Abstract
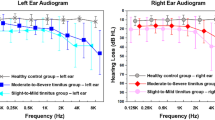
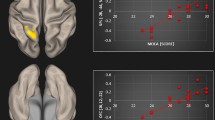
Wide-ranging functional remodeling is involved in sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), which has been demonstrated to have accumulated risk of cognitive and emotional dysfunction. Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) has close connections with the auditory area and plays a vital role in regulating the cognitive, emotional and auditory processing. However, the functional reorganization of the ACC and its associations with potential cognitive and emotional impairments involved in SNHL have never been explored. Thirty-five patients with long-term bilateral SNHL and thirty-five well-matched healthy controls were recruited for this study. We analyzed resting-state functional MRI data and neuropsychological test scores from these participants. Functional connectivity of the ACC subdivisions, voxel-wise degree centrality (DC) and intra−/internetwork connectivity were computed to evaluate the functional changes related to cognitive, emotional and multiple sensory functions. ANCOVA and post hoc analyses were conducted to identify differences between normal controls and patients for each measure. Widespread alterations of functional coupling with the subdivisions of the ACC were observed in regions involved in cognitive, emotional and multiple sensory processing, particularly within the cingulo-opercular network (CON), default mode network (DMN) and auditory network (AN) in the SNHL patients. Outstandingly increased DC was found in the ACC. Network analyses showed significant intra- and inter-network hypo-synchronization in the SNHL patients. Importantly, the functional alterations were associated with the anxiety states and the processing speed. The functional reorganization in the ACC and the disturbance of intrinsic multiple network functional connectivity among the CON, DMN, and AN were found in the SNHL patient, which might shed more lights on potential substrates underlying the cognitive and emotional impairments related to the SNHL.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaerts, K., Swinnen, S., & Wenderoth, N. (2011). Action perception in individuals with congenital blindness or deafness: How does the loss of a sensory modality from birth affect perception-induced motor facilitation? Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 23(5), 1080–1087.
Andersen, S. L., & Teicher, M. H. (2008). Stress, sensitive periods and maturational events in adolescent depression. Trends in Neurosciences, 31(4), 183–191.
Bedwell, S. A., Billett, E. E., Crofts, J. J., & Tinsley, C. J. (2017). Differences in anatomical connections across distinct areas in the rodent prefrontal cortex. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 45(6), 859–873.
Bonnici, H., Richter, F., Yazar, Y., & Simons, J. (2016). Multimodal feature integration in the angular gyrus during episodic and semantic retrieval. The Journal of Neuroscience, 36(20), 5462–5471.
Brier, M. R., Thomas, J. B., Snyder, A. Z., Benzinger, T. L., Zhang, D., Raichle, M. E., Holtzman, D. M., Morris, J. C., & Ances, B. M. (2012). Loss of intranetwork and internetwork resting state functional connections with Alzheimer's disease progression. The Journal of Neuroscience, 32(26), 8890–8899.
Burgess, P., Gilbert, S., & Dumontheil, I. (2007). Function and localization within rostral prefrontal cortex (area 10). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci., 362(1481), 887–899.
Bush, G., Luu, P., & Posner, M. (2000). Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends Cogn. Sci. (Regul. Ed.), 4(6), 215–222.
Calvert, G. A., Campbell, R., & Brammer, M. J. (2000). Evidence from functional magnetic resonance imaging of crossmodal binding in the human heteromodal cortex. Current Biology, 10(11), 649–657.
Cardon, G., & Sharma, A. (2018). Somatosensory cross-modal reorganization in adults with age-related, early-stage hearing loss. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12, 172.
Chen, Y. C., Chen, H., Jiang, L., Bo, F., Xu, J. J., Mao, C. N., Salvi, R., Yin, X., Lu, G., & Gu, J. P. (2018a). Presbycusis disrupts spontaneous activity revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 12, 44.
