Abstract
Introduction
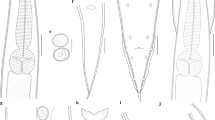
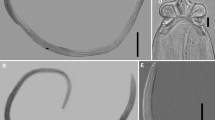
A new species of the nematode genus Parastrongyloides Morgan, 1928 was found in the caecum of six short-beaked echidnas Tachyglossus aculeatus (Shaw, 1792) collected from southwestern Australia between August 1964 and March 2020.
Methods
Specimens were prepared for microscopic examination as temporary wet mounts, measurements were made using an Olympus DP71 camera with cellSens standard software, figures were drawn using a drawing tube and light micrographs taken. DNA was extracted using a Qiagen blood and tissue kit, amplified targeting the COX1 gene region. Sequences obtained were analysed and edited using Geneious v.8.1 and aligned to existing sequences published in Genbank using MUSCLE.
Results
Parastrongyloides spratti n. sp. can be distinguished from all other species of Parastrongyloides in having the male caudal papillae arranged as a single median dome-shaped pre-cloacal papilla, three tiny pairs of ventral papillae immediately pre-cloacal, a tiny ventral pair of papillae post-cloacal and the female with four to five pairs of dorsoventral papillae immediately anterior to the vulva. A revised key to the species of Parastrongyloides found in Australia is given. Sequence analysis of the COX1 gene corroborated the species status of P. spratti.
Discussion
Morphological and molecular analyses support the status of P. spratti as a new species. Parastrongyloides may have an ancient origin in the Australian portion of Gondwanaland.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spratt DM (2017) Parastrongyloides spp. nov. (Nematoda: Rhabditoidea: Strongyloididae) from the small intestine of a monotreme from Australia and a marsupial from the Republic of Columbia. Trans R Soc S Aust 141:253–266. https://doi.org/10.1080/03721426.2017.1348048
Spratt DM (2018) A review of species of Parastrongyloides (Nematoda: Strongyloididae) from Australian marsupials with descriptions of three new species. Trans R Soc S Aust 142:162–182. https://doi.org/10.1080/03721426.2018.1500761
Grant TR (2008) Family Tachyglossidae Echidnas. In: Van Dyck S, Strahan R (eds) The Mammals of Australia. Reed New Holland, Sydney, pp 36–39
Spratt DM, Beveridge I (2016) Helminth parasites of Australian monotremes and marsupials. Zootaxa. 4132(1):1–198. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4123.1.1
Smales LR, Elliot A, Chisholm L (2021) A survey of the nematode parasites of the short-beaked echidna Tachyglossus aculeatus (Monotremata: Tachglossidae) from southwestern Australia with the description of a new subfamily, genus and species of the Subuluridae Travassos, 1914 (Nematoda: Ascaridida). Acta Parasitol. 66(1):228–235. https://doi.org/10.10007/s11686-020-00277-0
Bowles J, Blair D, McManus DP (1992) Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol Biochem Parasitol 54:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-6851(92)90109-w
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Anderson RC, Bain O (2009) Rhabditida. In: Anderson RG, Chabaud AG. Willmott S (eds) Keys to the nematode parasites of vertebrates, Archival Volume CABI, Wallingford, pp 30–43.
Hunt VL, Tsai IJ, Coghlan A, Reid AJ, Holroyd N, Foth BJ, Tracey A, Cotton JA, Stanley EJ, Beasley H, Bennett HM, Brooks K, Harsha B, Kajitani R, Kulkarni A, Harbecke D, Nagayasu E, Nichol S, Ogura Y, Quail MA, Randle N, Xia D, Brattig NW, Soblik H, Ribeiro DM, Sanchez-Flores A, Hayashi T, Itoh T, Denver DR, Grant W, Stolzfus JD, Lok JB, Murayama H, Wastling J, Streit A, Kikuchi T, Viney M, Berriman M (2016) The genomic basis of parasitism in the Strongyloides clade of nematodes. Nat Genet 48:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3495
Ko PP, Suzuki K, Canales-Ramos M, Aung MPPTHH, Htike WW, Yoshida A, Montes M, Morishita K, Gotuzzo E, Maruyama H, Nagayasu E (2020) Phylogenetic relationships of Strongyloides species in carnivore hosts. Parasitol Int 78:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2020.102151
Mackerras MJ (1959) Strongyloides and Parastrongyloides (Nematoda: Rhabdiasoidea) in Australian marsupials. Aust J Zool 7:87–104. https://doi.org/10.1071/zo9590087
Augee ML, Carriuck FN, Grant TR, Temple-Smith PD (2008) Order Monotremata, Platypus and Echidnas. In: Van Dyck S, Strahan R (eds) The Mammals of Australia. Reed New Holland, Sydney, pp 30–35
Acknowledgements
We thank Kanyana Wildlife Rehabilitation Centre Lesmurdie WA, the Anatomy Department of Murdoch University and Tayla van der Kroft and Sarah Comer from the Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions for providing us access to echidna carcases. We are also grateful to Kenny Travouillon at the Western Australian Museum for access to their echidna collection. The authors would like to thank the State Agricultural Biotechnology Centre for their use of facilities and Frances Brigg for her help with sequencing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that all applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1736415F-8564–4014-AA5E-804FE9F73953. This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited using the doi number. This is the Version of Record.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smales, L., Elliot, A., Keatley, S. et al. Morphological and Molecular Characterisation of a New Species of Parastrongyloides (Rhabditida: Strongyloididae) from the Short-Beaked Echidna Tachyglossus aculeatus from Western Australia. Acta Parasit. 67, 153–160 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-021-00443-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-021-00443-y