Abstract
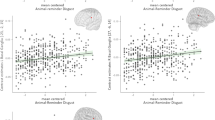
Mind pops or involuntary semantic memories refer to words, phrases, images, or melodies that suddenly pop into one’s mind without any deliberate attempt to recall them. Despite their prevalence in everyday life, research on mind pops has started only recently. Notably, mind pops are very similar to clinical involuntary phenomena such as hallucinations in schizophrenia, suggesting their potential role in pathology. The present study aimed to investigate the relationship between mind pops and the brain morphometry measured in 302 healthy young adults; after exclusions, 256 participants were included in our analyses. Specifically, the Mind Popping Questionnaire (MPQ) was employed to measure the degree of individual mind pops, whereas the Voxel-Based Morphometry (VBM) was used to compute the volumes of both gray and white matter tissues. Multiple regression analyses on MPQ and VBM metrics indicated that high-frequency mind pops were significantly associated with smaller gray matter volume in the left middle temporal gyrus as well as with larger gray and white matter volume in the right medial prefrontal cortex. This increase in mind pops is also linked to higher creativity and the personality trait of ‘openness’. These data not only suggest a key role of the two regions in generating self-related thoughts, but also open a possible link between brain and creativity or personality.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews-Hanna, J. R. (2012). The brain’s default network and its adaptive role in internal mentation. The Neuroscientists, 18, 251–270.
Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Smallwood, J., & Spreng, R. N. (2014). The default network and self-generated thought: component processes, dynamic control, and clinical relevance. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1316, 29–52.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2000). Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. NeuroImage, 11, 805–821.
Baird, B., Smallwood, J., Mrazek, M. D., Kam, J. W., Franklin, M. S., & Schooler, J. W. (2012). Inspired by distraction mind wandering facilitates creative incubation. Psychological Science, 23, 1117–1122.
Banissy, M. J., Kanai, R., Walsh, V., & Rees, G. (2012). Inter-individual differences in empathy are reflected in human brain structure. NeuroImage, 62(3), 2034–2039.
Benes, F. M. (1989). Myelination of cortical-hippocampal relays during late adolescence. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 15, 585–593.
Bernhardt, B. C., Smallwood, J., Tusche, A., Ruby, F. J., Engen, H. G., Steinbeis, N., et al. (2014). Medial prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortical thickness predicts shared individual differences in self-generated thought and temporal discounting. NeuroImage, 90, 290–297.
Binder, J. R., & Desai, R. H. (2011). The neurobiology of semantic memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15, 527–536.
Binder, J. R., Desai, R. H., Graves, W. W., & Conant, L. L. (2009). Where Is the Semantic System? A critical review and meta-analysis of 120 functional neuroimaging studies. Cerebral Cortex, 19, 2767–2796.
Bleich-Cohen, M., Kupchik, M., Gruberger, M., Kotler, M., & Hendler, T. (2012). Never resting region — mPFC in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 140, 155–158.
Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2008). The brain’s default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1124, 1–38.
Chenn, A., & Walsh, C. A. (2002). Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural precursors. Science, 297(5580), 365–369.
Christoff, K., Ream, J. M., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2004). Neural basis of spontaneous thought processes. Cortex, 40, 623–630.
Christoff, K., Gordon, A. M., Smallwood, J., Smith, R., & Schooler, J. W. (2009). Experience sampling during fMRI reveals default network and executive system contributions to mind wandering. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106, 8719–8724.
Coane, J. H., & Balota, D. A. (2009). Priming the holiday spirit: persistent activation due to extraexperimental experiences. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16(6), 1124–1128.
Costa, P. T., & McCrae, R. R. (1992). NEO-PI-R, professional manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources, 396, 653–665.
Damasio, A. R., & Van Hoesen, G. W. (1983). Emotional disturbances associated with focal lesions of the limbic frontal lobe. Neuropsychology of Human Emotion, 1, 85–110.
