Abstract
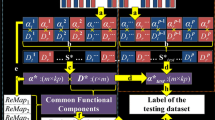
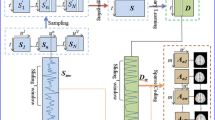
Assessing functional brain activation patterns in neuropsychiatric disorders such as cocaine dependence (CD) or pathological gambling (PG) under naturalistic stimuli has received rising interest in recent years. In this paper, we propose and apply a novel group-wise sparse representation framework to assess differences in neural responses to naturalistic stimuli across multiple groups of participants (healthy control, cocaine dependence, pathological gambling). Specifically, natural stimulus fMRI (N-fMRI) signals from all three groups of subjects are aggregated into a big data matrix, which is then decomposed into a common signal basis dictionary and associated weight coefficient matrices via an effective online dictionary learning and sparse coding method. The coefficient matrices associated with each common dictionary atom are statistically assessed for each group separately. With the inter-group comparisons based on the group-wise correspondence established by the common dictionary, our experimental results demonstrated that the group-wise sparse coding and representation strategy can effectively and specifically detect brain networks/regions affected by different pathological conditions of the brain under naturalistic stimuli.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron-Cohen, S., Ring, H. A., Wheelwright, S., Bullmore, E. T., Brammer, M. J., Simmons, A., et al. (1999). Social intelligence in the normal and autistic brain: an fMRI study. European Journal of Neuroscience, 11(6), 1891–1898.
Bartels, A., & Zeki, S. (2004). The chronoarchitecture of the human brain—natural viewing conditions reveal a time-based anatomy of the brain. NeuroImage, 22(1), 419–433.
Beckmann, C. F., & Smith, S. M. (2005). Tensorial extensions of independent component analysis for multisubject FMRI analysis. NeuroImage, 25(1), 294–311.
Bigler, E. D., Mortensen, S., Neeley, E. S., Ozonoff, S., Krasny, L., Johnson, M., et al. (2007). Superior temporal gyrus, language function, and autism. Developmental Neuropsychology, 31(2), 217–238.
Bordier, C., Puja, F., & Macaluso, E. (2013). Sensory processing during viewing of cinematographic material: Computational modeling and functional neuroimaging. NeuroImage, 67, 213–226.
Childress, A. R., Mozley, P. D., McElgin, W., Fitzgerald, J., Reivich, M., & O’brien, C. P. (1999). Limbic activation during cue-induced cocaine craving. American Journal of Psychiatry, 156, 11–18.
Codispoti, M., Surcinelli, P., & Baldaro, B. (2008). Watching emotional movies: Affective reactions and gender differences. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 69(2), 90–95.
Crockford, D. N., Goodyear, B., Edwards, J., Quickfall, J., & el-Guebaly, N. (2005). Cue-induced brain activity in pathological gamblers. Biological Psychiatry, 58(10), 787–795.
Damasio, A. R., Grabowski, T. J., Bechara, A., Damasio, H., Ponto, L. L., Parvizi, J., et al. (2000). Subcortical and cortical brain activity during the feeling of self-generated emotions. Nature Neuroscience, 3(10), 1049–1056.
Decety, J., & Jackson, P. L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3(2), 71–100.
Friston, K. J., Holmes, A. P., Worsley, K. J., Poline, J. P., Frith, C. D., & Frackowiak, R. S. (1994). Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Human Brain Mapping, 2(4), 189–210.
Garavan, H. (2010). Insula and drug cravings. Brain Structure and Function, 214(5–6), 593–601.
Gazzaniga, M. S. (2004). The cognitive neurosciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT press.
Goldstein, R. Z., Tomasi, D., Rajaram, S., Cottone, L. A., Zhang, L., Maloney, T. E., et al. (2007). Role of the anterior cingulate and medial orbitofrontal cortex in processing drug cues in cocaine addiction. Neuroscience, 144(4), 1153–1159.
Goudriaan, A. E., De Ruiter, M. B., Van Den Brink, W., Oosterlaan, J., & Veltman, D. J. (2010). Brain activation patterns associated with cue reactivity and craving in abstinent problem gamblers, heavy smokers and healthy controls: an fMRI study. Addiction Biology, 15(4), 491–503.
Gur, R. C., Alsop, D., Glahn, D., Petty, R., Swanson, C. L., Maldjian, J. A., et al. (2000). An fMRI study of sex differences in regional activation to a verbal and a spatial task. Brain and Language, 74(2), 157–170.
Han, J., Ji, X., Hu, X., Guo, L., & Liu, T. (2015). Arousal recognition using audio-visual features and fmri-based brain response. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 6(4), 337–347.
Hasson, U., Malach, R., & Heeger, D. J. (2010). Reliability of cortical activity during natural stimulation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14(1), 40–48.
