Abstract
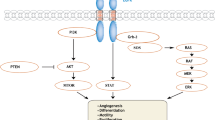
Lung cancer is one of the most common human cancers and the number one cancer killer in the United States. In general, lung cancer includes small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but NSCLC accounts for approximately 90% of lung cancer. The early diagnosis and therapy of lung cancer still presents a big challenge because validated screening tools, which can improve current early detection to reduce mortality from lung cancer, do not exist. Over the last decade, molecular genetic abnormalities have been described in NSCLC, including chromosomal aberrations, overexpression of oncogenes, and deletion and/or mutations in tumor suppressor genes. These molecular markers in NSCLC demonstrated close associations with the development of lung cancer such as Ras, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, or c-erbB-1), HER2 (c-erbB-2), c-Met, and Bcl-2. Therefore, this information may be applied for early cancer detection, classification, novel targeted therapy, and prognosis in NSCLC. Recent clinical data have revealed that targeted therapy might be the second-line therapy as an alternative approach. Currently, the targeted therapies are mainly focused on two lung cancer pathways, the EGFR and the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathways. Some clinical trials are very encouraging, but some of them are not. However, these trials have not identified a subgroup of NSCLC with biomarkers. Therefore, it is very important to select NSCLC patients with biomarkers to match targeted agents so that we can further identify effectiveness of targeted therapy in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin D M, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin, 2005, 55(2): 74–108
Alberg A J, Samet J M. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Chest, 2003, 123: 21S
Zang E A, Wynder E L. Differences in lung cancer risk between men and women: examination of the evidence. J Natl Cancer Inst, 1996, 88(34): 183–192
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun M J. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin, 2008, 58(2): 71–96
Molina J R, Adjei A A, Jett J R. Advances in chemotherapy of nonsmall cell lung cancer. Chest, 2006, 130(4): 1211–1219
Mariadason J M, Augenlicht L H, Arango D. Microarray analysis in the clinical management of cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 2003, 17(2): 377–387
Anglim P P, Alonzo T A, Laird-Offringa I A. DNA methylationbased biomarkers for early detection of non-small cell lung cancer: an update. Mol Cancer, 2008, 7: 81
Mountain C F. New prognostic factors in lung cancer. Biologic prophets of cancer cell aggression. Chest, 1995, 108(1): 246–254
Salgia R, Skarin AT. Molecular abnormalities in lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 1998, 16(3): 1207–1217
Strauss GM, Kwiatkowski D J, Harpole D H, Lynch T J, Skarin AT, Sugarbaker D J. Molecular and pathologic markers in stage I nonsmall cell carcinoma of the lung. J Clin Oncol, 1995, 13(5): 1265–1279
Rosell R, Felip E, Garcia-Campelo R, Balana C. The biology of nonsmall-cell lung cancer: identifying new targets for rational therapy. Lung Cancer, 2004, 46(2): 135–148
Devereux T R, Taylor J A, Barrett J C. Molecular mechanisms of lung cancer. Interaction of environmental and genetic factors. Giles F. Filley Lecture. Chest, 1996, 109(3 Suppl): 14S–19S
Killary A M, Wolf M E, Giambernardi T A, Naylor S L. Definition of a tumor suppressor locus within human chromosome 3p21-p22. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1992, 89(22): 10877–10881
Otterson G, Lin A, Kay F. Genetic etiology of lung cancer. Oncology (Huntingt), 1992, 6(9): 97–104, 107; discussion 108, 111-112
Hirao T, Nelson H H, Ashok T D, Wain J C, Mark E J, Christiani D C,Wiencke J K, Kelsey K T. Tobacco smoke-induced DNA damage and an early age of smoking initiation induce chromosome loss at 3p21 in lung cancer. Cancer Res, 2001, 61(2): 612–615
Hibi, K, Takahashi, T, Yamakawa, K, Ueda R, Sekido Y, Ariyoshi Y, Suyama M, Takagi H, Nakamura Y, Takahashi T. Three distinct regions involved in 3p deletion in human lung cancer. Oncogene, 1992, 7: 445–449
Hibi K, Takahashi T, Yamakawa K, Ueda R, Sekido Y, Ariyoshi Y, Suyama M, Takagi H, Nakamura Y, Takahashi T. Deletion mapping of the short arm of chromosome 8 in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 1993, 7(3): 85–88
