Abstract
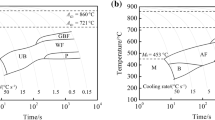
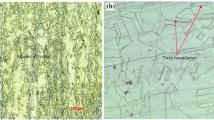
Acicular ferrite (AF) can significantly improve the mechanical properties of steel welds. One practical approach to enhance the formation of AF is to provide the heterogonous nucleation sites such as Ti oxides. In this study, Ti was added to different conventional welding processes including shield metal arc welding (SMAW), submerged arc welding (SAW) and tandem SAW (T-SAW). In the SMAW process, TiO2 particles as a source of Ti were inserted into the weld groove, while in the SAW and the T-SAW processes, the Ti-enriched S2MoTB wire was used as the filler metal. The microstructural evolution of weldments was characterized by employing optical and scanning electron microscopes. In addition, microhardness (Vickers, HV), Charpy impact and tensile tests were carried out to investigate the mechanical properties of weldments. Although the microhardness measurements of all weldments did not vary significantly and were in the range of 205-252 HV, there was a considerable difference in tensile and impact properties of the SAW and the T-SAW weldments. In the SMAW process, the addition of TiO2 results in no significant enhancement in tensile and impact toughness. This can be attributed to the inhomogeneous distribution of TiO2 particles as well as the formation of large inclusions in the structure. On the other hand, Ti addition to WM increased the yield strength from 489 to 552 MPa for the SAW process, and in contrast, it decreased the impact toughness from 75 to 33 J. This detrimental effect can be related to the higher deposition of other alloying elements in the WM and the formation of more ferrite side plate phase. By applying the T-SAW process, more Ti in WM led to a higher content of AF in the microstructure and increased both yield strength and impact toughness from 528 to 595 MPa and 100 to 180 J, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Avazkonandeh-Gharavol, M. Haddad-Sabzevar, and A. Haerian, Effect of Copper Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Multipass MMA, Low Alloy Steel Weld Metal Deposits, Mater. Des., 2009, 30(6), p 1902–1912
B. Beidokhti and R. Pouriamanesh, Effect of Filler Metal on Mechanical Properties of HSLA Welds, Weld. J., 2015, 94, p 334s–341s
S.S. Babu, The Mechanism of Acicular Ferrite in Weld Deposits, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2004, 8(3), p 267–278
A. Contreras, A. Albiter, M. Salazar, and R. Perez, Slow Strain Rate Corrosion and Fracture Characteristics of X-52 and X-70 Pipeline Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 407(1), p 45–52
H. Yu, Y. Sun, Q. Chen, H. Jiang, and L. Zhang, Precipitation Behaviors of X70 Acicular Ferrite Pipeline Steel, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater., 2006, 13(6), p 523–527
S.Y. Shin, B. Hwang, S. Kim, and S. Lee, Fracture Toughness Analysis in Transition Temperature Region of API, X70 Pipeline Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 429(1), p 196–204
S. Bhole, J. Nemade, L. Collins, and C. Liu, Effect of Nickel and Molybdenum Additions on Weld Metal Toughness in a Submerged Arc Welded HSLA Line-Pipe Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, 173(1), p 92–100
W. Bose-Filho, A. Carvalho, and M. Strangwood, Effects of Alloying Elements on the Microstructure and Inclusion Formation in HSLA Multipass Welds, Mater. Charact., 2007, 58(1), p 29–39
B. Beidokhti, A. Koukabi, and A. Dolati, Effect of Titanium Addition on the Microstructure and Inclusion Formation in Submerged arc Welded HSLA Pipeline Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209(8), p 4027–4035
T.K. Pal and U.K. Maity, Effect of nano Size TiO2 Particles on Mechanical Properties of AWS E 11018M Type Electrode, Mater. Sci. Appl., 2011, 2(09), p 1285
G. Thewlis, Classification and Quantification of Microstructures in Steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2004, 20(2), p 143–160
F.R. Xiao, B. Liao, Y.Y. Shan, G.Y. Qiao, Y. Zhong, C. Zhang, and K. Yang, Challenge of Mechanical Properties of an Acicular Ferrite Pipeline Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 431(1), p 41–52
X. Wan, H. Wang, L. Cheng, and K. Wu, The Formation Mechanisms of Interlocked Microstructures in Low-Carbon High-Strength Steel Weld Metals, Mater. Charact., 2012, 67, p 41–51
M.C. Zhao, K. Yang, and Y. Shan, The Effects of Thermo-Mechanical Control Process on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Commercial Pipeline Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 335(1), p 14–20
S. Nayak, R. Misra, J. Hartmann, F. Siciliano, and J. Gray, Microstructure and Properties of Low Manganese and Niobium Containing HIC Pipeline Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 494(1), p 456–463
K. Junhua, Z. Lin, G. Bin, L. Pinghe, W. Aihua, and X. Changsheng, Influence of Mo Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of High Strength Pipeline Steel, Mater. Des., 2004, 25(8), p 723–728
S. St-Laurent and G. L’Espérance, Effects of Chemistry, Density and Size Distribution of Inclusions on the Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite of C-Mn Steel Shielded-Metal-Arc-Welding Weldments, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1992, 149(2), p 203–216
