Abstract
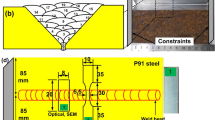
P91 steel weld joint was prepared using the shielded metal arc welding process and four different conditions of weld consumable that provide the different levels of diffusible hydrogen in deposited metal. In the present research, the effects of diffusible hydrogen content on the flexural strength, lower critical stress, and tensile strength of P91 steel welds were also determined with respect to different electrode conditions. To investigate the effect of diffusible hydrogen on multipass welding, top and root side flexural tests were performed. The residual stresses (axial stress and transverse stress) were also measured using the blind hole drilling method for different conditions of welding consumable. The peak value of residual stresses was measured at the center of the weld fusion zone. The maximum value of transverse stress was measured to be 355 MPa for case II (6.21 mL/100 g of diffusible hydrogen), while the maximum axial stress was about 218 MPa for case IV (12.43 mL/100 g of diffusible hydrogen). A three-dimensional finite element simulation was also performed to predict the residual stress distribution and thermal profile along the welded joint. The experimentally determined residual stresses correlated well with the numerically estimated residual stresses. The diffusible hydrogen content was not observed to have any significant effect on the residual stresses. The corrected residual stress values were also predicted by considering the plasticity-induced error. However, the flexural performance of the welded joint was affected by the diffusible hydrogen content. The top and root flexural strength was measured to be optimum for the low level of diffusible hydrogen content, and the values decreased with an increase in diffusible hydrogen content.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Aghajani, C. Somsen, and G. Eggeler: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 5093–5106.
C. Pandey and M.M. Mahapatra: J. Mater. Eng. Performance, 2016, vol. 25, pp. 2195–2210.
C. Pandey, M.M. Mahapatra, P. Kumar, R.S. Vidyrathy, and A. Srivastava: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, vol. 695, pp. 291–301.
M. Dewitte and C. Coussement: Mater. High Temp., 1991, vol. 9, pp. 178–84.
I. Fedorova, A. Kipelova, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018, vol. 49A.
B. Silwal, L. Li, A. Deceuster, and B. Griffiths: Weld. Res., 2013, vol. 92, pp. 80s–87s.
X. Li, M.T. Cabrillat, and Y. Lejeail: Study Modif. 9Cr-lMo Welds, 2006, vol. 43.
G.A. Webster and A.N. Ezeilo: Int. J. Fatigue, 2001, vol. 23, pp. 375–83.
P. Dong and P. Dong: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2004, vol. 10, pp. 389–98.
P.G. Kumar and K. Yu-ichi: Trans. JWRI, 2013, vol. 42, pp. 39–62.
C. Pandey, M.M. Mahapatra, and P. Kumar: Arch. Civil Mech. Eng., 2018, vol. 18, pp. 1000–11.
A.H. Yaghi, T.H. Hyde, A.A. Becker, and W. Sun: IMechE: J. Strain Analysis, 2008, vol. 43, pp. 275–93.
M. Zubairuddin, S.K. Albert, M. Vasudevan, S. Mahadevan, V. Chaudhri, and V.K. Suri: Mater. Manufact. Processes, 2016, vol. 31, pp. 366–71.
D. Dean and M. Hidekazu: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2006, vol. 37, pp. 209–19.
H. Murakawa, B. Miloslav, V. Adan, R. Sherif, D. Cartin, D. David, and N. Kamran: Trans. JWRI, 2008, vol. 37, pp. 75–80.
S. Paddea, J.A. Francis, A.M. Paradowska, P.J. Bouchard, and I.A. Shibli: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 534, pp. 663–72.
J.A. Francis, W. Mazur, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, vol. 22, pp. 1387–95.
K.A. Venkata, S. Kumar, H.C. Dey, D.J. Smith, and P.J. Bouchard: Proc. Eng., 2014, vol. 86, pp. 223–33.
T.C. Chuvas, P.S.P. Garcia, J.M. Pardal, and P.C. da Fonseca: Mater. Res., 2015, vol. 18, pp. 614–21.
