Abstract
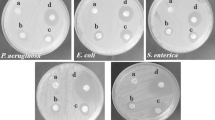
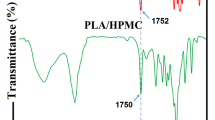
This study was aimed to fabricate a durable antimicrobial packaging film using electrospun polylactic acid (PLA) nanofibers containing Thymus daenensis essential oil (TDO), TDO-loaded mesoporous silica vesicles (MSVs/TDO), and MSVs/TDO combined with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Functional features including mechanical properties, heat resistance, water vapor permeability (WVP), antimicrobial and release behavior of TDO and AgNPs from the nanofibers were assessed. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy confirmed the presence of MSVs/TDO and embedded AgNPs in nanofibers. Application of MSV/TDO along with AgNPs could reduce significantly the WVP (0.43 ± 0.04 g m−1 Pa−1 s−1) and control the release of the EO from the electrospun PLA films (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the release of AgNPs from PLA nanofibers was increased in the presence of pure TDO (0.0135 ppm after 72 h). The combination of MSVs/TDO and AgNPs had a synergistic antibacterial effect on the tested bacteria both in culture and on ultra-filtered (UF) cheese. The controlled release ability of the EO in MSVs/TDO film resulted in its less antibacterial effect compared to the TDO film in the early times of antimicrobial assessments. The population growth of the inoculated pathogenic bacteria on the packed UF cheese with the films containing MSVs/TDO was controlled due to the long-lasting release of EO, so that the MSVs/TDO + AgNPs film reduced the count of E. coli and S. aureus by 1.56 and 2.97 log CFU g−1 on the 4th storage day, respectively. Thus, the electrospun PLA film containing MSVs/TDO + AgNPs bear a good potential for use in food packaging as a biocompatible packaging with long-term antimicrobial performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.H.H. in’t, Veld, Microbial and biochemical spoilage of foods: an overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 33(1), 1–18 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1605(96)01139-7
R. Coles, D. McDowell, M.J. Kirwan, Food Packaging Technology (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2003)
A. Sorrentino, G. Gorrasi, V. Vittoria, Potential perspectives of bio-nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol 18(2), 84–95 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2006.09.004
I.S. Tawakkal, M.J. Cran, J. Miltz, S.W. Bigger, A review of poly (lactic acid)-based materials for antimicrobial packaging. J. Food Sci. 79(8), R1477–R1490 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12534
S. Mihindukulasuriya, L.-T. Lim, Nanotechnology development in food packaging: a review. Trends Food Sci. Technol 40(2), 149–167 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2014.09.009
C. Zhang, Y. Li, P. Wang, H. Zhang, Electrospinning of nanofibers: potentials and perspectives for active food packaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 19(2), 479–502 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12536
S.M.B. Hashemi, D. Jafarpour, The efficacy of edible film from Konjac glucomannan and saffron petal extract to improve shelf life of fresh-cut cucumber. Food Sci. Nutr. 8(7), 3128–3137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1544
M. Sayadi, A. Mojaddar Langroodi, D. Jafarpour, Impact of zein coating impregnated with ginger extract and Pimpinella anisum essential oil on the shelf life of bovine meat packaged in modified atmosphere. J. Food Meas. Charact. 15(6), 5231 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-01096-1
M.A. Nassar, A.M. Youssef, Mechanical and antibacterial properties of recycled carton paper coated by PS/Ag nanocomposites for packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 89(1), 269 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.007
H. Poortavasoly, M. Montazer, T. Harifi, Simultaneous synthesis of nano silver and activation of polyester producing higher tensile strength aminohydroxylated fiber with antibacterial and hydrophilic properties. RSC Adv. 4(86), 46250 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA04835K
S. Ataei, P. Azari, A. Hassan, B. Pingguan-Murphy, R. Yahya, F. Muhamad, Essential oils-loaded electrospun biopolymers: A future perspective for active food packaging. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9040535
M.M. Zarshenas, L. Krenn, A critical overview on Thymus daenensis Celak.: phytochemical and pharmacological investigations. J. Integr. Med. 13(2), 91–98 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-4964(15)60166-2
S. Mansouri, M. Pajohi-Alamoti, N. Aghajani, B. Bazargani‐Gilani, A. Nourian, Stability and antibacterial activity of Thymus daenensis L. essential oil nanoemulsion in mayonnaise. J. Sci. Food Agric. 101(9), 3880 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11026