Chen, Y. C., Liu, S., Lv, H., Bo, F., Feng, Y., Chen, H., Xu, J. J., Yin, X., Wang, S., & Gu, J. P. (2018b). Abnormal resting-state functional connectivity of the anterior cingulate cortex in unilateral chronic tinnitus patients. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 12, 9.
Contrera, K., Betz, J., Deal, J., Choi, J., Ayonayon, H., Harris, T., et al. (2017). Association of Hearing Impairment and Anxiety in older adults. Journal of Aging and Health, 29(1), 172–184.
Dosenbach, N. U., Fair, D. A., Miezin, F. M., Cohen, A. L., Wenger, K. K., Dosenbach, R. A., et al. (2007). Distinct brain networks for adaptive and stable task control in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(26), 11073–11078.
Frith, C., Friston, K., Herold, S., Silbersweig, D., Fletcher, P., Cahill, C., et al. (1995). Regional brain activity in chronic schizophrenic patients during the performance of a verbal fluency task. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 167(3), 343–349.
Guerreiro, M., & Van Gerven, P. (2017). Disregarding hearing loss leads to overestimation of age-related cognitive decline. Neurobiology of Aging, 56, 180–189.
Gurgel, R., Ward, P., Schwartz, S., Norton, M., Foster, N., & Tschanz, J. (2014). Relationship of hearing loss and dementia: A prospective, population-based study. Otology & Neurotology, 35(5), 775–781.
Gusnard, D. A., Akbudak, E., Shulman, G. L., & Raichle, M. E. (2001). Medial prefrontal cortex and self-referential mental activity: Relation to a default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 98(7), 4259–4264.
Hort, J., Ford, R. A., Eldeghaidy, S., & Francis, S. T. (2016). Thermal taster status: Evidence of cross-modal integration. Human Brain Mapping, 37(6), 2263–2275.
Husain, F., Medina, R., Davis, C., Szymko-Bennett, Y., Simonyan, K., Pajor, N., et al. (2011). Neuroanatomical changes due to hearing loss and chronic tinnitus: A combined VBM and DTI study. Brain Research, 1369, 74–88.
Husain, F., Carpenter-Thompson, J., & Schmidt, S. (2014). The effect of mild-to-moderate hearing loss on auditory and emotion processing networks. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 8, 10.
Keller, C. J., Bickel, S., Honey, C. J., Groppe, D. M., Entz, L., Craddock, R. C., Lado, F. A., Kelly, C., Milham, M., & Mehta, A. D. (2013). Neurophysiological investigation of spontaneous correlated and anticorrelated fluctuations of the BOLD signal. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(15), 6333–6342.
Lahav, A., Saltzman, E., & Schlaug, G. (2007). Action representation of sound: Audiomotor recognition network while listening to newly acquired actions. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27(2), 308–314.
Laurienti, P., Wallace, M., Maldjian, J., Susi, C., Stein, B., & Burdette, J. (2003). Cross-modal sensory processing in the anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortices. Human Brain Mapping, 19(4), 213–223.
Lee, J. S., Lee, D. S., Oh, S. H., Kim, C. S., Kim, J.-W., Hwang, C. H., Koo, J., Kang, E., Chung, J. K., & Lee, M. C. (2003). PET evidence of neuroplasticity in adult auditory cortex of postlingual deafness. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 44(9), 1435–1439.
Leech, R., Kamourieh, S., Beckmann, C. F., & Sharp, D. J. (2011). Fractionating the default mode network: Distinct contributions of the ventral and dorsal posterior cingulate cortex to cognitive control. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(9), 3217–3224.
Li, Y., Booth, J., Peng, D., Zang, Y., Li, J., Yan, C., et al. (2013). Altered intra- and inter-regional synchronization of superior temporal cortex in deaf people. Cerebral Cortex, 23(8), 1988–1996.
Lin, F., Ferrucci, L., Metter, E., An, Y., Zonderman, A., & Resnick, S. (2011). Hearing loss and cognition in the Baltimore longitudinal study of aging. Neuropsychology, 25(6), 763–770.