Heatherton, T. F., Kozlowski, L. T., Frecker, R. C., & FAGERSTROM, K. O. (1991). The Fagerström test for nicotine dependence: a revision of the Fagerstrom Tolerance Questionnaire. British Journal of Addiction, 86(9), 1119–1127.
Hester, R., & Garavan, H. (2004). Executive dysfunction in cocaine addiction: evidence for discordant frontal, cingulate, and cerebellar activity. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(49), 11017–11022.
Hu, X., Lv, C., Cheng, G., Lv, J., Guo, L., Han, J., et al. (2015). Sparsity-constrained fMRI Decoding of visual saliency in naturalistic video streams. IEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental Development, 7(2), 65–75.
Jackson, P. L., Brunet, E., Meltzoff, A. N., & Decety, J. (2006). Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain. Neuropsychologia, 44(5), 752–761.
Kober, H., Lacadie, C. M., Wexler, B. E., Malison, R. T., Sinha, R., & Potenza, M. N. (2016). Brain activity during cocaine craving and gambling urges: an fMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology, 4(2), 628–637.
Kosten, T. R., Scanley, B. E., Tucker, K. A., Oliveto, A., Prince, C., Sinha, R., et al. (2006). Cue-induced brain activity changes and relapse in cocaine-dependent patients. Neuropsychopharmacology, 31(3), 644–650.
Kret, M. E., & De Gelder, B. (2012). A review on sex differences in processing emotional signals. Neuropsychologia, 50(7), 1211–1221.
Lahnakoski, J. M., Glerean, E., Salmi, J., Jääskeläinen, I. P., Sams, M., Hari, R., et al. (2012). Naturalistic FMRI mapping reveals superior temporal sulcus as the hub for the distributed brain network for social perception. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6, 233.
Lesieur, H. R., & Blume, S. B. (1987). The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS): a new instrument for the identification of pathological gamblers. American Journal of Psychiatry, 144(9), 1184–1188.
Lv, J., Jiang, X., Li, X., Zhu, D., Chen, H., Zhang, T., et al. (2015a). Sparse representation of whole-brain fMRI signals for identification of functional networks. Medical Image Analysis, 20(1), 112–134.
Lv, J., Jiang, X., Li, X., Zhu, D., Zhang, S., Zhao, S., et al. (2015b). Holistic atlases of functional networks and interactions reveal reciprocal organizational architecture of cortical function. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 62(4), 1120–1131.
Lv, J., Jiang, X., Li, X., Zhu, D., Zhao, S., Zhang, T., et al. (2015c). Assessing effects of prenatal alcohol exposure using group-wise sparse representation of fMRI data. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 233(2), 254–268.
Mairal, J., Bach, F., Ponce, J., & Sapiro, G. (2010). Online learning for matrix factorization and sparse coding. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 11, 19–60.
Manoach, D. S., Gollub, R. L., Benson, E. S., Searl, M. M., Goff, D. C., Halpern, E., et al. (2000). Schizophrenic subjects show aberrant fMRI activation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and basal ganglia during working memory performance. Biological Psychiatry, 48(2), 99–109.
Nielsen, F. Å., Balslev, D., & Hansen, L. K. (2005). Mining the posterior cingulate: segregation between memory and pain components. NeuroImage, 27(3), 520–532.
Pessoa, L. (2012). Beyond brain regions: network perspective of cognition–emotion interactions. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 35(03), 158–159.
Potenza, M. N. (2008). The neurobiology of pathological gambling and drug addiction: an overview and new findings. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B. Biological Sciences, 363(1507), 3181–3189.
Potenza, M. N., Steinberg, M. A., Skudlarski, P., Fulbright, R. K., Lacadie, C. M., Wilber, M. K., et al. (2003). Gambling urges in pathological Gambling: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 60(8), 828–836.
Tapert, S. F., Brown, G. G., Kindermann, S. S., Cheung, E. H., Frank, L. R., & Brown, S. A. (2001). fMRI measurement of brain dysfunction in alcohol-dependent young women. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 25(2), 236–245.
Wexler, B. E., Gottschalk, C. H., Fulbright, R. K., Prohovnik, I., Lacadie, C. M., Rounsaville, B. J., et al. (2001). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of cocaine craving. American Journal of Psychiatry, 158(1), 86–95.
Wolf, D. H., Satterthwaite, T. D., Calkins, M. E., Ruparel, K., Elliott, M. A., Hopson, R. D., et al. (2015). Functional neuroimaging abnormalities in youth with psychosis spectrum symptoms. JAMA Psychiatry, 72(5), 456–465.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by NSF CAREER Award (IIS-1,149,260), NIH R01 DA-033,393, NIH R01 AG-042,599, NSF CBET-1,302,089, NSF BCS-1,439,051 and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities 3102015ZY046.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1700 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Y., Fang, J., Lv, J. et al. Assessing the effects of cocaine dependence and pathological gambling using group-wise sparse representation of natural stimulus FMRI data. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1179–1191 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9596-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9596-4