Abstract
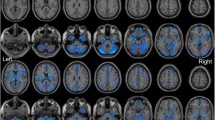
Accumulating evidence from brain structural imaging studies has supported that chronic pain could induce changes in brain gray matter volume. However, few studies have focused on the gray matter alterations of Trigeminal neuralgia (TN). In this study, twenty-eight TN patients (thirteen females; mean age, 45.86 years ±11.17) and 28 healthy controls (HC; thirteen females; mean age, 44.89 years ±7.67) were included. Using voxel-based morphometry (VBM), we detected abnormalities in gray matter volume in the TN patients. Based on a voxel-wise analysis, the TN group showed significantly decreased gray matter volume in the bilateral superior/middle temporal gyrus (STG/MTG), bilateral parahippocampus, left anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), caudate nucleus, right fusiform gyrus, and right cerebellum compared with the HC. In addition, we found that the gray matter volume in the bilateral STG/MTG was negatively correlated with the duration of TN. These results provide compelling evidence for gray matter abnormalities in TN and suggest that the duration of TN may be a critical factor associated with brain alterations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apkarian, A. V., Bushnell, M. C., Treede, R. D., & Zubieta, J. K. (2005). Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. European Journal of Pain, 9(4), 463–484. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2004.11.001.
Apkarian, A. V., Sosa, Y., Sonty, S., Levy, R. M., Harden, R. N., Parrish, T. B., et al. (2004). Chronic back pain is associated with decreased prefrontal and thalamic gray matter density. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(46), 10410–10415. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2541-04.2004.
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.007.
Baliki, M. N., Schnitzer, T. J., Bauer, W. R., & Apkarian, A. V. (2011). Brain morphological signatures for chronic pain. PloS One, 6(10), e26010. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026010.
Blankstein, U., Chen, J., Diamant, N. E., & Davis, K. D. (2010). Altered brain structure in irritable bowel syndrome: potential contributions of pre-existing and disease-driven factors. Gastroenterology, 138(5), 1783–1789. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.12.043.
Brett, M., Anton, J.-L., Valabregue, R., & Poline, J.-B. (2002). Region of interest analysis using the MarsBar toolbox for SPM 99. NeuroImage, 16(2), S497.
Buchsbaum, B. R., Hickok, G., & Humphries, C. (2001). Role of left posterior Superior temporal gyrus in phonological processing for speech perception and production. Cognitive Science, 25, 663–678.
Buvanendran, A., Ali, A., Stoub, T. R., Berger, R. A., & Kroin, J. S. (2007). The use of brain positron emission tomography to identify sites of postoperative pain processing with and without epidural analgesia. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 105, 1784–1786.
Chen, F. Y., Tao, W., & Li, Y. J. (2008). Advances in brain imaging of neuropathic pain. Chinese Medical Journal, 121(7), 653–657.
D’Amour, D., Dubois, C. A., Tchouaket, E., Clarke, S., & Blais, R. (2014). The occurrence of adverse events potentially attributable to nursing care in medical units: cross sectional record review. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 51(6), 882–891. doi:10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2013.10.017.
Desouza, D. D., Moayedi, M., Chen, D. Q., Davis, K. D., & Hodaie, M. (2013). Sensorimotor and pain modulation brain abnormalities in trigeminal neuralgia: A paroxysmal, sensory-triggered neuropathic pain. PloS One, 8(6), e66340. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066340.
Freund, W., Klug, R., Weber, F., Stuber, G., Schmitz, B., & Wunderlich, A. P. (2009). Perception and suppression of thermally induced pain: a fMRI study. Somatosensory & Motor Research, 26(1), 1–10. doi:10.1080/08990220902738243.
Geha, P. Y., Baliki, M. N., Harden, R. N., Bauer, W. R., Parrish, T. B., & Apkarian, A. V. (2008). The brain in chronic CRPS pain: abnormal gray-white matter interactions in emotional and autonomic regions. Neuron, 60(4), 570–581. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2008.08.022.
Gustin, S. M., Peck, C. C., Wilcox, S. L., Nash, P. G., Murray, G. M., & Henderson, L. A. (2011). Different pain, different brain: thalamic anatomy in neuropathic and non-neuropathic chronic pain syndromes. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(16), 5956–5964. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5980-10.2011.
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache S (2013). The international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia, 33(9), 629–808. doi:10.1177/0333102413485658.
Hsu, M. C., Harris, R. E., Sundgren, P. C., Welsh, R. C., Fernandes, C. R., Clauw, D. J., et al. (2009). No consistent difference in gray matter volume between individuals with fibromyalgia and age-matched healthy subjects when controlling for affective disorder. Pain, 143(3), 262–267. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2009.03.017.
Kim, J. H., Suh, S. I., Seol, H. Y., Oh, K., Seo, W. K., Yu, S. W., et al. (2008). Regional grey matter changes in patients with migraine: a voxel-based morphometry study. Cephalalgia, 28(6), 598–604. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01550.x.
Kuchinad, A., Schweinhardt, P., Seminowicz, D. A., Wood, P. B., Chizh, B. A., & Bushnell, M. C. (2007). Accelerated brain gray matter loss in fibromyalgia patients: premature aging of the brain? The Journal of Neuroscience, 27(15), 4004–4007. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0098-07.2007.
