Abstract
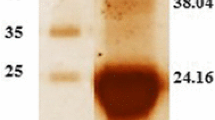
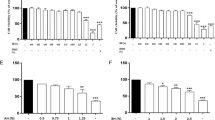
The protein constituent of honey exhibits therapeutic activities in inflammation, and parasitic infections. The biological activities of honey depend on multiple factors such as types of flora, honeybee species, and geographical region. The immunomodulatory activities of proteins of honey of many floral types have not been performed so far. In this study, the proteins composition in seven types of honeys of different flora (Acacia, Thyme, Pine, Khairpur, Chinaberry, Gum tree and Citrus honeys), and geographical regions was determined using gel filtration chromatography (GFC), and their anti-inflammatory activity was studied by determining the inhibition of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in zymogen activated human polymorph nuclear leucocytes (PMNLs). The analysis showed that natural honeys differ in their proteins composition, containing 3–6 proteins fractions. The concentration dependent inhibition of ROS production was observed with precipitated as well as fractionated honey proteins (IC50 0.6–18 ng/mL). The crude proteins of acacia honey exhibited IC50 of 11.3 ng/mL, thyme 5.3 ng/mL, pine 3.1 ng/mL, Khairpur 7.5 ng/mL, and Chinaberry 16.5 ng/mL. Different GFC fractions of honey samples under study also showed significantly low IC50 values in the range of 0.2–9.8 ng/mL. The results of this study show, for the first time, that protein fractions of natural honeys of different botanical flora possess varying yet high potential to suppress ROS production in macrophages, suggesting their tissue protective role by alleviating oxidative stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Governa, G. Carullo, M. Biagi, V. Rago, F. Aiello, Evaluation of the in vitro wound-healing activity of Calabrian honeys. Antioxidants 8(2), 36 (2019)
S. Kolayli, Z. Can, O. Yildiz, H. Sahin, S.A. Karaoglu, A comparative study of the antihyaluronidase, antiurease, antioxidant, antimicrobial and physicochemical properties of different unifloral degrees of chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) honeys. J. Enzyme Inhibit. Med. Chem. 31(sup3), 96–104 (2016)
F. Iftikhar, M.A. Masood, E.S. Waghchoure, Comparison of, and honey from different areas of Pakistan. Asian J. Exper. Biol. Sci. 2(3), 399–403 (2011)
L. Cornara, M. Biagi, J. Xiao, B. Burlando, Therapeutic properties of bioactive compounds from different honeybee products. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 412 (2017)
M. Waheed, M.B. Hussain, A. Javed, Z. Mushtaq, S. Hassan, M.A. Shariati, M.U. Khan, M. Majeed, M. Nigam, A.P. Mishra, Honey and cancer: a mechanistic review. Clin. Nutr. 38(6), 2499–2503 (2019)
D.M. Borsato, A.S. Prudente, P.M. Döll-Boscardin, A.V. Borsato, C.F. Luz, B.H. Maia, D.A. Cabrini, M.F. Otuki, M.D. Miguel, P.V. Farago, Topical anti-inflammatory activity of a monofloral honey of Mimosa scabrella provided by Melipona marginata during winter in Southern Brazil. J. Med. Food 17(7), 817–825 (2014)
Z. Can, O. Yildiz, H. Sahin, E.A. Turumtay, S. Silici, S. Kolayli, An investigation of Turkish honeys: their physico-chemical properties, antioxidant capacities and phenolic profiles. Food Chem. 180, 133–141 (2015)
A. Gohar, M. Shakeel, R.L. Atkinson, D.J. Haleem, Potential mechanisms of improvement in body weight, metabolic profile, and liver metabolism by honey in rats on a high fat diet. PharmaNutrition 14, 100227 (2020)
S. Samarghandian, T. Farkhondeh, F. Samini, Honey and health: a review of recent clinical research. Pharmacogn. Res. 9(2), 121 (2017)
S. Szabo, J.S. Trier, P.W. Frankel, Sulfhydryl compounds may mediate gastric cytoprotection. Science 214(4517), 200–202 (1981)
S.J. Forrester, D.S. Kikuchi, M.S. Hernandes, Q. Xu, K.K. Griendling, Reactive oxygen species in metabolic and inflammatory signaling. Circ. Res. 122(6), 877–902 (2018)
M. Mittal, M.R. Siddiqui, K. Tran, S.P. Reddy, A.B. Malik, Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 20(7), 1126–1167 (2014)
S.B. Almasaudi, N.A. El-Shitany, A.T. Abbas, U.A. Abdel-dayem, S.S. Ali, S.K. Al Jaouni, S. Harakeh, Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiulcer potential of manuka honey against gastric ulcer in rats. Oxidat. Med. Cell. Longev. (2016)
M.A. Mesaik, N. Dastagir, N. Uddin, K. Rehman, M.K. Azim, Characterization of immunomodulatory activities of honey glycoproteins and glycopeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63(1), 177–184 (2014)
L.S. Chua, J.Y. Lee, G.F. Chan, Characterization of the proteins in honey. Anal. Lett. 48(4), 697–709 (2015)
S.E.A. Mohammed, M.K. Azim, Characterisation of natural honey proteins: implications for the floral and geographical origin of honey. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 47(2), 362–368 (2012)
H.U. Khan, S.I. Anjum, N. Sultana, B. Khattak, Honey production potential of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) in Karak and Kohat, Pakistan (2016).