S. Kulkarni, P.K. Ghosh, and S. Ray: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 1560–69.
S. Kim, J. Kim, and W. Lee: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, vol. 209, pp. 3905–13.
Y. Sattari-Far and I. Javadi: Int. J. Press. Vess. Pip., 2008, vol. 85, pp. 265–74.
P. Dong: J. Press. Vess. Technol., 2001, vol. 123, pp. 207–13.
N. Saini, C. Pandey and M.M. Mahapatra: Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2017, 42, 17328-38.
C. Pandey, M.M. Mahapatra, P. Kumar, and N. Saini: J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 2017, vol. 139, pp. 1–11.
S.K. Albert, V. Ramasubbu, S.I.S. Raj, and A.K. Bhaduri: Weld. World, 2011, vol. 55, pp. 66–74.
X. Yue: Weld. World, 2014, vol. 59, pp. 77–89.
C. Pandey, M.M. Mahapatra, P. Kumar, N. Saini, and A. Srivastava: J. Manufact. Processes, 2017, vol. 28, pp. 220–34.
C. Pandey, M.M. Mahapatra, P. Kumar, and N. Saini (2017) Trans. Ind. Inst. Met. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017-1144-4.
J.N. Dupont and A.R. Marder: Weld. Res. Suppl., 1995, vol. 74, pp. 406–16.
C. Pandey, A. Giri, and M.M. Mahapatra: Int. J. Steel Struct., 2016, vol. 16, pp. 333–45.
C. Pandey, N. Saini, M.M. Mahapatra, and P. Kumar: Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, vol. 41, pp. 17695–17712.
A. Giri, C. Pandey, M.M. Mahapatra, K. Sharma, and P.K. Singh: Meas, 2015, vol. 65, pp. 41–49.
A.H. Yaghi, T.H. Hyde, A.A. Becker, W. Sun, G. Hilson, S. Simandjuntak, P.E.J. Flewitt, and D.J. Smith: J. Press. Vess. Technol., 2010, vol. 132, pp. 1–10.
L.X. Jang, X.F. Peng, and B.X. Wang: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2001, vol. 44, pp. 4465–73.
J. Goldak: Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 17–26.
B. Brickstad and B.L. Josefson: Int. J. Press. Vess. Pip., 1998, vol. 75, pp. 11–25.
C. Liu, J.X. Zhang, and C.B. Xue: Fus. Eng. Design, 2011, vol. 86, pp. 288–95.
C. Pandey, N. Saini, M.M. Mahapatra, and P. Kumar: Eng. Fail. Analysis, 2016, vol. 71, pp. 131–47.
C. Pandey, A. Giri, M.M. Mahapatra, and P. Kumar: Met. Mater. Int., 2017, vol. 23, pp. 148–62.
Y. Wang, R. Kannan, and L. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47A, pp. 5680–84.
C. Pandey and M.M. Mahapatra: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, vol. 25, pp. 2761–75.
M.M. Mahapatra, G.L. Datta, B. Pradhan, and N.R. Mandal: Int. J. Press. Vess. Pip., 2006, vol. 83, pp. 721–29.
N. Guo, Z. Yang, M. Wang, X. Yuan, and J. Feng: Strength Mater., 2015, vol. 47, pp. 12–18.
H.L. Li, D. Liu, Y.T. Yan, N. Guo, and J.C. Feng: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2016, vol. 238, pp. 423–30.
C.A. Hippsley: Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 2399–2416.
B.K. Choudhary and E. Isaac Samuel: J. Nucl. Mater., 2011, vol. 412, pp. 82–89.
S. Sathyanarayanan, A. Moitra, K.G. Samuel, G. Sasikala, S.K. Ray, and V. Singh: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 488, pp. 519–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 24, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, C., Mahapatra, M.M., Kumar, P. et al. Effect of Weld Consumable Conditioning on the Diffusible Hydrogen and Subsequent Residual Stress and Flexural Strength of Multipass Welded P91 Steels. Metall Mater Trans B 49, 2881–2895 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1314-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1314-8