Nakachi K, Imai K, Hayashi S, Watanabe J, Kawajiri K. Genetic susceptibility to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung in relation to cigarette smoking dose. Cancer Res, 1991, 51(19): 5177–5180
Ambrosone C B, Rao U, Michalek A M, Cummings K M, Mettlin C J. Lung cancer histologic types and family history of cancer. Analysis of histologic subtypes of 872 patients with primary lung cancer. Cancer, 1993, 72(4): 1192–1198
Slebos R J, Kibbelaar R E, Dalesio O, Kooistra A, Stam J, Meijer C J, Wagenaar S S, Vanderschueren R G, van Zandwijk N, Mooi W J. K-ras oncogene activation as a prognostic marker in adenocarcinoma of the lung. N Engl J Med, 1990, 323(9): 561–565
Rodenhuis S, Slebos R J. Clinical significance of ras oncogene activation in human lung cancer. Cancer Res, 1992, 52(Suppl): 2665–2669
Graziano S L, Gamble G P, Newman N B, Abbott L Z, Rooney M, Mookherjee S, Lamb M L, Kohman L J, Poiesz B J. Prognostic significance of K-ras codon 12 mutations in patients with resected stage I and II non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 1999, 17(2): 668–675
Graziano S L, Gamble G P, Newman N B, Abbott L Z, Rooney M, Mookherjee S, Lamb M L, Kohman L J, Poiesz B J. Cigarette smoking is strongly associated with mutation of the k-ras gene in patients with primary adenocarcinomaof the lung. Cancer, 2001, 92 (6): 1525–1530
Velu T J, Beguinot L, Vass W C, Willingham M C, Merlino G T, Pastan I, Lowy D R. Epidermal-growth-factor-dependent transformation by a human EGF receptor proto-oncogene. Science, 1987, 238(4832): 1408–1410
To C T, Tsao M S. The roles of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and met receptor in human cancers (Review). Oncol Rep, 1998, 5(5): 1013–1024
Ichimura, E, Maeshima, A, Nakajima, T, Nakamura, T. Expression of c-met/HGF receptor in human non-small cell lung carcinomas in vitro and in vivo and its prognostic significance. Jpn J Cancer Res, 1996, 87(10): 1063–1069
Hockenbery D, Nuñez G, Milliman C, Schreiber R D, Korsmeyer S J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature, 1990, 348(6299): 334–336
Anton R C, Brown RW, Younes M, Gondo M M, Stephenson M A, Cagle P T. Absence of prognostic significance of bcl-2 immunopositivity in non-small cell lung cancer: analysis of 427 cases. Hum Pathol, 1997, 28(9): 1079–1082
Ohmura Y, Aoe M, Andou A, Shimizu N. Telomerase activity and Bcl-2 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2000, 6(8): 2980–2987
Laudanski J, Chyczewski L, Niklinska W E, Kretowska M, Furman M, Sawicki B, Niklinski J. Expression of bcl-2 protein in non-small cell lung cancer: correlation with clinicopathology and patient survival. Neoplasma, 1999, 46(1): 25–30
Groeger A M, Caputi M, Esposito V, De Luca A, Salat A, Murabito M, Giordano G G, Baldi F, Giordano A, Wolner E. Bcl-2 protein expression correlates with nodal status in non small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res, 1999, 19(1B): 821–824
Pezzella F, Turley H, Kuzu I, Tungekar M F, Dunnill M S, Pierce C B, Harris A, Gatter K C, Mason D Y. bcl-2 protein in non-small cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 1993, 329(10): 690–694
Silvestrini R, Costa A, Lequaglie C, Mochen C, Veneroni S, Leutner M, Ravasi G. Bcl-2 protein and prognosis in patients with potentially curable non-small-cell lung cancer. Virchows Arch, 1998, 432(5): 441–444
Huang C I, Neuberg D, Johnson B E, Wei J Y, Christiani D C. Expression of bcl-2 protein is associated with shorter survival in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer, 2003, 98(1): 135–143
Sharp T V, Munoz F, Bourboulia D, Presneau N, Darai E, Wang H W, Cannon M, Butcher D N, Nicholson A G, Klein G, Imreh S, Boshoff C. LIM domains-containing protein 1 (LIMD1), a tumor suppressor encoded at chromosome 3p21.3, binds pRB and represses E2F-driven transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2004, 101(47): 16531–16536
Zhang S Y, Liu S C, Johnson D G, Klein-Szanto A J. E2F-1 gene transfer enhances invasiveness of human head and neck carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res, 2000, 60(21): 5972–5976
Banerjee D, Gorlick R, Liefshitz A, Danenberg K, Danenberg P C, Danenberg P V, Klimstra D, Jhanwar S, Cordon-Cardo C, Fong Y, Kemeny N, Bertino J R. Levels of E2F-1 expression are higher in lung metastasis of colon cancer as compared with hepatic metastasis and correlate with levels of thymidylate synthase. Cancer Res, 2000, 60(9): 2365–2367
