Abstract
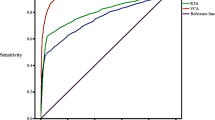
Objective: To evaluate the value of combined assays of serum EBNA1-IgA and EA-IgG for serological diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Methods: The serum EBNA1-IgA and EA-IgG were tested by use of ELISA for 56 patients with NPC and 58 healthy adults. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, accuracy rate and odds ratio of the 2 tests used singly or in combination were compared with each other. Results: The sensitivity of EBNA1-IgA test (91.09%) was higher than that (87.50%) of EA-IgG test. The specificity of EA-IgG test (87.93%) was higher than that (84.48%) of EBNA1-IgA test. The combined usage of EBNA1-IgA and EA-IgG could enhance the specificity (94.83%), predictive value of a positive test (0.9375), likelihood ratio of a positive test (15.5435) and odds ratio (75.0) for serological diagnosis of NPC. Forty-five NPC patients showed positivity to EBNA1-IgA and EA-IgG concurrently. A positive EA-IgG reaction was demonstrated in 4 out of 5 NPC patients with negative EBNA1-IgA result and a positive EBNA1-IgA reaction in 6 out of 7 NPC patients with negative EA-IgG result as well. Conclusion: Though high sensitivity and specificity could be obtained by EBNA1-IgA and EA-IgG test, respectively, the combined use of these 2 tests is able to enhancing the reliability of serological diagnosis of NPC. The majority of NPC patients showed positivity to ENBA1-IgA and EA-IgG concurrently. There is a complementary effect through using EBNA1-IgA and EA-IgG for serological diagnosis of NPC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henle G, Henle W. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgA serum antibodies as an outstanding feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma [J]. Int J Cancer 1976; 17:1.
Li JT, Zong YS. Study on the relationship between the serum IgA antibody titres to EB VCA and the pathological changes in untreated nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients (in Chinese) [J]. Chin J Oncol 1986; 15:122.
Zong YS, Sham JS, Ng MH, et al. Immunoglobulin A against viral capsid antigen of Epstein-Barr virus and indirect mirror examination of the nasopharynx in the detection of asymptomatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma [J]. Cancer 1992; 69:3.
Zong YS, Li JY, Peng XY, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) mortality rate in two districts of Guangdong province and their relation to IgA antibody level against EB virus capsid antigen (in Chinese) [J]. Chin J Oncol 1992; 14:103.
Zeng Y, Zhang LG, Li HY, et al. Serological mass survey for early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Wuzhou City, China [J]. Int J Cancer 1982; 29:139.
Zhang CQ, Zong YS, Huang BZ, et al. Enhancing the efficiency of Epstein-Barr viral serological test in the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (in Chinese) [J]. Chin J Oncol 2002; 24:356.
Ng MH, Chen HL, Luo RX, et al. Serological diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay: optimization, standardization and diagnostic criteria [J]. Chin Med J 1998; 111:531.
Cheng WM, Chan KH, Chen HL, et al. Assessing the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma on the basis of EBV antibody spectrum. Int J Cancer 2002; 97:489.
Zong YS, Zhang RF, Chen XH, et al. Titration of EB virus EA-IgG in untreated patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (in Chinese) [J]. Chin Med J 1980; 60:488.
Chen MR, Liu MY, Hsu SM, et al. Use of bacterially expressed EBNA-1 protein cloned from a nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) biopsy as a screening test for NPC patients [J]. J Med Virol 2001; 64:51.
Hsu MM, Hsu WC, Sheen TS, et al. Specific IgA antibodies to recombinant early and nuclear antigens of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma [J]. Clin Otolaryngol 2001; 26:334.
Feng P, Chan SH, Soo MY, et al. Antibody response to Epstein-Barr virus Rta protein in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a new serologic parameter for diagnosis [J]. Cancer 2001; 92:1872
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 39730200-II), the National “Ten-five” Key Project of China (No. 2001BA703B07) and the Department of Public Health, Guangdong Province (No. 1998218).
Biography: ZHANG Chang-qing (1946–), female, associate professor, Affiliated Tumor Hospital, Sun Yat-san University, majors in tumor immunology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Cq., Zong, Ys., Sun, Y. et al. Evaluation of combined EBNA1-IgA and EA-IgG assays in serological diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 15, 1–4 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-003-0001-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-003-0001-7