Abstract
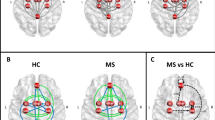
We investigated how resting state (RS) functional connectivity (FC) of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) correlates with cognitive rehabilitation in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) patients. A neuropsychological assessment and RS fMRI at baseline and after 12 weeks were obtained from 20 RRMS patients, who were assigned randomly to undergo treatment (n = 10) (treatment group-TG), which entailed computer-assisted cognitive rehabilitation of attention/information processing and executive functions for 3 days/week, or not to receive any cognitive rehabilitation (n = 10) (control group-CG). Voxel-wise changes of ACC RS FC were assessed using SPM8. In both groups, at the two study time points, ACC activity was correlated with the bilateral middle and inferior frontal gyrus, basal ganglia, posterior cingulate cortex, cerebellum, precuneus, middle temporal gyrus, and inferior parietal lobule (IPL). At follow up, compared to baseline, the TG showed an increased FC of the ACC with the right middle frontal gyrus (MFG) and right IPL, while the CG showed a decreased FC of the ACC with the right cerebellum and right inferior temporal gyrus (ITG). A significant “treatment × time” interaction was found for the increased FC of the right IPL and for the decreased FC of the right ITG. In the TG only, significant correlations (p < 0.001) were found between improvement of PASAT performance and RS FC of the ACC with the right MFG (r = 0.88) and right IPL (r = 0.76). In MS, cognitive rehabilitation correlates with changes in RS FC of brain regions subserving the trained functions. fMRI might be useful to monitor rehabilitative strategies in MS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, G., Buxton, R. B., Wong, E. C., & Courchesne, E. (1997). Attentional activation of the cerebellum independent of motor involvement. Science, 275, 1940–1943.
Allen, G., McColl, R., Barnard, H., et al. (2005). Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebellar-prefrontal and cerebellar-parietal functional connectivity. NeuroImage, 28, 39–48.
Amato, M. P., Zipoli, V., & Portaccio, E. (2006). Multiple sclerosis-related cognitive changes: a review of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Journal of Neurological Sciences, 245, 41–46.
Au Duong, M. V., Audoin, B., Boulanouar, K., et al. (2005). Altered functional connectivity related to white matter changes inside the working memory network at the very early stage of MS. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 25, 1245–1253.
Audoin, B., Au Duong, M. V., Ranjeva, J. P., et al. (2005). Magnetic resonance study of the influence of tissue damage and cortical reorganization on PASAT performance at the earliest stage of multiple sclerosis. Human Brain Mapping, 24, 216–228.
Baddeley, A. (2003). Working memory: looking back and looking forward. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 4, 829–839.
Bonnet, M. C., Allard, M., Dilharreguy, B., et al. (2010). Cognitive compensation failure in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 75, 1241–1248.
Bush, G., Luu, P., & Posner, M. I. (2000). Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4, 215–222.
Cader, S., Cifelli, A., Abu-Omar, Y., Palace, J., & Matthews, P. M. (2006). Reduced brain functional reserve and altered functional connectivity in patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain, 129, 527–537.
Calhoun, V. D., Adali, T., Pearlson, G. D., & Pekar, J. J. (2001). A method for making group inferences from functional MRI data using independent component analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 14, 140–151.
Chiaravalloti, N. D., & DeLuca, J. (2008). Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurology, 7, 1139–1151.
Collette, F., & Van der Linden, M. (2002). Brain imaging of the central executive component of working memory. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 26, 105–125.
Demirci, O., Stevens, M. C., Andreasen, N. C., et al. (2009). Investigation of relationships between fMRI brain networks in the spectral domain using ICA and Granger causality reveals distinct differences between schizophrenia patients and healthy controls. NeuroImage, 46, 419–431.
Desmond, J. E., & Fiez, J. A. (1998). Neuroimaging studies of the cerebellum: language, learning and memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2, 355–362.
Filippi, M., Riccitelli, G., Mattioli, F., et al. (2012). Effects of cognitive rehabilitation on structural and functional MRI measures in multiple sclerosis: an explorative study. Radiology, 262, 932–940.
Gottwald, B., Wilde, B., Mihajlovic, Z., & Mehdorn, H. M. (2004). Evidence for distinct cognitive deficits after focal cerebellar lesions. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 75, 1524–1531.
