Abstract
Objective
To explore the effects of Huxin formula (HXF) in curtailing atherosclerosis and its underlying mechanism.
Methods
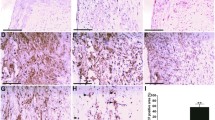
According to random number table method, 24 specific pathogen free male ApoE-/- mice were randomly divided into model group, HXF low-dose (HXF-L) group (8.4 g/kg daily), HXF high-dose (HXF-H) group (16.8 g/kg daily), and pravastatin (8 mg/kg daily) group in Experiment I (n=6 per group). C57BL/6J mice served as the control group (n=6). ApoE-/- mice in HXF-L, HXF-H, pravastatin groups were fed a Western diet and administered continuously by gavage for 12 weeks, while C57BL/6J mice in the control group were fed conventional lab mouse chow for 12 weeks. Further, Tregs were depleted by weekly intraperitoneal injection of purified anti-mouse CD25 antibody (PC61, 250 µg per mouse) for 4 weeks in Experiment II (n=6 per group). Oil Red O and Masson staining were used to evaluate the plaque area and aortic root fibrosis. The CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Treg counts in the lymph nodes and spleen cells were detected using flow cytometric analysis. The transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), interleukin (IL)-10, and IL-6 serum levels were examined by MILLIPLEX® MAP technology. Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot were utilized to assess the expression of TGF-β mRNA and protein in the aorta. The expression of CD4+T lymphocytes, macrophages and smooth muscle cells in the aortic root were detected by immunofluorescence staining.
Results
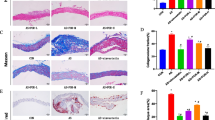
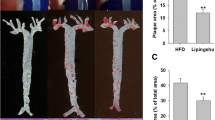
HXF reduced plaque area in ApoE-/- mice (P<0.01). HXF increased the Treg counts in the lymph nodes and spleen cells (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Moreover, HXF alleviated inflammatory response via elevating IL-10 and TGF-β 1 serum levels (P<0.05), while decreasing the IL-6 serum levels in ApoE-/- mice (P>0.05). Also, HXF upregulated the expression of TGF-β mRNA and protein in the aorta (P<0.05). Additionally, HXF attenuated CD4+T lymphocytes, macrophages and smooth muscle cells in aortic root plaque (P<0.01). Furthermore, the depletion of Tregs with CD25 antibody (PC61) curtailed the reduction in plaque area and aortic root fibrosis by HXF (P<0.01).
Conclusion
HXF relieved atherosclerosis, probably by restraining inflammatory response, reducing inflammatory cell infiltration and attenuating aortic root fibrosis by increasing Treg counts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjorkegren JLM, Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis: recent developments. Cell 2022;185:1630–1645.
Sharma M, Schlegel MP, Afonso MS, Brown EJ, Rahman K, Weinstock A, et al. Regulatory T cells license macrophage pro-resolving functions during atherosclerosis regression. Circ Res 2020;127:335–353.
Wolf D, Ley K. Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res 2019;124:315–327.
Ley K. Role of the adaptive immune system in atherosclerosis. Biochem Soc Trans 2020;48:2273–2281.
Roy P, Orecchioni M, Ley K. How the immune system shapes atherosclerosis: roles of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2022;22:251–265.
Lecis D, Massaro G, Benedetto D, Di Luozzo M, Russo G, Mauriello A, et al. Immunomodulation therapies for atherosclerosis: the past, the present, and the future. Int J Mol Sci 2023;24:10979.
Saigusa R, Winkels H, Ley K. T cell subsets and functions in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol 2020;17:387–401.
Wang Q, Wang YR, Xu DY. Research progress on Th17 and T regulatory cells and their cytokines in regulating atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022;9:929078.
Ait-Oufella H, Lavillegrand JR, Tedgui A. Regulatory T cell-enhancing therapies to treat atherosclerosis. Cells 2021;10:723.
Ali AJ, Makings J, Ley K. Regulatory T cell stability and plasticity in atherosclerosis. Cells 2020;9:2665.
Klingenberg R, Gerdes N, Badeau RM, Gistera A, Strodthoff D, Ketelhuth DF, et al. Depletion of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells promotes hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest 2013;123:1323–1334.
Spitz C, Winkels H, Burger C, Weber C, Lutgens E, Hansson GK, et al. Regulatory T cells in atherosclerosis: critical immune regulatory function and therapeutic potential. Cell Mol Life Sci 2016;73:901–922.
Mallat Z, Gojova A, Brun V, Esposito B, Fournier N, Cottrez F, et al. Induction of a regulatory T cell type 1 response reduces the development of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e-knockout mice. Circulation 2003;108:1232–1237.
Feng J, Zhang Z, Kong W, Liu B, Xu Q, Wang X. Regulatory T cells ameliorate hyperhomocysteinaemia-accelerated atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Cardiovasc Res 2009;84:155–163.