Davey, J., Rueschemeyer, S. A., Costigan, A., Murphy, N., Krieger-Redwood, K., Hallam, G., et al. (2015). Shared neural processes support semantic control and action understanding. Brain and Language, 142, 24–35.
DeYoung, C. G., Hirsh, J. B., Shane, M. S., Papademetris, X., Rajeevan, N., & Gray, J. R. (2010). Testing predictions from personality neuroscience. Brain structure and the big five. Psychological Science, 21(6), 820–828.
Elua, I., Laws, K. R., & Kvavilashvili, L. (2012). From mind-pops to hallucinations? A study of involuntary semantic memories in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 196, 165–170.
Fields, R. D. (2008). White matter matters. Scientific American, 298, 54–61.
Fjell, A. M., Westlye, L. T., Greve, D. N., Fischl, B., Benner, T., van der Kouwe, A. J. W., Salat, D., Bjørnerud, A., Due-Tønnessen, P., & Walhovd, K. B. (2008). The relationship between diffusion tensor imaging and volumetry as measures of white matter properties. NeuroImage, 42, 1654–1668.
Good, C. D., Johnsrude, I. S., Ashburner, J., Henson, R. N. A., Friston, K. J., & Frackowiak, R. S. J. (2001). A voxel-based Morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. NeuroImage, 14, 21–36.
Guo, W., Hu, M., Fan, X., Liu, F., Wu, R., Chen, J., et al. (2014). Decreased gray matter volume in the left middle temporal gyrus as a candidate biomarker for schizophrenia: a study of drug naive, first-episode schizophrenia patients and unaffected siblings. Schizophrenia Research, 159(1), 43–50.
Gusnard, D. A., & Raichle, M. E. (2001). Searching for a baseline: functional imaging and the resting human brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2, 685–694.
Hayasaka, S., Phan, K. L., Liberzon, I., Worsley, K. J., & Nichols, T. E. (2004). Nonstationary cluster-size inference with random field and permutation methods. NeuroImage, 22, 676–687.
Hoseinifar, J., Siedkalan, M. M., Zirak, S. R., Nowrozi, M., Shaker, A., Meamar, E., et al. (2011). An investigation of the relation between creativity and five factors of personality in students. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 30, 2037–2041.
Jabr, F. (2012). Mind-pops: psychologists begin to study an unusual form of proustian memory. Scientific American. com
Kvavilashvili, L., & Mandler, G. (2004). Out of one’s mind: a study of involuntary semantic memories. Cognitive Psychology, 48, 47–94.
la Fougere, C., Grant, S., Kostikov, A., Schirrmacher, R., Gravel, P., Schipper, H. M., et al. (2011). Where in-vivo imaging meets cytoarchitectonics: the relationship between cortical thickness and neuronal density measured with high-resolution [18F]flumazenil-PET. NeuroImage, 56(3), 951–960.
Mason, M. F., Norton, M. I., Van Horn, J. D., Wegner, D. M., Grafton, S. T., & Macrae, C. N. (2007). Wandering minds: the default network and stimulus-independent thought. Science, 315, 393–395.
McGuire, P. K., Silbersweig, D. A., Wright, I., Murray, R. M., David, A. S., Frackowiak, R. S., et al. (1995). Abnormal monitoring of inner speech: a physiological basis for auditory hallucinations. Lancet, 346(8975), 596–600.
Naccache, L., & Dehaene, S. (2001). Unconscious semantic priming extends to novel unseen stimuli. Cognition, 80(3), 223–237.
Nagy, Z., Westerberg, H., & Klingberg, T. (2004). Maturation of white matter is associated with the development of cognitive functions during childhood. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 16, 1227–1233.
Onitsuka, T., Shenton, M. E., Salisbury, D. F., Dickey, C. C., Kasai, K., Toner, S. K., et al. (2004). Middle and inferior temporal gyrus gray matter volume abnormalities in chronic schizophrenia: an MRI study. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 161(9), 1603–1611.
Panizzon, M. S., Fennema-Notestine, C., Eyler, L. T., Jernigan, T. L., Prom-Wormley, E., Neale, M., et al. (2009). Distinct genetic influences on cortical surface area and cortical thickness. Cerebral Cortex, 19(11), 2728–2735.