Hamame, C. M., Vidal, J. R., Ossandon, T., et al. (2012). Reading the mind’s eye: online detection of visuo-spatial working memory and visual imagery in the inferior temporal lobe. NeuroImage, 59, 872–879.
Krupp, L. B., Christodoulou, C., Melville, P., et al. (2004). Donepezil improved memory in multiple sclerosis in a randomized clinical trial. Neurology, 63, 1579–1585.
Kurtzke, J. F. (1983). Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology, 33, 1444–1452.
Li, Y., Chiaravalloti, N. D., Hillary, F. G., et al. (2004). Differential cerebellar activation on functional magnetic resonance imaging during working memory performance in persons with multiple sclerosis. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 85, 635–639.
Lowe, M. J., Mock, B. J., & Sorenson, J. A. (1998). Functional connectivity in single and multislice echoplanar imaging using resting-state fluctuations. NeuroImage, 7, 119–132.
Maldjian, J. A., Laurienti, P. J., Kraft, R. A., & Burdette, J. H. (2003). An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. NeuroImage, 19, 1233–1239.
Margulies, D. S., Kelly, A. M., Uddin, L. Q., et al. (2007). Mapping the functional connectivity of anterior cingulate cortex. NeuroImage, 37, 579–588.
Mattioli, F., Stampatori, C., Zanotti, D., Parrinello, G., & Capra, R. (2010). Efficacy and specificity of intensive cognitive rehabilitation of attention and executive functions in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurological Sciences, 288, 101–105.
Osaka, M., Osaka, N., Kondo, H., et al. (2003). The neural basis of individual differences in working memory capacity: an fMRI study. NeuroImage, 18, 789–797.
Patti, F., Amato, M. P., Trojano, M., et al. (2009). Cognitive impairment and its relation with disease measures in mildly disabled patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: baseline results from the Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis (COGIMUS) study. Multiple Sclerosis, 15, 779–788.
Penner, I. K., Kappos, L., Rausch, M., Opwis, K., & Radu, E. W. (2006). Therapy-induced plasticity of cognitive functions in MS patients: insights from fMRI. Journal of Physiology, Paris, 99, 455–462.
Rao, S. M., Leo, G. J., Bernardin, L., & Unverzagt, F. (1991). Cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. I. Frequency, patterns, and prediction. Neurology, 41, 685–691.
Riva, D., & Giorgi, C. (2000). The cerebellum contributes to higher functions during development: evidence from a series of children surgically treated for posterior fossa tumours. Brain, 123(Pt 5), 1051–1061.
Rocca, M. A., Valsasina, P., Ceccarelli, A., et al. (2009). Structural and functional MRI correlates of Stroop control in benign MS. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 276–290.
Rypma, B., Prabhakaran, V., Desmond, J. E., Glover, G. H., & Gabrieli, J. D. (1999). Load-dependent roles of frontal brain regions in the maintenance of working memory. NeuroImage, 9, 216–226.
Sastre-Garriga, J., Alonso, J., Renom, M., et al. (2011). A functional magnetic resonance proof of concept pilot trial of cognitive rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis, 17, 457–467.
Simon, S. S., Yokomizo, J. E., & Bottino, C. M. (2012). Cognitive intervention in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 36, 1163–1178.
Solari, A., Motta, A., Mendozzi, L., et al. (2004). Computer-aided retraining of memory and attention in people with multiple sclerosis: a randomized, double-blind controlled trial. Journal of Neurological Sciences, 222, 99–104.
Takeuchi, H., Taki, H., Hashizume, H., et al. (2011). Effects of training of processing speed on neural systems. Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 12139–12148.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., et al. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage, 15, 273–289.
Wang, L., Liu, X., Guise, K. G., et al. (2010). Effective connectivity of the fronto-parietal network during attentional control. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22, 543–553.
Yu, C., Zhou, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2011). Functional segregation of the human cingulate cortex is confirmed by functional connectivity based neuroanatomical parcellation. NeuroImage, 54(4), 2571–2581.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parisi, L., Rocca, M.A., Valsasina, P. et al. Cognitive rehabilitation correlates with the functional connectivity of the anterior cingulate cortex in patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain Imaging and Behavior 8, 387–393 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-012-9160-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-012-9160-9