Wu HL, Wang YF, Li JZ, Zhang MZ, Sheng XG, Wang X, et al. A multicentre randomized clinical trial on efficacy and safety of Huxin Formula in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014;2014:143064.
Lin Y, Wang YF, Lin DQ, Chen JW, Li JZ, Lan TH, et al. Efficacy and safety of Huxin Formula in patients after CABG: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Forsch Komplementmed 2014;21:351–359.
Jiang W, Li S, Mao W, Yang G, Li XM, Zheng GJ, et al. Effect of Huxin Formula on reverse cholesterol transport in apoe-gene knockout mice. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18:451–456.
Ou HX, Guo BB, Liu Q, Li YK, Yang Z, Feng WJ, et al. Regulatory T cells as a new therapeutic target for atherosclerosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2018;39:1249–1258.
Tanaka T, Sasaki N, Rikitake Y. Recent advances on the role and therapeutic potential of regulatory T cells in atherosclerosis. J Clin Med 2021;10:5907.
Wang XT, Zhou H, Liu Q, Cheng PP, Zhao TY, Yang TS, et al. Targeting regulatory T cells for cardiovascular diseases. Front Immunol 2023;14:1126761.
Handke J, Kummer L, Weigand MA, Larmann J. Modulation of peripheral CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells ameliorates surgical stress-induced atherosclerotic plaque progression in apoe-deficient mice. Front Cardiovasc Med 2021;8:682458.
Zhu XY, Li QZ, George V, Spanoudis C, Gilkes C, Shrestha N, et al. A novel interleukin-2-based fusion molecule, HCW9302, differentially promotes regulatory T cell expansion to treat atherosclerosis in mice. Front Immunol 2023;14:1114802.
Kasahara K, Sasaki N, Amin HZ, Tanaka T, Horibe S, Yamashita T, et al. Depletion of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells augments CD4+ T cell immune responses in atherosclerosis-prone hypercholesterolemic mice. Heliyon 2022;8:e09981.
Joly AL, Seitz C, Liu S, Kuznetsov NV, Gertow K, Westerberg LS, et al. Alternative splicing of Foxp3 controls regulatory T cell effector functions and is associated with human atherosclerotic plaque stability. Circ Res 2018;122:1385–1394.
Klingenberg R, Brokopp CE, Grives A, Courtier A, Jaguszewski M, Pasqual N, et al. Clonal restriction and predominance of regulatory T cells in coronary thrombi of patients with acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J 2015;36:1041–1048.
Potekhina AV, Pylaeva E, Provatorov S, Ruleva N, Masenko V, Noeva E, et al. Treg/Th17 balance in stable cad patients with different stages of coronary atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2015;238:17–21.
Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, et al. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1119–1131.
Tardif JC, Kouz S, Waters DD, Bertrand OF, Diaz R, Maggioni AP, et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 2019;381:2497–2505.
Baardman J, Lutgens E. Regulatory T cell metabolism in atherosclerosis. Metabolites 2020;10:279.
Hu WL, Li JY, Cheng X. Regulatory T cells and cardiovascular diseases. Chinese Med J 2023;136:2812–2823.
Garshick MS, Ward NL, Krueger JG, Berger JS. Cardiovascular risk in patients with psoriasis: JACC review topic of the week. J Am Coll Cardiol 2021;77:1670–1680.
Forrester SJ, Kikuchi DS, Hernandes MS, Xu Q, Griendling KK. Reactive oxygen species in metabolic and inflammatory signaling. Circ Res 2018;122:877–902.
Tousoulis D, Oikonomou E, Economou EK, Crea F, Kaski JC. Inflammatory cytokines in atherosclerosis: current therapeutic approaches. Eur Heart J 2016;37:1723–1732.
Maguire EM, Pearce SWA, Xiao Q. Foam cell formation: a new target for fighting atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Vascul Pharmacol 2019;112:54–71.
Ford HZ, Byrne HM, Myerscough MR. A lipid-structured model for macrophage populations in atherosclerotic plaques. J Theor Biol 2019;479:48–63.
Grootaert MOJ, Bennett MR. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis: time for a re-assessment. Cardiovasc Res 2021;117:2326–2339.
Singh S, Torzewski M. Fibroblasts and their pathological functions in the fibrosis of aortic valve sclerosis and atherosclerosis. Biomolecules 2019;9:472.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ou XM performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. Cai J performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Hu XY conducted the literature search and data collection. Zeng QH performed the experiments. Lan TH directed and revised the manuscript. Jiang W conceived and designed the experiments. All authors confirmed the final manuscript and approved it for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81874432) and Traditional Chinese Medicine Bureau of Guangdong Province (No. 20221172)
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, Xm., Cai, J., Hu, Xy. et al. Treg Immunomodulation Contributes to the Anti-atherosclerotic Effects of Huxin Formula in ApoE-/- Mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-024-3663-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-024-3663-2