Abstract
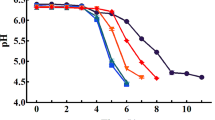
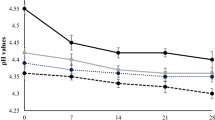
Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) juice was used to replace water by 10% and 20% (w/w), respectively, while the diluted yam juice was used to disperse skimmed milk powder. Set-style skimmed yoghurt samples were thereby prepared using a commercial direct vat set starter at 42 °C. Assaying results indicated that yam juice had a slight impact on the contents of total proteins and total solids of yoghurt samples but could promote yoghurt fermentation and induce texture changes. Firstly, yam juice shortened fermentation time by about 1 h and caused a higher post-acidification during yoghurt storage at 4 °C. Secondly, yam juice reduced syneresis extent during the preformed yoghurt storage, led to value increases for these textural and rheological indices like hardness, adhesiveness, cohesiveness, viscosity as well as elastic/viscous moduli, and caused a finer and compact microstructure. Furthermore, yam juice also resulted in higher viable numbers for two starter microorganisms Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus in the stored yoghurt samples. However, replacing water with yam juice by 20% other than 10% occasionally showed a negative impact on some textural attributes of yoghurt samples. It is thus concluded that yam juice at suitable level could be used in the production of set-style yoghurt without significant negative effect on yoghurt compositions or its fermentation, when aiming to obtain a firm yoghurt texture and endow yoghurt with enhanced health benefits from the starter strains.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Mostafai, S.M. Nachvakc, R. Mohammadi, R.S. Rocha, M.C. da Silva, E.A. Esmerino, K.O. Nascimento, A.G. Cruz, A.M. Mortazavian, Effects of vitamin D-fortified yogurt in comparison to oral vitamin D supplement on hyperlipidemia in pre-diabetic patients: a randomized clinical trial. J. Funct. Foods 52, 116–120 (2019)
T. Paseephol, D.M. Small, F. Sherkat, Rheology and texture of set yogurt as affected by inulin addition. J. Texture Stud. 39, 617–634 (2008)
F.S. Vianna, A.C.V.C.S. Canto, B.R.C. da Costa-Lima, A.P.A.A. Salim, M.P. Costa, C.F. Balthazar, B.R. Oliveira, R.P. Rachid, R.M. Franco, C.A. Conte-Junior, A.C.O. Silva, Development of new probiotic yoghurt with a mixture of cow and sheep milk: effects on physicochemical, textural and sensory analysis. Small Ruminant Res. 149, 154–162 (2017)
M.S. Santos, L.M. Estevinho, C.A.L. de Carvalho, A.L.D. Conceicao, R.C.D. Almeida, Rheological and sensorial evaluation of yogurt incorporated with red propolis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 57, 1080–1089 (2020)
O.J. Ujiroghene, L. Liu, S. Zhang, J. Lu, X.Y. Pang, J.P. Lv, α-Glucosidase and ACE dual inhibitory protein hydrolysates and peptide fractions of sprouted quinoa yoghurt beverages inoculated with Lactobacillus casei. Food Chem. 229, e124985 (2019)
F. Bimbo, A. Bonanno, G. Nocella, R. Viscecchia, G. Nardone, B. de Devitiis, D. Carlucci, Consumers’ acceptance and preferences for nutrition-modified and functional dairy products: a systematic review. Appetite 113, 141–154 (2017)
E. Kiros, E. Seifu, G. Bultosa, W.K. Solomon, Effect of carrot juice and stabilizer on the physicochemical and microbiological properties of yoghurt. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 69, 191–196 (2016)
X.Y. Wang, E. Kristo, G. LaPointe, Adding apple pomace as a functional ingredient in stirred-type yogurt and yogurt drinks. Food Hydrocolloid. 100, e105453 (2020)
K.O. Shin, J.R. Jeon, J.S. Lee, J.Y. Kim, C.H. Lee, S.D. Kim, Y.S. Yu, D.H. Nam, Lactic acid fermentation of Chinese yam (Dioscorea batatas Decne) flour and its pharmacological effect on gastrointestinal function in rat model. Biotechnol. Bioproc. E 11, 240–244 (2006)
T. Yamazaki, K. Arai, Y. Tokuji, M. Kawahara, K. Ohba, M. Kinoshita, M. Ohnishi, Nutrient composition, amylase titer, and superoxide anion-scavenging activity of Chinese yam tubers harvested in Hokkaido. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. 59, 538–543 (2012)
I.S. Son, J.H. Kim, H.Y. Sohn, K.H. Son, J.S. Kim, C.S. Kwon, Antioxidative and hypolipidemic effects of diosgenin, a steroidal saponin of yam (Dioscorea spp.), on high-cholesterol fed rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 71, 3063–3071 (2007)