Lane D P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature, 1992, 358 (6381): 15–16
Tsao M S, Aviel-Ronen S, Ding K, Lau D, Liu N, Sakurada A, Whitehead M, Zhu C Q, Livingston R, Johnson D H, Rigas J, Seymour L, Winton T, Shepherd F A. Prognostic and predictive importance of p53 and RAS for adjuvant chemotherapy in non small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2007, 25(33): 5240–5247
Knudson A G Jr. The ninth Gordon Hamilton-Fairley memorial lecture. Hereditary cancers: clues to mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Br J Cancer, 1989, 59(5): 661–666
Xu H J, Quinlan D C, Davidson A G, Hu S X, Summers C L, Li J, Benedict W F. Altered retinoblastoma protein expression and prognosis in early-stage non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst, 1994, 86(9): 695–699
Xu H J, Cagle P T, Hu S X, Li J, Benedict W F. Altered retinoblastoma and p53 protein status in non-small cell carcinoma of the lung: potential synergistic effects on prognosis. Clin Cancer Res, 1996, 2(7): 1169–1176
Shapiro G I, Rollins B J. p16INK4A as a human tumor suppressor. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1996, 18; 1242(3): 165–169
Hannon G J, Beach D. p15INK4B is a potential effector of TGFbeta-induced cell cycle arrest. Nature, 1994, 371(6494): 257–261
Shapiro G I, Edwards C D, Kobzik L, Godleski J, Richards W, Sugarbaker D J, Rollins B J. Reciprocal Rb inactivation and p16INK4 expression in primary lung cancers and cell lines. Cancer Res, 1995, 55(3): 505–509
Kratzke R A, Greatens T M, Rubins J B, Maddaus M A, Niewoehner D E, Niehans G A, Geradts J. Rb and p16INK4a expression in resected non-small cell lung tumors. Cancer Res, 1996, 56(15): 3415–3420
Gonzalez-Quevedo R, Iniesta P, Moran A, de Juan C, Sanchez-Pernaute A, Fernandez C, Torres A, Diaz-Rubio E, Balibrea J L, Benito M. Cooperative role of telomerase activity and p16 expression in the prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2002, 20(1): 254–262
Gautam A, Li Z R, Bepler G. RRM1-induced metastasis suppression through PTEN-regulated pathways. Oncogene, 2003, 22(14): 2135–2142
Zheng Z, Chen T, Li X, Haura E, Sharma A, Bepler G. DNA synthesis and repair genes RRM1 and ERCC1 in lung cancer. N Engl J Med, 2007, 356(8): 800–808
Ohta Y, Nozaki Z, Nozawa H, Kamesui T, Tsunezuka Y, Oda M, Watanabe G. The predictive value of vascular endothelial growth factor and nm23 for the diagnosis of occult metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res, 2001, 92(3): 361–366
Tomita M, Ayabe T, Matsuzaki Y, Onitsuka T. Immunohistochemical analysis of nm23-H1 gene product in node-positive lung cancer and lymph nodes. Lung Cancer, 1999, 24(1): 11–16
Higashiyama M, Taki T, Ieki Y, Adachi M, Huang C L, Koh T, Kodama K, Doi O, Miyake M. Reduced motility related protein-1 (MRP-1/CD9) gene expression as a factor of poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Res, 1995, 55(24): 6040–6044
Lau L F, Lam S C. The CCN family of angiogenic regulators: the integrin connection. Exp Cell Res, 1999, 248(1): 44–57
Chen N, Leu S J, Todorovic V, Lam S C, Lau L F. Identification of a novel integrin alphavbeta3 binding site in CCN1 (CYR61) critical for pro-angiogenic activities in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(42): 44166–44176
Xie D, Yin D, Wang H J, Liu G T, Elashoff R, Black K, Koeffler H P. Levels of expression of CYR61 and CTGF are prognostic for tumor progression and survival of individuals with gliomas. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10(6): 2072–2081
Chen C C, Chen N, Lau L F. The angiogenic factors Cyr61 and connective tissue growth factor induce adhesive signaling in primary human skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(13): 10443–10452
Tong X, Xie D, O’Kelly J, Miller C W, Muller-Tidow C, Koeffler H P. Cyr61, a member of CCN family, is a tumor suppressor in nonsmall cell lung cancer. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(50): 47709–47714
Chang C C, Shih J Y, Jeng Y M, Su J L, Lin B Z, Chen S T, Chau Y P, Yang P C, Kuo M L. Connective tissue growth factor and its role in lung adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2004, 96(5): 364–375