A. Kumar, R. Kanwar, S.K. Mehta, Recent development in essential oil-based nanocarriers for eco-friendly and sustainable agri-food applications: a review. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2(5), 823–837 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsagscitech.2c00100
A. Bernardos, T. Marina, P. Žáček, É Pérez-Esteve, R. Martínez-Mañez, M. Lhotka, L. Kouřimská, J. Pulkrábek, P. Klouček, Antifungal effect of essential oil components against Aspergillus niger when loaded into silica mesoporous supports. J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(14), 2824 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7022
A.D. Erem, G. Ozcan, H. Erem, M. Skrifvars, Antimicrobial activity of poly (L-lactide acid)/silver nanocomposite fibers. Text. Res. J. 83(20), 2111 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517513481875
W. Lu, R. Cui, B. Zhu, Y. Qin, G. Cheng, L. Li, M. Yuan, Influence of clove essential oil immobilized in mesoporous silica nanoparticles on the functional properties of poly (lactic acid) biocomposite food packaging film. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 11, 1152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.01.098
F. Farjadian, A. Roointan, S. Mohammadi-Samani, M. Hosseini, Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: synthesis, pharmaceutical applications, biodistribution, and biosafety assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 359, 684–705 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.156
X. Zhong, F. Gao, H. Wei, H. Zhou, X. Zhou, Functionalization of mesoporous silica as an effective composite carrier for essential oils with improved sustained release behavior and long-term antibacterial performance. Nanotechnol 33(3), 035706 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ac2fe2
Y. Zhang, Q. Yue, Y. Jiang, W. Luo, A.A. Elzatahry, A. Alghamdi, Y. Deng, D. Zhao, A facile biliquid-interface co-assembly synthesis of mesoporous vesicles with large pore sizes. CrystEngComm 18(23), 4343 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CE02592C
L. Nedorostova, P. Kloucek, L. Kokoska, M. Stolcova, J. Pulkrabek, Antimicrobial properties of selected essential oils in vapour phase against foodborne bacteria. Food control 20(2), 157–160 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2008.03.007
B. Melendez-Rodriguez, K.J. Figueroa-Lopez, A. Bernardos, R. Martínez-Máñez, L. Cabedo, S. Torres-Giner, J.M. Lagaron, Electrospun antimicrobial films of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) containing eugenol essential oil encapsulated in mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 9(2), 227 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020227
R. Zhang, W. Lan, T. Ji, D.E. Sameen, S. Ahmed, W. Qin, Y. Liu, Development of polylactic acid/ZnO composite membranes prepared by ultrasonication and electrospinning for food packaging. LWT 135, 110072 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110072
S. Cai, B. Pourdeyhimi, E.G. Loboa, Industrial-scale fabrication of an osteogenic and antibacterial PLA/silver‐loaded calcium phosphate composite with significantly reduced cytotoxicity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. 107(4), 900 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.34185
Y. Chen, Y. Qiu, W. Chen, Q. Wei, Electrospun thymol-loaded porous cellulose acetate fibers with potential biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 109, 110536 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110536
A.G. Pirbalouti, M. Hashemi, F.T. Ghahfarokhi, Essential oil and chemical compositions of wild and cultivated Thymus daenensis celak and Thymus vulgaris L. Ind. Crops Prod. 48, 43–48 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.04.004
V. Rowshan, A. Bahmanzadegan, M.J. Saharkhiz, Influence of storage conditions on the essential oil composition of Thymus daenensis Celak. Ind. Crops Prod. 49, 97–101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.04.029
M. Shahriarinour, F. Divsar, Z. Eskandari, Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of thymol loaded SBA-15 mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Inorg. Nano-Met Chem. 49(6), 182–189 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2019.1624569
A. Altan, Z. Aytac, T. Uyar, Carvacrol loaded electrospun fibrous films from zein and poly (lactic acid) for active food packaging. Food Hydrocoll. 81, 48–59 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.02.028
N. Bhardwaj, S.C. Kundu, Electrospinning: a fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 28(3), 325–347 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.01.004
Y. Liu, S. Wang, R. Zhang, W. Lan, W. Qin, Development of poly (lactic acid)/chitosan fibers loaded with essential oil for antimicrobial applications. Nanomaterials 7(7), 194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7070194
R. Scaffaro, F. Lopresti, Processing, structure, property relationships and release kinetics of electrospun PLA/Carvacrol membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 100, 165–171 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.01.035