Liotti, M., Mayberg, H. S., Brannan, S. K., McGinnis, S., Jerabek, P., & Fox, P. T. (2000). Differential limbic–cortical correlates of sadness and anxiety in healthy subjects: implications for affective disorders. Biological Psychiatry, 48, 30–42.
May, A. (2011). Structural brain imaging: a window into chronic pain. The Neuroscientist, 17(2), 209–220. doi:10.1177/1073858410396220.
Obermann, M., Rodriguez-Raecke, R., Naegel, S., Holle, D., Mueller, D., Yoon, M. S., et al. (2013). Gray matter volume reduction reflects chronic pain in trigeminal neuralgia. NeuroImage, 74, 352–358. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.02.029.
Parise, M., Kubo, T. T., Doring, T. M., Tukamoto, G., Vincent, M., & Gasparetto, E. L. (2014). Cuneus and fusiform cortices thickness is reduced in trigeminal neuralgia. The Journal of Headache and Pain, 15, 17. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-15-17.
Rainville, P., Duncan, G. H., Price, D. D., Carrier, B., & Bushnell, M. C. (1997). Pain affect encoded in human anterior cingulate but not somatosensory cortex. Science, 277(5328), 968–971.
Richardson, M. P., Strange, B. A., & Dolan, R. J. (2004). Encoding of emotional memories depends on amygdala and hippocampus and their interactions. Nature Neuroscience, 7(3), 278–285. doi:10.1038/nn1190.
Rocca, M. A., Ceccarelli, A., Falini, A., Colombo, B., Tortorella, P., Bernasconi, L., et al. (2006). Brain gray matter changes in migraine patients with T2-visible lesions: a 3-T MRI study. Stroke, 37(7), 1765–1770. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000226589.00599.4d.
Rocca, M. A., Messina, R., Colombo, B., Falini, A., Comi, G., & Filippi, M. (2014). Structural brain MRI abnormalities in pediatric patients with migraine. Journal of Neurology, 261(2), 350–357. doi:10.1007/s00415-013-7201-y.
Rottmann, S., Jung, K., Vohn, R., & Ellrich, J. (2010). Long-term depression of pain-related cerebral activation in healthy man: an fMRI study. European Journal of Pain, 14(6), 615–624. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2009.10.006.
Schmidt-Wilcke, T. (2008). Variations in brain volume and regional morphology associated with chronic pain. Current Rheumatology Reports, 10(6), 467–474.
Schmidt-Wilcke, T., Hierlmeier, S., & Leinisch, E. (2010). Altered regional brain morphology in patients with chronic facial pain. Headache, 50(8), 1278–1285. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01637.x.
Schmidt-Wilcke, T., Leinisch, E., Straube, A., Kampfe, N., Draganski, B., Diener, H. C., et al. (2005). Gray matter decrease in patients with chronic tension type headache. Neurology, 65(9), 1483–1486. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000183067.94400.80.
Schmidt-Wilcke, T., Luerding, R., Weigand, T., Jurgens, T., Schuierer, G., Leinisch, E., et al. (2007). Striatal grey matter increase in patients suffering from fibromyalgia–a voxel-based morphometry study. Pain, 132 Suppl 1, S109-116. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2007.05.010.
Schweinhardt, P. & Bushnell, M. C. (2010). Pain imaging in health and disease–how far have we come? The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 120(11), 3788–3797. doi:10.1172/JCI43498.
Smallwood, R. F., Laird, A. R., Ramage, A. E., Parkinson, A. L., Lewis, J., Clauw, D. J., et al. (2013). Structural brain anomalies and chronic pain: a quantitative meta-analysis of gray matter volume. The Journal of Pain, 14(7), 663–675. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2013.03.001.
Ter Minassian, A., Ricalens, E., Humbert, S., Duc, F., Aube, C., & Beydon, L. (2013). Dissociating anticipation from perception: acute pain activates default mode network. Human Brain Mapping, 34(9), 2228–2243. doi:10.1002/hbm.22062.
Valet, M., Gundel, H., Sprenger, T., Sorg, C., Muhlau, M., Zimmer, C., et al. (2009). Patients with pain disorder show gray-matter loss in pain-processing structures: a voxel-based morphometric study. Psychosomatic Medicine, 71(1), 49–56. doi:10.1097/PSY.0b013e31818d1e02.
Valfre, W., Rainero, I., Bergui, M., & Pinessi, L. (2008). Voxel-based morphometry reveals gray matter abnormalities in migraine. Headache, 48(1), 109–117. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00723.x.
Villarreal, G., Hamilton, D. A., Petropoulos, H., Driscoll, I., Rowland, L. M., Griego, J. A., et al. (2002). Reduced hippocampal volume and total white matter volume in posttraumatic stress disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 52(2), 119–125.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers: 81471639), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (Grant numbers: 2012A030400019 and 2013B021800172).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
Author Meng Li, Jianhao Yan, Shumei Li, Tianyue Wang, Wenfeng Zhan, Hua Wen, Xiaofen Ma, Yong Zhang, Junzhang Tian, Guihua Jiang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Yan, J., Li, S. et al. Reduced volume of gray matter in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 486–492 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9529-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9529-2