Background
Lipid accumulation and other histological liver markers characterize patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The identification of non-invasive prognostic factors of liver steatosis and NASH are relevant for the unravelling of the mechanisms of this disease, as well as for the clinical diagnoses of these patients.
Methods
36 patients with morbid obesity and 12 healthy subjects were consecutively enrolled in this cross-sectional study to determine the serological parameters associated with the degree of hepatic steatosis and NASH. Clinical, biochemical and histologic variables were examined in blood and liver biopsies by descriptive, univariate and multivariate regression analysis.
Results
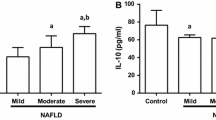
The patients were distributed as non-NASH (14), probably-NASH (13) and NASH (9), according to the Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Activity Score (NAS). The study identified remarkable differences in liver steatosis, and glucose, insulin, IL-6 and IGF-1 concentrations in blood among patients with morbid obesity. IL-6 was correlated with the degree of liver steatosis until the morbidly obese patients fulfil the criteria of NASH. The patients with NASH reduced IL-6 concentration in blood. IGF-1 decreased throughout the progression of NASH. TNF-α concentration was not related to liver steatosis or NASH in morbidly obese patients.The multivariate regression analysis identified glucose >110 mg/dL, IL-6 >4.81 pg/mL and IGF-1 <130 ng/mL, and homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) >4.5 and IGF-1 <110 ng/mL as independent predictors of hepatic steatosis and NASH, respectively.
Conclusions
The concentration of glucose, insulin, IL-6 and IGF-1 in blood are useful markers for the selection of patients with liver steatosis or NASH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HOMA:
-
Homeostasis model assessment
- IL-6:
-
interleukin-6
- IGF-1:
-
insulin-like growth factor-1
- IR:
-
insulin resistance
- NAFLD:
-
non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
- NASH:
-
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- NAS:
-
NAFLD activity score
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM, Campbell SM et al. Increasing prevalence of overweight among US adults. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1960 to 1991. JAMA 1994; 272: 205–1.
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kuczmarski RJ et al. Overweight and obesity in the United States: prevalence and trends, 1960–994. Int J Obes 1998; 22: 39–7.
Braillon A, Capron JP, Herve MA et al. Liver in obesity. Gut 1985; 26: 133–.
Andersen T, Gluud C. Liver morphology in morbid obesity: a literature study. Int J Obes 1984; 8: 97–06.
Bacon BR, Farahvash MJ, Janney CG et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: an expanded clinical entity. Gastroenterology 1994; 107: 1103–.
Leevy CM. Fatty liver: a study of 270 patients with biopsy proven fatty liver and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1962; 41: 249–6.
Adler M, Schaffner F. Fatty liver hepatitis and cirrhosis in obese patients. Am J Med 1979; 67: 811–.
Pessayre D, Berson A, Fromenty B et al. Mitochondria in steatohepatitis. Semin Liver Dis 2001; 21: 57–9.
Teli MR, James OF, Burt AD et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver: a follow-up study. Hepatology 1995; 22: 1714–.
Rust C, Gores GJ. Apoptosis and liver disease. Am J Med 2000; 108: 567–4.
Tracey KJ, Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor, other cytokines and disease. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1993; 9: 317–3.
Andus T, Bauer J, Gerok W. Effects of cytokines on the liver. Hepatology 1991; 13: 364–5.
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1111–.
Hotamisligil GS, Spiegelman BM. Tumor necrosis factor alpha: a key component of the obesity-diabetes link. Diabetes 1994; 43: 1271–.
Shiba T, Higashi N, Nishimura Y. Hyperglycaemia due to insulin resistance caused by interferon-gamma. Diabet Med 1998; 15: 435–.
Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Marino MW et al. Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature 1997; 389: 610–.
Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C et al. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2001; 280: E745–1.
