Abstract
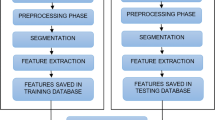
Implementing reliable, fast, and low-cost analysis is gaining popularity in the food industry. One alternative for this type of analysis is an artificial intelligence based on image analysis. This study aimed to use image analysis to develop classification models for discriminating the acceptability of mayonnaises. A semi-trained panel comprised of 8 evaluators classified 300 pictures of mayonnaises. Features extracted from the images include the mean, standard deviation, minimum and maximum intensity values, skewness, and kurtosis from Red–Green–Blue (RGB), Hue-Saturation-Value (HSV), and the Commission Internationale d’Eclairage L* a* b* (CIELab) color spaces. Haralick Features and the intensity differences between the region of interest and the background were calculated using gray-level intensity values. A Support Vector Machine (SVM), Gradient Boosting, and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) models were used and evaluated in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-measure with tenfold cross-validation. Color features revealed to be the most important data for the models; these models demonstrated 92.60–93.30% accuracy, 89.00–93.30% precision, 91.40–96.43% recall, and 91.90–92.30% F1-measure. Tested models showed similar results among them. Every tested model did not exhibit significant difference compared to the panel, which presented 88.33, 94.37, 93.54, and 93.75% of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-measure, respectively. The models obtained herein, showed to be a possible approach for a fast, low-cost, and simple methodology to estimate the acceptability of mayonnaise in sensory analysis or shelf-life studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Mirzanajafi-Zanjani, M. Yousefi, A. Ehsani, Food Sci. Nutr. 7, 2471 (2019)
S. Ghorbani Gorji, H.E. Smyth, M. Sharma, M. Fitzgerald, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 56, 88–102 (2016)
D. Kaur, A.A. Wani, D.P. Singh, D.S. Sogi, Int. J. Food Prop. 14, 1217 (2011)
P. Jackman, D.-W. Sun, Emerg. Technol. Food Qual. Food Saf. Eval. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1201/b10710-5
N.R. Mavani, J.M. Ali, S. Othman, M.A. Hussain, H. Hashim, N.A. Rahman, Food Eng. Rev. 2021(1), 1 (2021)
J. Ueda, C. Spence, K. Okajima, Scientific Rep. 10, 1 (2020)
P. Yu, M.Y. Low, W. Zhou, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 71, 202 (2018)
S.M. Azcarate, C.M. Teglia, F. Karp, J.M. Camiña, H.C. Goicoechea, Microchem. J. 133, 182 (2017)
U.G. Indahl, N.S. Sahni, B. Kirkhus, T. Næs, Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 49, 19 (1999)
S. Fuentes, E. Tongson, and C. Gonzalez Viejo Curr Opin Food Sci. 41, 99 (2021)
W. D. N. Pacheco and F. R. J. López, 2019 22nd Symposium on image, signal processing and artificial vision, STSIVA 2019-Conference Proceedings (2019).
K. Koyama, M. Tanaka, B.H. Cho, Y. Yoshikawa, S. Koseki, PLoS ONE 16, e0248769 (2021)
A. Taheri-Garavand, S. Fatahi, M. Omid, Y. Makino, Meat Sci. 156, 183 (2019)
B.H. Cho, K. Koyama, E. Olivares Díaz, S. Koseki, Food Bioproc. Tech. 13, 1579 (2020)
D. Olivares Puerto, Ó. Cáceres Moreno, D.M. Martínez Gila, J. Gómez Ortega, J. Gámez García, J. Food Meas. Charact. 13, 716 (2019)
A. Rehman, Z. Tariq, S. ul din Memon, A. Zaib, M.U. Khan, S. Aziz, International Conference on. Artif. Intell. (IEEE, 2021) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAI52203.2021.9445237