W. Li, C. Zhang, H. Chi, L. Li, T. Lan, P. Han, H. Chen, Y. Qin, Development of antimicrobial packaging film made from poly (lactic acid) incorporating titanium dioxide and silver nanoparticles. Molecules 22(7), 1170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071170
A. Jobdeedamrong, R. Jenjob, D. Crespy, Encapsulation and release of essential oils in functional silica nanocontainers. Langmuir 34(44), 13235 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01652
S.F. Hosseini, M. Rezaei, M. Zandi, F.F. Ghavi, Preparation and functional properties of fish gelatin-chitosan blend edible films. Food Chem. 136(3–4), 1490 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.081
X. Liu, J. Jia, S. Duan, X. Zhou, A. Xiang, Z. Lian, F. Ge, Zein/MCM-41 nanocomposite film incorporated with cinnamon essential oil loaded by modified supercritical CO2 impregnation for long-term antibacterial packaging. Pharmaceutics 12(2), 169 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020169
S. Salmieri, F. Islam, R.A. Khan, F.M. Hossain, H.M. Ibrahim, C. Miao, W.Y. Hamed, M. Lacroix, Antimicrobial nanocomposite films made of poly (lactic acid)-cellulose nanocrystals (PLA-CNC) in food applications-part B: effect of oregano essential oil release on the inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in mixed vegetables. Cellul 21(6), 4271 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0406-0
M. Hassannia-Kolaee, F. Khodaiyan, R. Pourahmad, I. Shahabi-Ghahfarrokhi, Development of ecofriendly bionanocomposite: whey protein isolate/pullulan films with nano-SiO2. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 86, 139–144 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.01.032
H.S. Sofi, T. Akram, A.H. Tamboli, A. Majeed, N. Shabir, F.A. Sheikh, Novel lavender oil and silver nanoparticles simultaneously loaded onto polyurethane nanofibers for wound-healing applications. Int. J. Pharm. 569, 118590 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118590
S. Ray, R.P. Cooney. Thermal degradation of polymer and polymer composites, in Handbook of Environmental Degradation of Materials (William Andrew Publishing, Norwich, 2018), pp. 185–206
E. Gámez, H. Elizondo-Castillo, J. Tascon, S. García-Salinas, N. Navascues, G. Mendoza, M. Arruebo, S. Irusta, Antibacterial effect of thymol loaded SBA-15 nanorods incorporated in PCL electrospun fibers. Nanomaterials 10(4), 616 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040616
F.N. Almajhdi, H. Fouad, K.A. Khalil, H.M. Awad, S.H. Mohamed, T. Elsarnagawy, A.M. Albarrag, F.F. Al-Jassir, H.S. Abdo, In-vitro anticancer and antimicrobial activities of PLGA/silver nanofiber composites prepared by electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 25(4), 1045 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-5131-y
X. Xu, Q. Yang, Y. Wang, H. Yu, X. Chen, X. Jing, Biodegradable electrospun poly (L-lactide) fibers containing antibacterial silver nanoparticles. Eur. Polym. J. 42(9), 2081 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2006.03.032
EFSA Scientific Committee, Guidance on the risk assessment of the application of nanoscience and nanotechnologies in the food and feed chain. EFSA J. 9(5), 2140 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2140
T. Min, X. Sun, Z. Yuan, L. Zhou, X. Jiao, J. Zha, Z. Zhu, Y. Wen, Novel antimicrobial packaging film based on porous poly (lactic acid) nanofiber and polymeric coating for humidity-controlled release of thyme essential oil. LWT 135, 110034 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110034
F. Nazzaro, F. Fratianni, L. De Martino, R. Coppola, V. De Feo, Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 6(12), 1451–1474 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6121451
R.J. Holmila, S.A. Vance, S.B. King, A.W. Tsang, R. Singh, C.M. Furdui, Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondrial protein oxidation in lung cells impacting cell cycle and proliferation. Antioxidants 8(11), 552 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110552
M. Cristani, M. D’Arrigo, G. Mandalari, F. Castelli, M.G. Sarpietro, D. Micieli, Interaction of four monoterpenes contained in essential oils with model membranes: implications for their antibacterial activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 55(15), 6300 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf070094x
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the support of the Research Deputy of Bu-Ali Sina University, Hamedan, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bamian, M., Pajohi-Alamoti, M., Azizian, S. et al. An electrospun polylactic acid film containing silver nanoparticles and encapsulated Thymus daenensis essential oil: release behavior, physico-mechanical and antibacterial studies. Food Measure 17, 3450–3463 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01890-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01890-z