Bugianesi E, Zannoni C, Vanni E et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver and insulin resistance: a cause-effect relationship?. Dig Liver Dis 2004; 36: 165–73.
Schmid C. Insulin-like growth factors. Cell Biol Int 1995; 19: 445–7.
Scharf JG, Schmitz F, Frystyk J et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I serum concentrations and patterns of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in patients with chronic liver disease. J Hepatol 1996; 25: 689–9.
Castilla-Cortazar I, Garcia M, Muguerza B et al. Hepatoprotective effects of insulin-like growth factor I in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1997; 113: 1682–1.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS et al. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005; 41: 1313–1.
Brunt EM, Janney ChG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94: 2467–4.
Matteoni CA, Younossi ZM, Gramlich T et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology 1999; 116: 1413–.
Dixon JB, Bhathal PS, O’Brien PE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: predictors of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in the severely obese. Gastroenterology 2001; 121: 91–00.
Younossi ZM, Diehl AM, Ong JP. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an agenda for clinical research. Hepatology 2002; 35: 746–2.
Gramlich T, Kleiner DE, McCullough AJ et al. Pathologic features associated with fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hum Pathol 2004; 35: 196–.
Angulo P, Keach JC, Batts KP et al. Independent predictors of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 1999; 30: 1356–2.
Rinella ME, Alonso E, Rao S et al. Body mass index as a predictor of hepatic steatosis in living liver donors. Liver Transpl 2001; 7: 409–4.
Pagano G, Pacini G, Musso G et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome: further evidence for an etiologic association. Hepatology 2002; 35: 367–2.
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Morselli-Labate AM et al. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with insulin resistance. Am J Med 1999; 107: 450–.
Feinstein R, Kanety H, Papa MZ et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppresses insulin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor and its substrates. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 26055–.
Senn JJ, Klover PJ, Nowak IA et al. Interleukin-6 induces cellular insulin resistance in hepatocytes. Diabetes 2002; 51: 3391–.
Kanemaki T, Kitade H, Kaibori M et al. Interleukin 1beta and interleukin 6, but not tumor necrosis factor alpha, inhibit insulin-stimulated glycogen synthesis in rat hepatocytes. Hepatology 1998; 27: 1296–03.
Seppala-Lindroos A, Vehkavaara S, Hakkinen AM et al. Fat accumulation in the liver is associated with defects in insulin suppression of glucose production and serum free fatty acids independent of obesity in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 3023–.
Bruun JM, Lihn AS, Verdich C et al. Regulation of adiponectin by adipose tissue-derived cytokines: in vivo and in vitro investigations in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 285: E527–3.
Wolf AM, Busch B, Kuhlmann HW et al. Histological changes in the liver of morbidly obese patients: correlation with metabolic parameters. Obes Surg 2005; 15: 228–7.
Sorbi D, Boynton J, Lindor KD. The ratio of aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase: potential value in differentiating non-alcoholic steatohepatitis from alcoholic liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94: 1018–2
Cortez-Pinto H, de Moura MC, Day CP. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: From cell biology to clinical practice. J Hepatol 2006; 44: 197–08.
Perez-Carreras M, Del Hoyo P, Martin MA et al. Defective hepatic mitochondrial respiratory chain in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2003; 38: 999–007.
Letteron P, Fromenty B, Terris B et al. Acute and chronic hepatic steatosis lead to in vivo lipid peroxidation in mice. J Hepatol 1996; 24: 200–.
Daughaday WH, Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene structures, serum, and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev 1989; 10: 68–1.
Donaghy A, Ross R, Wicks C et al. Growth hormone therapy in patients with cirrhosis: a pilot study of efficacy and safety. Gastroenterology 1997; 113: 1617–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Galiano, D., Sánchez-Garrido, M.A., Espejo, I. et al. IL-6 and IGF-1 are Independent Prognostic Factors of Liver Steatosis and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Morbidly Obese Patients. OBES SURG 17, 493–503 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-007-9087-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-007-9087-1