single-center study of early perioperative outcomes at a community hospital. Surg Endosc 30:3792–3796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4675-y
Khorgami Z et al (2017) Cost of bariatric surgery and factors associated with increased cost: an analysis of national inpatient sample. Surg Obes Relat Dis 13:1284–1289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2017.04.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Oviedo and Dr. Nayak have no conflicts of interests to report. Ms. Long and Ms. Yan have no conflicts of interests to report.
Consent statement
The retrospective chart review for all patients who belong to both cohorts in this study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Winchester Medical Center in Winchester, VA, USA. The IRB committee approved the retrospective chart review and consented to its statistical analysis and the writing of this manuscript after ensuring that the patients’ confidential information was fully protected, per ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oviedo, R.J., Nayak, T., Long, Z. et al. Robotic Roux en Y gastric bypass can be safe and cost-effective in a rural setting: clinical outcomes from a community hospital bariatric program. J Robotic Surg 15, 929–936 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-021-01193-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-021-01193-9