Price, C. J. (2012). A review and synthesis of the first 20 years of PET and fMRI studies of heard speech, spoken language and reading. NeuroImage, 62, 816–847.
Rakic, P. (1995). A small step for the cell, a giant leap for mankind: a hypothesis of neocortical expansion during evolution. Trends in Neurosciences, 18(9), 383–388.
Raven, J. (1958). Guide to using the coloured progressive matrices.
Raven, J. C. (1960). Guide to the standard progressive matrices: sets A, B, C, D and E. HK: Lewis.
Ridgway, G. R., Omar, R., Ourselin, S. B., Hill, D. L., Warren, J. D., & Fox, N. C. (2009). Issues with threshold masking in voxel-based morphometry of atrophied brains. NeuroImage, 44, 99–111.
Rissman, J., Eliassen, J. C., & Blumstein, S. E. (2003). An event-related fMRI investigation of implicit semantic priming. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 15, 1160–1175.
Schnack, H.G., van Haren, N.E., Brouwer, R.M., Evans, A., Durston, S., Boomsma, D.I., et al. (2014). Changes in thickness and surface area of the human cortex and their relationship with intelligence. Cereb Cortex.
Shenton, M. E., Dickey, C. C., Frumin, M., & McCarley, R. W. (2001). A review of MRI findings in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 49(1–2), 1–52.
Silver, M., Montana, G., & Nichols, T. E. (2010). False positives in neuroimaging genetics using voxel-based morphometry data. NeuroImage, 54, 992–1000.
Smallwood, J. (2013). Distinguishing how from why the mind wanders: a process–occurrence framework for self-generated mental activity. Psychological Bulletin, 139, 519.
Stokes, M., Thompson, R., Cusack, R., & Duncan, J. (2009). Top-down activation of shape-specific population codes in visual cortex during mental imagery. Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 1565–1572.
Takeuchi, H., Taki, Y., Sassa, Y., Hashizume, H., Sekiguchi, A., Fukushima, A., & Kawashima, R. (2010). Regional gray matter volume of dopaminergic system associate with creativity: evidence from voxel-based morphometry. NeuroImage, 51, 578–585.
Takeuchi, H., Taki, Y., Sassa, Y., Hashizume, H., Sekiguchi, A., Fukushima, A., et al. (2011). Regional gray matter density associated with emotional intelligence: evidence from voxel-based morphometry. Human Brain Mapping, 32(9), 1497–1510.
Tang, Z., Liu, W., Yin, H., Wang, P., Dong, J., Wang, Y. & Chen, J. (2007). Investigation of intelligence quotient and psychomotor development in schoolchilren in areas with different degrees of iodine deficiency. Asia Pacific journal of clinical nutrition, 16, 731.
Thomson, D. R., Milliken, B., & Smilek, D. (2010). Long-term conceptual implicit memory: a decade of evidence. Memory & Cognition, 38(1), 42–46.
Torrance, E.P. (1968). Torrance tests of creative thinking. Personnel Press, Incorporated.
Wible, C. G., Han, S. D., Spencer, M. H., Kubicki, M., Niznikiewicz, M. H., Jolesz, F. A., McCarley, R. W., & Nestor, P. (2006). Connectivity among semantic associates: An fMRI study of semantic priming. Brain and Language, 97, 294–305.
Zatorre, R. J., & Halpern, A. R. (2005). Mental concerts: musical imagery and auditory cortex. Neuron, 47, 9–12.
Acknowledgments
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470981) supported this research.
Conflicts of interest
Lei Zhang, Wenfu Li, Dongtao Wei, Wenjing Yang, Ning Yang, Lei Qiao, Jiang Qiu, Xi-Nian Zuo, and Qinglin Zhang declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Li, W., Wei, D. et al. The association between the brain and mind pops: a voxel-based morphometry study in 256 Chinese college students. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 332–341 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9396-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9396-2