Abstract
Background
The laparoscopic approach is utilized in greater than 90% of bariatric surgeries. With the growing prevalence of robotic-assisted surgery in bariatrics, there has been limited consensus on the superiority of either laparoscopic or robotic approaches, especially in revisional procedures (conversion from sleeve gastrectomy (SG) to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB)).
Methods
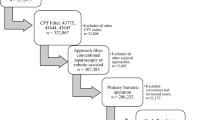
A retrospective analysis was performed of the MBSAQIP PUF database of patients who underwent conversion from SG to RYGB procedures in either laparoscopic or robotic-assisted approaches. The groups underwent 2:1 propensity matching and primary outcomes included post-conversion days until discharge (POD), conversion operation length, total and major morbidity, 30-day readmission, 30-day reoperation, 30-day reintervention, and 30-day mortality after conversion.
Results
After 2:1 propensity score matching, 3411 patients (2274 laparoscopic vs 1137 robotic) were included in the study. Intraoperatively, no significant difference was found in total morbidity (6.5% lap vs 5.9% robotic) or major morbidity (1.9% lap vs 1.7% robotic); however, the operative times were significantly longer robotically (126 min vs 164 min). Post-operatively, no significant differences were found in discharge day (1.8 lap vs 1.8 robotic), 30-day readmission (7.6% lap vs 8.6% robotic), reoperation rate (2.9% lap vs 3.7% robotic), additional intervention rate (2.5% lap vs 3.3% robotic), or 30-day mortality (0.1% vs 0.1%).
Conclusion
There is no significant difference in perioperative or intraoperative outcomes between laparoscopic and robotic-assisted SG to RYGB conversion procedures other than a longer operative time in the robotic approach, suggesting increased efficiency with the laparoscopic approach.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Estimate of bariatric surgery numbers, 2011–2020. American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. https://asmbs.org/resources/estimate-of-bariatric-surgery-numbers. Published June 27, 2022. Accessed August 3, 2022.
Huynh D, Mazer L, Tung R, Cunneen S, Shouhed D, Burch M. Conversion of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: patterns predicting persistent symptoms after revision. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2021;17(10):1681–8.
Saber AA, Elgamal MH, McLeod MK. Bariatric surgery: the past, present, and future. Obes Surg. 2008;18(1):121–8.
Puzziferri N, Austrheim-Smith IT, Wolfe BM, Wilson SE, Nguyen NT. Three-year follow-up of a prospective randomized trial comparing laparoscopic versus open gastric bypass. Ann Surg. 2006;243(2):181.
Aiolfi A, Tornese S, Bonitta G, Rausa E, Micheletto G, Bona D. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis comparing open, laparoscopic, and robotic approach. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15(6):985–94.
Nguyen NT, Goldman C, Rosenquist CJ, Arango A, Cole CJ, Lee SJ, Wolfe BM. Laparoscopic versus open gastric bypass: a randomized study of outcomes, quality of life, and costs. Ann Surg. 2001;234(3):279.
Sundbom M. Laparoscopic revolution in bariatric surgery. World J Gastroenterol: WJG. 2014;20(41):15135.
Dudash M, Kuhn J, Dove J, Fluck M, Horsley R, Gabrielsen J, Daouadi M, Petrick AT, Parker DM. The longitudinal efficiency of robotic surgery: an MBSAQIP propensity matched 4-year comparison of robotic and Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery. Obes Surg. 2020;30(10):3706–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-04712-z.
Papasavas P, Seip RL, Stone A, Staff I, McLaughlin T, Tishler D (2019) Robot-assisted sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: results from the metabolic and bariatric surgery accreditation and quality improvement program data registry. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases. Apr
Wesley Vosburg R, Haque O, Roth E. Robotic vs. laparoscopic metabolic and bariatric surgery, Outcomes over 5 Years in Nearly 800,000 Patients. Obesity Surgery. 2022 May 2:1–8.
Sebastian R, Howell MH, Chang KH, Adrales G, Magnuson T, Schweitzer M, Nguyen H. Robot-assisted versus laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: a propensity score-matched comparative analysis using the 2015–2016 MBSAQIP database. Surg Endosc. 2019;33(5):1600–12.
Falvo AM, Vacharathit V, Dove J, et al. A 3-Year MBSAQIP propensity-matched analysis of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass with concomitant cholecystectomy: is the robotic or laparoscopic approach preferred? Surg Endosc. 2021;35(8):4712–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07939-0.
Nasser H, Munie S, Kindel TL, Gould JC, Higgins RM. Comparative analysis of robotic versus laparoscopic revisional bariatric surgery: perioperative outcomes from the MBSAQIP database. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020;16(3):397–405.
Acevedo E, Mazzei M, Zhao H, Lu X, Edwards MA. Outcomes in conventional laparoscopic versus robotic-assisted revisional bariatric surgery: a retrospective, case–controlled study of the MBSAQIP database. Surg Endosc. 2020;34(4):1573–84.
King K, Galvez A, Stoltzfus J, Claros L, El Chaar M. Robotic-assisted surgery results in a shorter hospital stay following revisional bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2021;31(2):634–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-05022-0.
El Chaar M, King K, Pastrana M, Galvez A, Stoltzfus J. Outcomes of robotic surgery in revisional bariatric cases: a propensity score-matched analysis of the MBSAQIP registry. J Robot Surg. 2021;15(2):235–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-020-01098-z.
Pokala B, Samuel S, Yanala U, Armijo P, Kothari V. Elective robotic-assisted bariatric surgery: is it worth the money? A national database analysis. Am J Surg. 2020;220(6):1445–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2020.08.040.
El Chaar M, Gacke J, Ringold S, Stoltzfus J. Cost analysis of robotic sleeve gastrectomy (R-SG) compared with laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (L-SG) in a single academic center: debunking a myth! Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15(5):675–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2019.02.012.
Bailey JG, Hayden JA, Davis PJB, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) in obese adults ages 18 to 65 years: a systematic review and economic analysis. Surg Endosc. 2014;28:414–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3217-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed Consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required. Informed consent does not apply.
Conflict of Interest
Authors Tristan Seton MD, Mark Mahan DO, James Dove BS, Hugo Villanueva MD, Vladan Obradovic MD, Alexandra Falvo MD, Ryan Horsley DO, Anthony Petrick MD, and David M Parker MD express no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key Points
• There is no significant difference in intraoperative and 30-day post-operative outcomes in bariatric revisional procedures when comparing laparoscopic and robotic approaches.
• Revisions with the robotic approach took significantly longer intraoperatively than with the laparoscopic approach.
• The results of this analysis suggest that laparoscopy is a more efficient method than the robotic approach.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Seton, T., Mahan, M., Dove, J. et al. Is Robotic Revisional Bariatric Surgery Justified? An MBSAQIP Analysis. OBES SURG 32, 3863–3868 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-022-06293-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-022-06293-5