K.A. Khan, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, M.J. Ansari, The characterization of blossom honeys from two provinces of Pakistan. Italian J. Food Sci. 28(4) (2016)
S.E. Lee, J.S. Seo, Y.S. Keum, K.J. Lee, Q.X. Li, Fluoranthene metabolism and associated proteins in Mycobacterium sp. JS14. Proteomics 7(12), 2059–2069 (2007)
H. Schägger, Tricine–sds-page. Nat. Protoc. 1(1), 16 (2006)
M.T. Iglesias, P.J. Martín-Álvarez, M.C. Polo, C. De Lorenzo, E. Pueyo, Protein analysis of honeys by fast protein liquid chromatography: application to differentiate floral and honeydew honeys. J. Agric. Food Chem. 54(21), 8322–8327 (2006)
M.Y. Memar, R. Ghotaslou, M. Samiei, K. Adibkia, Antimicrobial use of reactive oxygen therapy: current insights. Infect. Drug Resist. 11, 567 (2018)
K.K. Griendling, R.M. Touyz, J.L. Zweier, S. Dikalov, W. Chilian, Y.-R. Chen, D.G. Harrison, A. Bhatnagar, A. H. A. C. O. B. C. Sciences, Measurement of reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, and redox-dependent signaling in the cardiovascular system: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circ. Res. (2016)
P. Libby, Inflammatory mechanisms: the molecular basis of inflammation and disease. Nutr. Rev. 65(suppl_3), S140–S146 (2007)
E.R. Sherwood, T. Toliver-Kinsky, Mechanisms of the inflammatory response. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 18(3), 385–405 (2004)
M. Gasparrini, S. Afrin, T.Y. Forbes-Hernández, D. Cianciosi, P. Reboredo-Rodriguez, A. Amici, M. Battino, F. Giampieri, Protective effects of Manuka honey on LPS-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Part 2: control of oxidative stress induced damage, increase of antioxidant enzyme activities and attenuation of inflammation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 120, 578–587 (2018)
A. Gohar, M. Shakeel, Assessment of environmental impact on essential and toxic elements composition in natural honeys by using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 1–12 (2020)
B. Bilal, M.K. Azim, Nematicidal activity of ‘major royal jelly protein’-containing glycoproteins from Acacia honey. Exp. Parasitol. 192, 52–59 (2018)
M.A. Mesaik, N. Dastagir, N. Uddin, K. Rehman, M.K. Azim, Characterization of immunomodulatory activities of honey glycoproteins and glycopeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63(1), 177–184 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the ICCBS Research Institutions for providing research facilities.
Funding
No grant was received from any funding agency for this work. The study was carried out using the institutional indigenous resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AG: performed experimentation, data acquisition and analysis, manuscript preparation, ND: ROS assay, AJ: manuscript review and intellectual input, MKA: conceived and supervised the study as PI.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors of this study (Atia Gohar, Nida Dastagir, Almas Jabeen, and Muhammad Kamran Azim) declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee (No: ICCBS/IEC-008-BC-2015/Protocol/1.0) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
An informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gohar, A., Dastagir, N., Jabeen, A. et al. Characterization of immunomodulatory activity of proteins of natural honeys. Food Measure 15, 4475–4481 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-01033-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-01033-2