J. Gregg, H. Bhadeshia, and L.E. Svensson, Inoculation of Steel Welds with Non-metallic Particles, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, 223(1–2), p 146–157
M. Fattahi, N. Nabhani, M. Hosseini, N. Arabian, and E. Rahimi, Effect of Ti-Containing Inclusions on the Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite and Mechanical Properties Of Multipass Weld Metals, Micron, 2013, 45, p 107–114
G. Thewlis, J. Whiteman, and D. Senogles, Dynamics of Austenite to Ferrite Phase Transformation in Ferrous Weld Metals, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1997, 13(3), p 257–274
Z. Zhang and R. Farrar, Role of Non-metallic Inclusions in Formation of Acicular Ferrite in Low Alloy Weld Metals, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1996, 12(3), p 237–260
C.J. Zhang, L.N. Gao, and L.G. Zhu, Effect of Inclusion Size and Type on the Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite in High Strength Ship Plate Steel, ISIJ Int., 2018, 58(5), p 965–969
J.H. Shim, Y. Cho, S. Chung, J.D. Shim, and D. Lee, Nucleation of Intragranular Ferrite at Ti2O3 Particle in Low Carbon Steel, Acta Mater., 1999, 47(9), p 2751–2760
B. Wang, X. Liu, and G. Wang, Inclusion Characteristics and Acicular Ferrite Nucleation in Ti-Containing Weld Metals of X70 Pipeline Steel, Steel Res. Int., 2018, 89(2), p 1700316
H. Liu, J. Feng, H. Fujii, and K. Nogi, Wear Characteristics of a WC–Co Tool in Friction Stir Welding of AC4A + 30vol% SiCp Composite, Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf., 2005, 45(14), p 1635–1639
R. Ale, J. Rebello, and J. Charlier, A Metallographic Technique for Detecting Martensite-Austenite Constituents in the Weld Heat-Affected Zone of a Micro-Alloyed Steel, Mater. Charact., 1996, 37(2), p 89–93
Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, E8/E8M − 15a, ASTM Standard, 2015, p. 1–29
Standard Test Methods for Notched Bar Impact Testing of Metallic Materials, E23 − 12c, ASTM Standard, 2012, p. 1–25
Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials, E384 − 16, ASTM Standard, 2016, p. 1–28
J.B. Ju, W.S. Kim, and J.I. Jang, Variations in DBTT and CTOD Within Weld Heat-Affected Zone of API, X65 Pipeline Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 546, p 258–262
S. Barnes, A. Bhatti, A. Steuwer, R. Johnson, J. Altenkirch, and P. Withers, Friction Stir Welding in HSLA-65 Steel: Part I. Influence of Weld Speed and Tool Material on Microstructural Development, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, 43(7), p 2342–2355
M. Sinfield, J. Lippold, B. Alexandrov, D. Forrest, in TWI Ltd., Abington, UK, 2008
A. Lambert-Perlade, A.-F. Gourgues, and A. Pineau, Austenite to Bainite Phase Transformation in the Heat-Affected Zone of a High Strength Low Alloy Steel, Acta Mater., 2004, 52(8), p 2337–2348
J.C. Lippold, Welding metallurgy and weldability, Wiley, London, 2014, p 65
T. Zhang, Z. Li, F. Young, H.J. Kim, H. Li, H. Jing, and W. Tillmann, Global Progress on Welding Consumables for HSLA Steel, ISIJ Int., 2014, 54(7), p 1472–1484
J. Wang, P. Van Der Wolk, and S. Van Der Zwaag, On the Influence of Alloying Elements on the Bainite Reaction in Low Alloy Steels During Continuous Cooling, J. Mater. Sci., 2000, 35(17), p 4393–4404
J.H. Shim, Y.W. Cho, J.D. Shim, Y.J. Oh, J.S. Byun, and D.N. Lee, Effects of Si and Al on acicular ferrite formation in C-Mn steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, 32(1), p 75–83
J.S. Byun, J.H. Shim, and Y.W. Cho, Influence of Mn on Microstructural Evolution in Ti-Killed C-Mn Steel, Scr. Mater., 2003, 48(4), p 449–454
Z. Zhang and R. Farrar, Influence of Mn and Ni on the Microstructure and Toughness of C-Mn-Ni Weld Metals, Weld. J., 1997, 76(5), p 183
D. Crockett, J. Rhone, R. Young, and D. Noernberg, Design Considerations for Submerged arc Consumables Intended for the Manufacture of Line Pipe, Pipeline Technol., 1995, 1, p 151–162
G. Evans, The Effect of Nickel on the Microstructure and Properties of C-Mn All-Weld Metal Deposits, Weld. Res. Abroad, 1991, 37(2/3), p 70–83
B. Beidokhti, A. Koukabi, and A. Dolati, Influences of Titanium and Manganese on High Strength Low Alloy SAW Weld Metal Properties, Mater. Charact., 2009, 60(3), p 225–233
Y. Peng, W. Chen, and Z. Xu, Study of High Toughness Ferrite Wire for Submerged Arc Welding of Pipeline Steel, Mater. Charact., 2001, 47(1), p 67–73
Specification for Line Pipe, 5L, API Standard, 2012, p. 27–50
S. Araki, K. Fujii, D. Akama, T. Tsuchiyama, S. Takaki, T. Ohmura, and J. Takahashi, Effect of Low Temperature Aging on Hall-Petch Coefficient in Ferritic Steels Containing a Small Amount of Carbon and Nitrogen, Testu To Hagane, 2017, 103(8), p 491–497
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pouriamanesh, R., Dehghani, K., Vallant, R. et al. Effect of Ti Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Weld Metals in HSLA Steels. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 6058–6068 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3686-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3686-y