H. Lin, G. Zhou, A. Chen, J. Li, M. Li, W. Zhang, Y. Hu, W. tao Yu, J. Food Meas. Charact. 15, 4696 (2021)
H. Su, C. Lien, T. Lee, J. Ho, J. Sci. Food Agric. 90, 806 (2010)
S.S. Amiri Aghdaei, M. Aalami, S. Babaei Geefan, A. Ranjbar, J Food Sci Technol 51, 2748 (2012)
V. Olsson, A. Håkansson, J. Purhagen, K. Wendin, Foods 7, 9 (2018)
M.J. Santa Cruz, M.C. Martínez, G. Hough, J. Sens. Stud. 17, 309 (2002)
J. Lukinac, M. Jukić, K. Mastanjević, M. Lučan, Ukrainian Food J. 7, 192–214 (2018)
J. Mukherjee, I.K. Maitra, K. Nath Dey, S.K. Bandyopadhyay, D. Bhattacharyya, T.-H. Kim, Int. J. Softw. Eng. Appl. 10, 15 (2016)
W. Castro, J. Oblitas, M. De-La-Torre, C. Cotrina, K. Bazan, H. Avila-George, IEEE Access 7, 27389 (2019)
T. Löfstedt, P. Brynolfsson, T. Asklund, T. Nyholm, A. Garpebring, PLoS ONE 14, e0212110 (2019)
M. Sarayreh, M.M. Reis, W.Q. Yan, R. Klette, Int. Conf. Image Vision Comput. NZ (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29888-3_22
L. Goel, S. Raman, S.S. Dora, A. Bhutani, A.S. Aditya, A. Mehta, Artif. Intell. Rev. 53, 1415 (2020)
R. Kohavi, G.H. John, Artif. Intell. 97, 273 (1997)
M. Koklu, I.A. Ozkan, Comput. Electron. Agric. 174, 105507 (2020)
U. Patil, S. Benjakul, Food Biophys. 14, 260 (2019)
D. Savaghebi, M. Ghaderi-Ghahfarokhi, M. Barzegar, Food Bioproc. Tech. 14, 1311 (2021)
A. Sanaeifar, A. Jafari, Inf. Process. Agric. 6, 20 (2019)
P. Cano Marchal, D. Martínez Gila, J. Gámez García, J. Gómez Ortega, J Food Eng 119, 220 (2013)
T. Sarkar, A. Mukherjee, K. Chatterjee, M.A. Shariati, M. Rebezov, S. Rodionova, D. Smirnov, R. Dominguez, J.M. Lorenzo, Food Anal. Methods 15, 917 (2022)
D. Pietro Cavallo, M. Cefola, B. Pace, A.F. Logrieco, G. Attolico, Comput. Electron. Agric. 156, 558 (2019)
J. Ni, J. Gao, J. Li, H. Yang, Z. Hao, Z. Han, J. Food Meas. Charact. 15, 4530 (2021)
W. Zhang, A. Tan, G. Zhou, A. Chen, M. Li, X. Chen, M. He, Y. Hu, J. Food Meas. Charact. 15, 2877 (2021)
P.S. Teo, A.W.B. van Langeveld, K. Pol, E. Siebelink, C. de Graaf, C. Martin, S. Issanchou, S.W. Yan, M. Mars, Food Qual. Prefer. 65, 49 (2018)
G. Van Doorn, S. Watson, J. Timora, C. Spence, Food Qual. Prefer. 79, 103778 (2020)
S. Ghorbani Gorji, M. Calingacion, H.E. Smyth, M. Fitzgerald, Metabolomics 15, 1 (2019)
L. Zhu, P. Spachos, E. Pensini, K.N. Plataniotis, Curr. Res. Food Sci. 4, 233 (2021)
L. Myllyaho, M. Raatikainen, T. Männistö, T. Mikkonen, J.K. Nurminen, J. Syst. Softw. 181, 111050 (2021)
L.F. Batista, C.S. Marques, A.C.S. dos Pires, L.A. Minim, N.F.F. de Soares, M.C.T.R. Vidigal, Food Bioprod. Process. 126, 164 (2021)
Acknowledgements
Authors Metri and Solana gratefully acknowledge the National Council for Science and Technology of Mexico (CONACyT) and Universidad de las Américas Puebla (UDLAP) for their PhD scholarships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: JMO, DBA, EP; Methodology: JMO, GSL; Formal analysis and investigation: JMO, GSL, RRR; Writing - original draft preparation: JMO, DBA; Writing - review and editing: RRR, EP, MRR, DBA; Supervision: RRR, EP, MRR, DBA.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. All authors agree with the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Metri-Ojeda, J., Solana-Lavalle, G., Rosas-Romero, R. et al. Rapid screening of mayonnaise quality using computer vision and machine learning. Food Measure 17, 2792–2804 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01814-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01814-x