Abstract
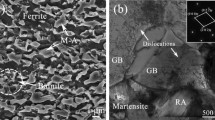
We have used transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and nanoindentation to characterize the dominant phases present in the weld zone of a diode-laser-welded transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steel, examining the unaffected base metal as a baseline. The microstructure of the base metal consists predominantly of ferrite, retained austenite, martensite, and occasional large carbide particles. The dominant microstructure of the weld zone is of differently oriented packets having a bainitic morphology. The weld also contains allotriomorphic ferrite, idiomorphic ferrite, as well some twinned martensite that is surrounded by austenite. The TEM analysis of the bainitic-morphology packets indicates that they consist of a lath ferrite phase separated by an interlath carbon-enriched retained austenite. In most cases, the orientation relationship (OR) between the lath ferrite and the interlath retained austenite can be approximated as Nishiyama–Wasserman (N-W). We used site-specific nanoindentation to further characterize the packets and the allotriomorphic ferrite, confirming through the hardness values the conclusions reached by TEM. While martensite was regularly present in the base metal, it was only sparsely distributed within the weld zone, boding well for the weld’s mechanical properties.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
Desktop Microscopist is a trademark of Desktop Microscopist.
NANOVISION is a trademark of MTS Systems Corporation, Eden Prairie, MN.
References
S. Zaefferer, J. Ohlert, W. Bleck: Acta Mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 2765–78
P.J. Jacques: Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 8, pp. 259–65
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: ISIJ Int., 2002, vol. 42, pp. 1059–60.
T.K. Han, S.S. Park, K.H. Kim, C.Y. Kang, I.S. Woo, J.B. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 60–65
T.K. Han, K.H. Kim, B.I. Kim, C.Y. Kang, I.S. Woo, J.B. Lee: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2004, vols. 449–452, pp. 409–12.
P.L. Moore, D.S. Howse, and E.R. Wallach: 6th Int. Conf. on Trends in Welding Research, Pine Mountain, GA, May 2002, oral presentation and private communication
S. Lawson, X. Li, and Y. Zhou: Sheet Metal Welding Conf. XII, Livonia, MI, May 2006, p. 9
K.W. Andrews, D.J. Dyson, S.R. Keown: Interpretation of Electron Diffraction Patterns, 2nd ed., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1971, pp. 210–11
G.R. Speich, W.C. Leslie: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, p. 1043.
A.Z. Hanzaki, P.D. Hodgson, S. Yue: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28A, pp. 2405–14
B. Verlinden, P. Bocher, E. Girault, E. Aernoudt: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 45, pp. 909–16
R.W.K. Honeycombe, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Steels Microstructure and Properties, 2nd ed., Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2000, pp. 115–39
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: private communication, University of Cambridge, UK, Dec 2006
Q. Furnemont, M. Kempf, P.J. Jacques, M. Goken, F. Delannay: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. 328, pp. 26–32.
J. Angeli, A.C. Kneissl: Z. Metallkd., 2004, vol. 95, pp. 601–06
M. De Meyer, D. Vanderschueren, B.C. De Cooman: ISIJ Int., 1999, vol. 39, pp. 813–22.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, D.V. Edmonds: Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 895–07
B.C. De Cooman: Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 8, pp. 285–03
R.W.K. Honeycombe, F.B. Pickering: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, p. 1099
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Bainite in Steels: Transformations, Microstructure and Properties, 2nd ed., IOM Communications, Ltd., London, 2001, pp. 19–61
T. Maki, C.M. Wayman: Acta Metall., 1977, vol. 25, pp. 695–710
T.V. Eterashvili, L.M. Utevskiy, M.N. Spasskiy: Fiz. Met. Metall., 1979, vol. 48, pp. 807–15
G. Spanos, R.W. Fonda, R.A. Vandermeer, A. Matuszeski: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 3277–93
R.W. Fonda, G. Spanos: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 2145–53
P.M. Kelly, A. Jostsons, R.G. Blake: Acta. Metall. Mater., 1990, vol. 38, pp. 1075–81
S. Morito, H. Tanaka, R. Konishi, T. Furuhara, T. Maki: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 1789–99.
J.E. Gould, S.P. Khurana, T. Li: Welding J., 2006, vol. 85, pp. 111S–116S
O. Akselsen, O. Grong, J. Solberg: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1987, vol. 3, pp. 649–55
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Harry Bhadeshia and Velimir Radmilovic for the critical presubmission reviews of this manuscript. We also thank Ryan O′Hagan, MTS, for assistance with the nanoindentation testing and for very useful discussions. One of the authors (JC) wants to thank Dr. Fu-Gao Wei, National Institute for Materials Science of Japan, for the discussion. This research is financially supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada and AUTO21 Network Centres of Excellence of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted February 27, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Sand, K., Xia, M. et al. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Nanoindentation Study of the Weld Zone Microstructure of Diode-Laser-Joined Automotive Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 39, 593–603 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9389-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9389-x