McGuire, P., David, A., Murray, R., Frackowiak, R., Frith, C., Wright, I., et al. (1995). Abnormal monitoring of inner speech: A physiological basis for auditory hallucinations. The Lancet, 346(8975), 596–600.
Medalla, M., & Barbas, H. (2010). Anterior cingulate synapses in prefrontal areas 10 and 46 suggest differential influence in cognitive control. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30(48), 16068–16081.
Metzak, P., Feredoes, E., Takane, Y., Wang, L., Weinstein, S., Cairo, T., Ngan, E. T. C., & Woodward, T. S. (2011). Constrained principal component analysis reveals functionally connected load-dependent networks involved in multiple stages of working memory. Human Brain Mapping, 32(6), 856–871.
Micarelli, A., Chiaravalloti, A., Viziano, A., Danieli, R., Schillaci, O., & Alessandrini, M. (2017). Early cortical metabolic rearrangement related to clinical data in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Hearing Research, 350, 91–99.
Morrone, M. C. (2010). Brain development: Critical periods for cross-sensory plasticity. Current Biology, 20(21), R934–R936.
Mulert, C., Leicht, G., Pogarell, O., Mergl, R., Karch, S., Juckel, G., Möller, H. J., & Hegerl, U. (2007). Auditory cortex and anterior cingulate cortex sources of the early evoked gamma-band response: Relationship to task difficulty and mental effort. Neuropsychologia, 45(10), 2294–2306.
O’Reilly, R. C. (2010). The what and how of prefrontal cortical organization. Trends in Neurosciences, 33(8), 355–361.
Peelle, J. E., & Wingfield, A. (2016). The neural consequences of age-related hearing loss. Trends in Neurosciences, 39(7), 486–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2016.05.001.
Petrovic, P., Dietrich, T., Fransson, P., Andersson, J., Carlsson, K., & Ingvar, M. (2005). Placebo in emotional processing—Induced expectations of anxiety relief activate a generalized modulatory network. Neuron, 46(6), 957–969.
Rosemann, S., & Thiel, C. (2018). Audio-visual speech processing in age-related hearing loss: Stronger integration and increased frontal lobe recruitment. Neuroimage, 175, 425–437.
Ruff, C. C. (2013). Sensory processing: who's in (top-down) control? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1296(1), 88–107.
Rutherford, B. R., Brewster, K., Golub, J. S., Kim, A. H., & Roose, S. P. (2018). Sensation and psychiatry: Linking age-related hearing loss to late-life depression and cognitive decline. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 175(3), 215–224.
Schmidt, S. A., Akrofi, K., Carpenter-Thompson, J. R., & Husain, F. T. (2013). Default mode, dorsal attention and auditory resting state networks exhibit differential functional connectivity in tinnitus and hearing loss. PLoS One, 8(10), e76488.
Schmithorst, V., Plante, E., & Holland, S. (2014). Unilateral deafness in children affects development of multi-modal modulation and default mode networks. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 164.
Scott, S. K., McGettigan, C., & Eisner, F. (2009). A little more conversation, a little less action--candidate roles for the motor cortex in speech perception. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 10(4), 295–302.
Smith, S., & Pichora-Fuller, M. (2015). Associations between speech understanding and auditory and visual tests of verbal working memory: Effects of linguistic complexity, task, age, and hearing loss. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1394.
Smith, S. M., Fox, P. T., Miller, K. L., Glahn, D. C., Fox, P. M., Mackay, C. E., Filippini, N., Watkins, K. E., Toro, R., Laird, A. R., & Beckmann, C. F. (2009). Correspondence of the brain's functional architecture during activation and rest. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(31), 13040–13045.
Suo, X., Lei, D., Li, K., Chen, F., Li, F., Li, L., Huang, X., Lui, S., Li, L., Kemp, G. J., & Gong, Q. (2015). Disrupted brain network topology in pediatric posttraumatic stress disorder: A resting-state fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 36(9), 3677–3686.