F.C. Wu, J.G. Jiang, Effects of diosgenin and its derivatives on atherosclerosis. Food Funct. 10, 7022–7036 (2019)
C.H. Huang, J.Y. Cheng, M.C. Deng, C.H. Chou, T.R. Jan, Prebiotic effect of diosgenin, an immunoactive steroidal sapogenin of the Chinese yam. Food Chem. 132, 428–432 (2012)
F.Y. Ma, R.J. Wang, X.J. Li, W.Y. Kang, A.E. Bell, D.B. Zhao, X.H. Liu, W.Z. Chen, Physical properties of mucilage polysaccharides from Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Food Chem. 311, e126039 (2020)
R. Huang, J. Xie, Y. Yu, M. Shen, Recent progress in the research of yam mucilage polysaccharides: isolation, structure and bioactivities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 155, 1262–1269 (2019)
L.X. Hao, X.H. Zhao, Immunomodulatory potentials of the water-soluble yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb) polysaccharides for the normal and cyclophosphamide-suppressed mice. Food Agric. Immunol. 27, 667–677 (2016)
L.X. Hao, X.H. Zhao, In vitro immune potentials of a water-soluble polysaccharide extract from Dioscorea opposita planted in Henan Province, China. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 30, 1383–1388 (2017)
S.H. Kim, S.Y. Lee, G. Palanivel, H.S. Kwak, Effect of Dioscorea opposita Thunb. (yam) supplementation on physicochemical and sensory characteristics of yogurt. J. Dairy Sci. 94, 1705–1712 (2011)
C. Ramirez-Santiago, L. Ramos-Solis, C. Lobato-Calleros, C. Peña-Valdivia, E.J. VernonCarter, J. Alvarez-Ramírez, Enrichment of stirred yogurt with soluble dietary fiber from Pachyrhizus erosusL. urban: effect on syneresis, microstructure and rheological properties. J. Food Eng. 101, 229–235 (2010)
W.J. Lee, J.A. Lucey, Formation and physical properties of yogurt. Asian-Austral. J. Anim. Sci. 23, 1127–1136 (2010)
AOAC, Official Methods of Analysis of Association of Official Analytical Chemists International, 19th edn. (Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Gaithersburg, 2012).
S.B. Barker, W.H. Summerson, The colorimetric determination of lactic acid in biological material. J. Biol. Chem. 138, 535–554 (1941)
Y.P. Han, M. Fu, X.H. Zhao, The quality of set-style yoghurt responsible to partial lactose hydrolysis followed by protein cross-linking of the skimmed milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 68, 427–433 (2015)
K. Tatjana, S. Jolanta, G. Pawel, Rheological and textural properties of yogurts enriched with Jerusalem artichoke flour. Czech J. Food Sci. 35, 432–439 (2017)
C.H. Chang, B.H. Kong, X.H. Zhao, Quality attributes of the set-style yoghurt from whole bovine milk as affected by an enzymatic oxidative cross-linking. CyTA-J. Food 12, 249–255 (2014)
M. Abdel-Hamid, E. Romeih, Z. Huang, T. Enomoto, L. Huang, L. Li, Bioactive properties of probiotic set-yogurt supplemented with Siraitia grosvenorii fruit extract. Food Chem. 303, e125400 (2020)
B.N.P. Sah, T. Vasiljevic, S. McKechnie, O.N. Donkor, Effect of pineapple waste powder on probiotic growth, antioxidant and antimutagenic activities of yogurt. J. Food Sci. Tech. 53, 1698–1708 (2015)
A.P. do Espírito Santo, N.S. Cartolano, T.F. Silva, F.A.S.M. Soares, L.A. Gioielli, P. Perego, A. Converti, M.N. Oliveira, Fibers from fruit by-products enhance probiotic viability and fatty acid profile and increase CLA content in yoghurts. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 154, 135–144 (2012)
A.P. de Espírito Santo, P. Perego, A. Converti, M.N. Oliveira, Influence of milk type and addition of passion fruit peel powder on fermentation kinetics, texture profile and bacterial viability in probiotic yoghurts. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 47, 393–399 (2012)
M. Carocho, L. Barros, A.L. Antonio, J.C.M. Barreira, A. Bento, I. Kaluska, I.C.F.R. Ferreira, Analysis of organic acids in electron beam irradiated chestnuts (Castanea sativa Mill.): effects of radiation dose and storage time. Food Chem. Toxicol. 55, 348–352 (2013)
S.C. Da Silva, I.P. Fernandes, L. Barros, Â. Fernandes, M.J. Alves, R.C. Calhelha, M.F. Barreiro, Spray-dried Spirulina platensis as an effective ingredient to improve yogurt formulations: testing different encapsulating solutions. J. Funct. Foods 60, e103427 (2019)
