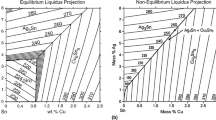
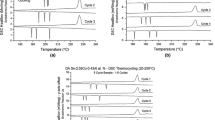
Because of their high thermal conductivity (K), low melting point (T m), and low shear strength, indium-based materials are excellent candidates for thermal interface material (TIM) applications. However, high In-content solders are expensive and possess low compressive creep strength, which may lead to structural instability following heat-sink attachment. Here, a radically different approach for producing microelectronic solder TIMs based on liquid phase sintering (LPS) is presented, which not only addresses the above problems, but also paves the way for the development of solder TIMs with even higher K than that of In for next generation packages. LPS Sn-In solders, the microstructure of which consists of particles of the high melting phase (HMP) Sn and a smaller amount of intergranular low melting phase (LMP) In, were processed and characterized. Flow stresses close to that of pure In, and electrical/thermal conductivities approximately half that of pure In, were obtained. LPS solder joints between Cu substrates were produced via a single step process combining LPS with joining. The contact thermal resistance of the internal grain boundaries was estimated, and it is inferred that, because of the numerous internal boundaries, the solder/substrate interfaces have a rela- tively small effect on the joint resistance. Based on the estimated boundary resistance, a previously developed model was utilized to predict the thermal conductivity of the LPS solder as a function of HMP type, volume fraction, and particle size. Preliminary results for LPS solders with Cu as the HMP phase are also presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L.F. Goldstein and J.W. Morris, J. Electron. Mater. 23, 477 (1994).
D.C. Lin, S. Liu, T.M. Guo, G.X. Wang, T.S. Srivatsan, and M. Petraoli, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 360, 285 (2003).
J.P. Liu, F. Guo, Y.F. Yan, W.B. Wang, and Y.W. Shi, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 958 (2004).
K. Mohankumar and A.A.O. Tay, Proceedings of the 6th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC) (IEEE, Singapore, 2004), p. 455.
F. Guo F, J. Lee, S. Choi, J.P. Lucas, T.R. Bieler, and K.N. Subramanian, J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1073 (2001).
S.G. Jadhav, T.R. Bieler, K.N. Subramanian, and J.P. Lucas, J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1197 (2001).
W.J. Huppman and R. Riegger, Acta Metall. 23, 965 (1975).
G. Petzow and W.A. Kaysser, Sintered Metal-Ceramic Composites, ed. G.S. Upadhyaya (Amsterdam: Elsevier Science, 1984), pp. 50–70. Included in S. Somiya and Y. Moriyoshi, eds. Sintering—Key Papers (Elsevier Applied Science, New York, 1990).
D. Pan, R.A. Marks, I. Dutta, and S. Jadhav, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75, 5244 (2004).
R. Raj, G. Rixecker, and M. Valentinotti, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 38, 628 (2007).
A.G. Every, Y. Tzou, D.P.H. Hasselman, and R. Raj, Acta Metall. Mater. 40, 123 (1992).
C.L. Yu, S.S. Wang, and T.H. Chuang, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 488 (2002).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by INTEL Corporation through the strategic research segment (SRS) program. Partial support from NSF grant CMII-0709506 is also acknowledged. The authors gratefully acknowledge their many discussions with Dr. R. Mahajan of INTEL, whose guidance and mentorship were invaluable to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, I., Raj, R., Kumar, P. et al. Liquid Phase Sintered Solders with Indium as Minority Phase for Next Generation Thermal Interface Material Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 2735–2745 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0898-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0898-9