Sylvester, C. M., Corbetta, M., Raichle, M. E., Rodebaugh, T. L., Schlaggar, B. L., Sheline, Y. I., Zorumski, C. F., & Lenze, E. J. (2012). Functional network dysfunction in anxiety and anxiety disorders. Trends in Neurosciences, 35(9), 527–535.
Vannson, N., James, C., Fraysse, B., Lescure, B., Strelnikov, K., Deguine, O., et al. (2017). Speech-in-noise perception in unilateral hearing loss: Relation to pure-tone thresholds and brainstem plasticity. Neuropsychologia, 102, 135–143.
Wang, X., Fan, Y., Zhao, F., Wang, Z., Ge, J., Zhang, K., Gao, Z., Gao, J. H., Yang, Y., Fan, J., Zou, Q., & Liu, P. (2014). Altered regional and circuit resting-state activity associated with unilateral hearing loss. PLoS One, 9(5), e96126.
Wang, X., Xu, P., Li, P., Wang, Z., Zhao, F., Gao, Z., Xu, L., Luo, Y. J., Fan, J., & Liu, P. (2016). Alterations in gray matter volume due to unilateral hearing loss. Scientific Reports, 6, 25811.
Willems, R. M., Ozyurek, A., & Hagoort, P. (2009). Differential roles for left inferior frontal and superior temporal cortex in multimodal integration of action and language. Neuroimage, 47(4), 1992–2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.066.
Wilson, B. S., Tucci, D. L., Merson, M. H., & O'Donoghue, G. M. (2017). Global hearing health care: New findings and perspectives. The Lancet, 390(10111), 2503–2515.
Wimmer, R., Schmitt, L., Davidson, T., Nakajima, M., Deisseroth, K., & Halassa, M. (2015). Thalamic control of sensory selection in divided attention. Nature, 526(7575), 705–709.
Yang, M., Chen, H. J., Liu, B., Huang, Z. C., Feng, Y., Li, J., Chen, J. Y., Zhang, L. L., Ji, H., Feng, X., Zhu, X., & Teng, G. J. (2014). Brain structural and functional alterations in patients with unilateral hearing loss. Hearing Research, 316, 37–43.
Zhang, G. Y., Yang, M., Liu, B., Huang, Z. C., Chen, H., Zhang, P. P., Li, J., Chen, J. Y., Liu, L. J., Wang, J., & Teng, G. J. (2015). Changes in the default mode networks of individuals with long-term unilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Neuroscience, 285, 333–342.
Zhang, Y., Mao, Z., Feng, S., Liu, X., Lan, L., Zhang, J., & Yu, X. (2018). Altered functional networks in long-term unilateral hearing loss: A connectome analysis. Brain and Behavior: A Cognitive Neuroscience Perspective, 8(2), e00912.
Zikopoulos, B., & Barbas, H. (2006). Prefrontal projections to the thalamic reticular nucleus form a unique circuit for attentional mechanisms. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(28), 7348–7361.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NOs. 81520108015 and 81230034), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (NO. 2242018 k30004) and the National Key Basic Research Program of China (NOs. 2013CB733800 and 2013CB733803). Y. Luan conducted the experiments, recruited the participants, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; C. Wang helped with the integration of the data; Y. Jiao, T. Tang and C. Lu helped with the analyses of the data. J. Zhang helped the data collection. R. Salvi provided suggestions and guidance in the discussion. G.J. Teng directed this study, designed the research and gave key advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have approved the manuscript. There are no potential conflicts of interest to declare. All the participants provided written informed consent before the experiment in the current study, which was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Zhongda Hospital of Southeast University.
Ethical approval and informed consent
This research was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Zhongda Hospital of Southeast University, and all the participants provided written informed consent before the experiment. All the procedures were conducted in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1880 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, Y., Wang, C., Jiao, Y. et al. Abnormal functional connectivity and degree centrality in anterior cingulate cortex in patients with long-term sensorineural hearing loss. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 682–695 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-0004-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-0004-0