A. Patel, J.B. Prajapati, Biological properties of xylooligosaccharides as an emerging prebiotic and future perspective. Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm. 9, 472–480 (2015)
B.N.P. Sah, T. Vasiljevic, S. McKechnie, O.N. Donkor, Physicochemical, textural and rheological properties of probiotic yogurt fortified with fibre-rich pineapple peel powder during refrigerated storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 65, 978–986 (2016)
S.G. Rudra, P. Nath, C. Kaur, S. Basu, Rheological, storage stability and sensory profiling of low-fat yoghurt fortified with red capsicum carotenoids and inulin. J. Food Process Pres. 41, e13067 (2016)
A. Żbikowska, I. Szymańska, M. Kowalska, Impact of inulin addition on properties of natural yogurt. Appl. Sci. 10, e4317 (2020)
J. Liu, A. Nakamura, M. Corredig, Addition of pectin and soy soluble polysaccharide affects the particle size distribution of casein suspensions prepared from acidified skim milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 54, 6241–6246 (2006)
Z.H. Pang, R.L. Xu, T.Q. Luo, X.N. Che, N. Bansal, X.Q. Liu, Physiochemical properties of modified starch under yogurt manufacturing conditions and its relation to the properties of yogurt. J. Food Eng. 245, 11–17 (2019)
K. Xu, M.M. Guo, J.H. Du, Z.H. Zhang, Okra polysaccharide: Effect on the texture and microstructure of set yoghurt as a new natural stabilizer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 133, 117–126 (2019)
Z. Pang, H. Deeth, N. Bansal, Effect of polysaccharides with different ionic charge on the rheological, microstructural and textural properties of acid milk gels. Food Res. Int. 72, 62–73 (2015)
B. Cui, Y.M. Lu, C.P. Tan, G.Q. Wang, G.H. Li, Effect of cross-linked acetylated starch content on the structure and stability of set yoghurt. Food Hydrocolloid. 35, 576–582 (2014)
C. Guyot, U. Kulozik, Effect of transglutaminase-treated milk powders on the properties of skim milk yoghurt. Int. Dairy J. 21, 628–635 (2011)
T. Șanli, E. Sezgin, O. Deveci, E. Șenel, M. Benli, Effect of using transglutaminase on physical, chemical and sensory properties of set-type yoghurt. Food Hydrocolloid. 25, 1477–1481 (2011)
Y. Wen, N. Liu, X.H. Zhao, Chemical composition and rheological properties of set yoghurt prepared from skimmed milk treated with horseradish peroxidase. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 50, 473–478 (2012)
P. Mudgil, B. Jumah, F. Hamed, M. Ahmed, S. Maqsood, Rheological, micro-structural and sensorial properties of camel milk yogurt as influenced by gelatin. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 98, 646–653 (2018)
M.W.W. Koh, L.M. Merino, E. Dickinson, Rheology of acid-induced sodium caseinate gels containing added gelatin. Food Hydrocolloid. 16, 619–623 (2002)
J. Shi, Y.P. Han, X.H. Zhao, Quality attributes of set-style skimmed yoghurt affected by the addition of a cross-linked bovine gelatin. CyTA-J. Food 15, 320–325 (2017)
A.G. Cruz, R.S. Cadena, E.H.M. Walter, A.M. Mortazavian, D. Granato, J.A.F. Faria, H.M.A. Bolini, Sensory analysis: Relevance for prebiotic, probiotic, and synbiotic product development. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. F 9, 358–373 (2010)
A.H. Ibrahim, S.A. Khafila, Bacteriological, physicochemical and sensory properties of probiotic fermented camel’s milk as affected by added inulin. Egypt. J. Appl. Sci. 28, 295–313 (2013)
R. Li, Q. Ding, X.H. Zhao, Impact of milk fortification on the microbiological and physicochemical properties of set-type skimmed yoghurt using three commercial soluble prebiotics. Foods 8, e181 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong University of Petrochemical Technology (Project No. 2020rc026) and Key Research Project in Science and Technology of The Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (Project No. 11551z018). The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, JL., Ma, CM., Zhao, XH. et al. Effects of yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) juice on fermentation and textural attributes of set-style skimmed yoghurt. Food Measure 15, 2220–2230 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-00830-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-00830-z