Shih J Y, Yang S C, Hong T M, Yuan A, Chen J J, Yu C J, Chang Y L, Lee Y C, Peck K, Wu C W, Yang P C. Collapsin response mediator protein-1 and the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2001, 93(18): 1392–1400
Pérez-Soler R, Chachoua A, Hammond L A, Rowinsky E K, Huberman M, Karp D, Rigas J, Clark G M, Santabárbara P, Bonomi P. Determinants of tumor response and survival with erlotinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(16), 3238–3247
Jackman DM, Yeap B Y, Lindeman N I, Fidias P, Rabin MS, Temel J, Skarin A T, Meyerson M, Holmes A J, Borras A M, Freidlin B, Ostler P A, Lucca J, Lynch T J, Johnson B E, Jänne P A. Phase II clinical trial of chemotherapy-naive patients > or = 70 years of age treated with erlotinib for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2007, 25(7): 760–766
Shepherd F A, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan E H, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, Campos D, Maoleekoonpiroj S, Smylie M, Martins R, van Kooten M, Dediu M, Findlay B, Tu D, Johnston D, Bezjak A, Clark G, Santabárbara P, Seymour L; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Erlotinib in previously treated nonsmall-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med, 2005, 353(2): 123–132
Herbst R S, Prager D, Hermann R, Fehrenbacher L, Johnson B E, Sandler A, Kris MG, Tran H T, Klein P, Li X, Ramies D, Johnson D H, Miller VA; TRIBUTE Investigator Group. TRIBUTE: A phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced non-smallcell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2005, 23(25): 5892–5899
Gatzemeier U, Pluzanska A, Szczesna A et al. Results of a phase III trial of erlotinib (OSI-774) combined with cisplatin and GC chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(suppl 14): 619s
Giaccone G, Herbst R S, Manegold C, Scagliotti G, Rosell R, Miller V, Natale R B, Schiller J H, Von Pawel J, Pluzanska A, Gatzemeier U, Grous J, Ochs J S, Averbuch S D, Wolf M K, Rennie P, Fandi A, Johnson D H. Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial-INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(5): 777–784
Herbst R S, Giaccone G, Schiller J H, Natale R B, Miller V, Manegold C, Scagliotti G, Rosell R, Oliff I, Reeves J A, Wolf M K, Krebs A D, Averbuch S D, Ochs J S, Grous J, Fandi A, Johnson D H. Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase III trial-INTACT 2. J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(5): 785–794
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard J Y, Nishiwaki Y, Vansteenkiste J, Kudoh S, Rischin D, Eek R, Horai T, Noda K, Takata I, Smit E, Averbuch S, Macleod A, Feyereislova A, Dong R P, Baselga J. Multi-institutional randomized Phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) [corrected]. J Clin Oncol, 2003, 21(12): 2237–2246
Thatcher N, Chang A, Parikh P, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, von Pawel J, Thongprasert S, Tan E H, Pemberton K, Archer V, Carroll K. Gefitinib plus best supportive care in previously treated patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicentre study (Iressa Survival Evaluation in Lung Cancer). Lancet, 2005, 366(6496): 1527–1537
Hanna N, Lilenbaum R, Ansari R, Lynch T, Govindan R, Jänne PA, Bonomi P. Phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2006, 24(33): 5253–5258
Pirker R, Szczesna A, von Pawel J, Krzakowski M, Ramlau R, Park K, Gatzemeier U, Bajeta E, Emig M, Pereira J R. A randomized, multicenter, phase III study of cetuximab in combination with cisplatin/vinorelbine (CV) versus CValone in the first-line treatment of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Oncol (Suppl), 2008, 26(15S): 3
Socinski MA. Antibodies to the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer: current status of matuzumab and panitumumab. Clinical Cancer Research, 2007, (13): 4597s–4601s
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry M C, Brahmer J, Schiller J H, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R, Johnson D H. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med, 2006, 355(24): 2542–2550
Johnson D H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W F, Herbst R S, Nemunaitis J J, Jablons D M, Langer C J, DeVore R F 3rd, Gaudreault J, Damico L A, Holmgren E, Kabbinavar F. Randomized phase II trial comparing bevacizumab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel with carboplatin and paclitaxel alone in previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(11): 2184–2191
