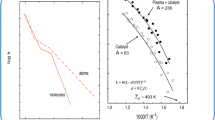
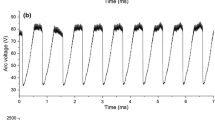
Abstract
The aim of this study is to provide the optimum operating conditions for enhancing in-flight alumina particle heating as much as possible for particle spheroidization and aggregation of melted particles using a DC-RF hybrid plasma flow system even at constant low operating power based on the thermofluid considerations. It is clarified that the swirl flow and higher operating pressure enhance the particle melting and aggregation of melted particles coupled with increasing gas temperature downstream of a plasma uniformly in the radial direction at constant electrical discharge conditions.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- d p :
-
particle diameter (μm)
- p :
-
operating pressure (kPa)
- Q c :
-
central gas flow rate (Nℓ/min)
- Q carrier :
-
particle carrier gas flow rate (Nℓ/min)
- Q q :
-
quench gas flow rate (Nℓ/min)
- Q sh :
-
sheath gas flow rate (Nℓ/min)
- Q sw :
-
swirl gas flow rate (Nℓ/min)
- T g :
-
gas temperature (K)
- T p :
-
particle temperature (K)
- V p :
-
particle velocity (m/s)
References
T. Yoshida, T. Tani, H. Nishimura, and K. Akashi, Characterization of a Hybrid Plasma and Its Application to Chemical Synthesis, J. Appl. Phys., 1983, 54(2), p 640-646
K.S. Kim, J.H. Seo, J.S. Nam, W.T. Ju, and S.H. Hong: Production of Hydrogen and Carbon Black by Methane Decomposition Using DC-RF Hybrid Thermal Plasmas, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 2005, 33(2), p 813-823.
L. Jia and F. Gitzhofer, Collection of Nano-powders Generated by Radio Frequency (RF) Plasma Spray Synthesis (PSS) Processing, Using a Sampling Probe, Proceedings of the 17th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry, J. Mostaghimi, T.W. Coyle, V.A. Pershin, H.R. Salimi Jazi, Ed., 7-12 Aug 2005 (Toronto), 2005, CD-ROM
Y. Kousaka, T. Nomura, M. Nishimoto, and E. Tenjiku, Experimental Studies on Gas-phase Nucleation and the Effect of Seed Particles on Homogeneous Nucleation Suppression, J. Aerosol Sci., 2000, 31(5), p 519-530
S.V. Joshi, Q. Liang, J.Y. Park, and J.A. Batdorf, Effect of Quenching Conditions on Particle Formation and Growth in Thermal Plasma Synthesis of Fine Powders, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 1990, 10(2), p 339-358
O. Kovářík, X. Fan, and M. Boulos, In Flight Properties of W Particles in an Ar-H2 Plasma, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2007, 16(2), p 229-237
J.W. McKelliget and N. El-Kaddah, Modeling of Materials Synthesis in Hybrid Plasma Reactors: Production of Silicon by Thermal Decomposition of SiCI4, Metall. Trans. B, 1990, 21(3), p 589-598
J.H. Seo, J.M. Park, and S.H. Hong, Influence of DC Arc Jets on Flow Fields Analyzed by an Integrated Numerical Model for a DC-RF Hybrid Plasma, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 2008, 17(2), p 025011
K. Kawajiri, T. Sato, and H. Nishiyama, Experimental Analysis of a DC-RF Hybrid Plasma Flow, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2003, 171(1-3), p 134-139
K. Kawajiri, K. Ramachandran, and H. Nishiyama, Statistical Optimization of a DC-RF Hybrid Plasma Flow System for In-flight Particle Treatment, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2005, 48(1), p 183-190
K. Kawajiri and H. Nishiyama, In-Flight Particle Characteristics in a DC-RF Hybrid Plasma Flow System, Thin Solid Films, 2006, 506-507, p 660-664
R. Ye, J.-G. Li, and T. Ishigaki, Controlled Synthesis of Alumina Nanoparticles Using Inductively Coupled Thermal Plasma with Enhanced Quenching, Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(9), p 4251-4257
H. Nishiyama, M. Onodera, J. Igawa, and T. Nakajima, Evaluation of In-Flight Particle Process Using a Small Power DC-RF Hybrid Plasma Flow System, Proceedings of the 18th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry, K. Tachibana, O. Takai, K. Ono, and T. Shirafuji, Ed., 26-31 Aug 2007 (Kyoto), 2007, CD-ROM
Y. Li and T. Ishigaki, Thermodynamic Analysis of Nucleation of Anatase and Rutile from TiO2 Melt, J. Cryst. Growth, 2002, 242(3-4), p 511-516
Y. Li and T. Ishigaki, Controlled One-Step Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Anatase and Rutile TiO2 Powders by In-Flight Thermal Plasma Oxidation, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, p 15536-15542
T. Ihara, M. Miyoshi, M. Ando, S. Sugihara, and Y. Iriyama, Preparation of a Visible-Light-Active TiO2 Photocatalyst by RF Plasma Treatment, J. Mater. Sci., 2001, 36(17), p 4201-4207
J.G. Li, H. Kamiyama, X.H. Wang, Y. Moriyoshi, and T. Ishigaki, TiO2 Nanopowders via Radio-frequency Thermal Plasma Oxidation of Organic Liquid Precursors: Synthesis and Characterization, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2006, 26, p 423-442
X. Chen and E. Pfender, Behavior of Small Particles in a Thermal Plasma Flow, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 1983, 3(3), p 351-366
P. Buchner, H. Schubert, J. Uhlenbusch, and M. Weiss, Diagnostics of an RF Plasma Flash Evaporation Process Using the Monochromatic Imaging Technique, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2001, 21(1), p 1-21
Acknowledgments
We would like to extend our sincere thanks to Dr. K. Kawajiri with National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology and Assistant Prof. H. Takana with Institute of Fluid Science, Tohoku University for their valuable discussions and to Mr. K. Katagiri with our institute for his technical support. This research was partially supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) (2005-2007) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and a 21st Century COE program Grant (2003-2007) of the International COE of Flow Dynamics from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishiyama, H., Onodera, M., Igawa, J. et al. Characterization of In-Flight Processing of Alumina Powder Using a DC-RF Hybrid Plasma Flow System at Constant Low Operating Power. J Therm Spray Tech 18, 593–599 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-009-9358-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-009-9358-6