Abstract
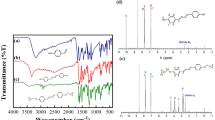
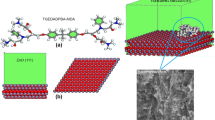
In a series of papers published recently, we clearly demonstrated that the most important factor governing the thermal conductivity of epoxy–Al2O3 composites is the backbone structure of the epoxy. In this study, three more epoxies based on diglycidyl ester-terminated liquid-crystalline epoxy (LCE) have been synthesized to draw conclusions regarding the effect of the epoxy backbone structure on the thermal conductivity of epoxy–alumina composites. The synthesized structures were characterized by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) and Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetric analysis, and optical microscopy were also employed to examine the thermal and optical properties of the synthesized LCEs and the cured composites. All three LCE resins exhibited typical liquid-crystalline behaviors: clear solid crystalline state below the melting temperature (T m), sharp crystalline melting at T m, and transition to nematic phase above T m with consequent isotropic phase above the isotropic temperature (T i). The LCE resins displayed distinct nematic liquid-crystalline phase over a wide temperature range and retained liquid-crystalline phase after curing, with high thermal conductivity of the resulting composite. The thermal conductivity values ranged from 3.09 W/m-K to 3.89 W/m-K for LCE–Al2O3 composites with 50 vol.% filler loading. The steric effect played a governing role in the difference. The neat epoxy resin thermal conductivity was obtained as 0.35 W/m-K to 0.49 W/m-K based on analysis using the Agari–Uno model. The results clearly support the objective of this study in that the thermal conductivity of the LCE-containing networks strongly depended on the epoxy backbone structure and the degree of ordering in the cured network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Lubin, Handbook of Composites (Ontario: Van Nostrand–Reinhold, 1982), p. 57.
J.E. Mark, Physical Properties of Polymers Handbook, 2nd ed. (New York: Springer, 2007), p. 155.
N. Masataka, O. Katsuhiko, K. Koichi, and S. Takao, JP Patent, 2010001427 A (2010).
M. Akatsuka and Y. Takezawa, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 89, 2464 (2003).
K. Fukushima, H. Takahashi, Y. Takezawal, M. Hattori, M. Itoh, and M. Yonekura, in Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (2004).
W.A. Su, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 31, 3251 (1993).
C. Lin and L. Chien, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 16, 869 (1995).
A. Mititelu and C.N. Cascaval, Polym. Plast. Tech. Eng. 44, 151 (2005).
J.J. Mallon and P.M. Adams, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 31, 2249 (1993).
C. Carfagn, E. Amendola, and M. Giamberini, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 195, 2307 (1994).
A. Mititelu-Mija, C.N. Cascaval, and P. Navard, Design. Monom. Polym. 8, 487 (2005).
P. Castell, M. Galià, and A. Serra, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 202, 1649 (2001).
B. Koscielny, A. Pfitzmann, and M. Fedtke, Polym. Bull. 32, 529 (1994).
Y. Yu, M. Wang, X. Liu, L. Zhao, X. Tang, and S. Li, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 101, 4366 (2006).
Y. Zheng, S. Ren, Y. Ling, and M. Lu, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 452, 3 (2006).
J.Y. Lee and J. Jang, Polymer 47, 3036 (2006).
J. Gao, G. Hou, Y. Wang, H. Li, and Y. Liu, Polym. Plast. Tech. Eng. 45, 947 (2006).
Z. Cai, J. Sun, Q. Zhou, and J. Xu, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 45, 727 (2007).
Z. Cai, J. Sun, D. Wang, and Q. Zhou, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 45, 3922 (2007).
L. Pottie, F. Costa-Torroa, M. Tessier, P. Davidson, and A. Fradet, Liq. Cryst. 35, 913 (2008).
C. Ortiz, R. Kim, E. Rodighiero, C.K. Ober, and E.J. Kramer, Macromolecules 31, 4074 (1998).
V. Ambrogi, C. Carfagna, M. Giamberini, E. Amendola, and E.P. Douglas, J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 16, 15 (2002).
T. Mihara, Y. Nishimiya, and N. Koide, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 68, 1979 (1998).
J. Jang, J. Bae, and K. Lee, Polymer 46, 3677 (2005).
S. Cho, E.P. Douglas, and J.Y. Lee, J. Polym. Eng. Sci. 46, 623 (2006).
A. Bruggeman, S.B. Damman, and A.H.A. Tinnemans, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 66, 1971 (1997).
H.J. Sue, J.D. Earls, and R.E. Hefner, J. Mater. Sci. 32, 4031 (1997).
Q. Lin and A.F. Yee, Polymer 35, 2679 (1994).
E. Amendola, C. Carfagna, M. Giamberini, and G. Pisaniello, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 196, 1577 (1995).
Z. Gao, Y. Yu, Y. Xu, and S. Li, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 105, 1861 (2007).
M. Ochi and H. Takashima, Polymer 42, 2379 (2001).
A. Mija, P. Navard, C. Peiti, D. Babor, and N. Guigo, Eur. Polym. 46, 1380 (2010).
E.J. Choi, H. Ahn, J.K. Lee, and J. Jin, Polymer 41, 7617 (2000).
D. Ribera, A. Mantecón, and A. Serra, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 202, 1658 (2001).
M. Akatsuka and Y. Takezawa, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 89, 2464 (2003).
N. Tokushige, T. Mihara, and N. Koide, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 428, 33 (2005).
M. Harada, M. Ochi, M. Tobita, T. Kimura, T. Isgigaki, N. Shimoyama, and H. Aoki, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 41, 1739 (2003).
T. Giang, J. Part, I. Cho, Y. Ko, and J. Kim, Polym. Composite. 34, 468 (2013).
T. Giang and J. Kim, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 30, 77 (2015).
T. Giang and J. Kim, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. (2015). doi:10.1080/15421406.2015.1107816.
J. McHugh, P. Fideu, A. Herrmann, and W. Stark, Polym. Test. 29, 759 (2010).
Y. Agari and T. Uno, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 30, 2225 (1985).
G.G. Barclay, C.K. Ober, K.I. Papathomas, and D.W. Wang, Macromolecules 25, 2947 (1992).
V. Krevelen, Properties of Polymers, 3rd ed. (New York: Elsevier, 1990), p. 525.
Y. Agari, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 49, 1625 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giang, T., Kim, J. Effect of Liquid-Crystalline Epoxy Backbone Structure on Thermal Conductivity of Epoxy–Alumina Composites. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 627–636 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4704-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4704-1