Socinski M A, Novello S, Sanchez J M. Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in previously treated, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Preliminary results of a multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol, 2006, 24(18S): 7001
Tateishi M, Ishida T, Mitsudomi T, Kaneko S, Sugimachi K. Prognostic value of c-erbB-2 protein expression in human lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer, 1991, 27(11): 1372–1375
Shi D, He G, Cao S, Pan W, Zhang H Z, Yu D, Hung M C. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2/neu-encoded p185 protein in primary lung cancer. Mol Carcinog, 1992, 5(3): 213–218
Harpole D H Jr, Herndon J E 2nd, Wolfe W G, Iglehart J D, Marks J R. A prognostic model of recurrence and death in stage I non-small cell lung cancer utilizing presentation, histopathology, and oncoprotein expression. Cancer Res, 1995, 55(1): 51–56
Hsieh C C, Chow K C, Fahn H J, Tsai C M, Li W Y, Huang M H, Wang L S. Prognostic significance of HER-2/neu overexpression in stage I adenocarcinoma of lung. Ann Thorac Surg, 1998, 66(4): 1159–1163
Cantero R, Torres A J, Maestro M L, Hernando F, Sanz M T, Del Barco V, Gomez A, Fernandez C, Balibrea J L. Prognostic value of the quantified expression of p185 in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2000, 119(6): 1119–1125
Ardizzoni A, Cafferata MA, Paganuzzi M, Filiberti R, Marroni P, Neri M, Fontana V, Nicolo G, Perdelli L, Stampino C G, Rosso R, Puntoni R. Study of pretreatment serum levels of HER-2/neu oncoprotein as a prognostic and predictive factor in patients with advanced nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer, 2001, 92(7): 1896–1904
Kase S, Sugio K, Yamazaki K, Okamoto T, Yano T, Sugimachi K. Expression of E-cadherin and beta-catenin in human non-small cell lung cancer and the clinical significance. Clin Cancer Res, 2000, 6 (12): 4789–4796
Hommura F, Furuuchi K, Yamazaki K, Ogura S, Kinoshita I, Shimizu M, Moriuchi T, Katoh H, Nishimura M, Dosaka-Akita H. Increased expression of beta-catenin predicts better prognosis in nonsmall cell lung carcinomas. Cancer, 2002, 94(3): 752–758
Bremnes R M, Veve R, Gabrielson E, Hirsch F R, Baron A, Bemis L, Gemmill R M, Drabkin H A, Franklin W A. High-throughput tissue microarray analysis used to evaluate biology and prognostic significance of the E-cadherin pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2002, 20(10): 2417–2428
Burbee D G, Forgacs E, Zochbauer-Muller S, Shivakumar L, Fong K, Gao B, Randle D, Kondo M, Virmani A, Bader S, Sekido Y, Latif F, Milchgrub S, Toyooka S, Gazdar A F, Lerman M I, Zabarovsky E, White M, Minna J D. Epigenetic inactivation of RASSF1A in lung and breast cancers and malignant phenotype suppression. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2001, 93(9): 691–699
Dammann R, Li C, Yoon J H, Chin P L, Bates S, Pfeifer G P. Epigenetic inactivation of a RAS association domain family protein from the lung tumour suppressor locus 3p21.3. Nat Genet, 2000, 25 (3): 315–319
Maruyama R, Sugio K, Yoshino I, Maehara Y, Gazdar A F. Hypermethylation of FHIT as a prognostic marker in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer, 2004, 100(7): 1472–1477
Huncharek M, Muscat J, Geschwind J F. K-ras oncogene mutation as a prognostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer: a combined analysis of 881 cases. Carcinogenesis, 1999, 20: 1507–1510
Higashiyama M, Kodama K, Yokouchi H, Takami K, Adachi M, Taki T, Ishiguro S, Nakamori S, Yoshie O, Miyake M. KAI1/CD82 expression in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma is a novel, favorable prognostic factor: an immunohistochemical analysis. Cancer, 1998, 83(3): 466–474
Takaoka A, Hinoda Y, Satoh S, Adachi Y, Itoh F, Adachi M, Imai K. Suppression of invasive properties of colon cancer cells by ametastasis suppressor KAI1 gene. Oncogene, 1998, 16(11): 1443–1453
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, B., Zhang, J., Woods, J.S. et al. Molecular markers and pathogenically targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Med. China 3, 245–255 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-009-0044-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-009-0044-3