Abstract
Objectives
To clarify the effects of acupuncture stimulation at Zusanli (ST 36) on the hormonal changes.
Methods
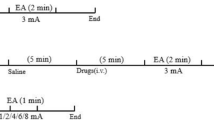
Eight-week-old male C57BL/6 mice received acupuncture stimulation at acupoint ST 36 or Quchi (LI 11) once a day for 3 or 5 days in the acupuncture-stimulated groups, but not received in the normal group (n=6 in each group). On day 3 or 5, animals were given 0.1 mL of charcoal orally with a bulbed steel needle, 30 min after the last acupuncture stimulation. Ten minutes later, mice were anesthetized, and the intestinal transit and the concentrations of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), motilin, ghrelin and gastrin in the serum were measured.
Results
Compared to no acupuncture stimulation, acupuncture stimulation at ST 36 for 5 days increased the intestinal transit and down-regulated the concentration of VIP and up-regulated the concentrations of motilin, ghrelin and gastrin (P<0.05 or 0.01), whereas acupuncture stimulation at LI 11 did not change them signifificantly (P>0.05).
Conclusion
Acupuncture stimulation at ST 36 for 5 days enhances the small intestinal motility and regulates the secretion of hormones related to small intestinal motility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takahashi T. Mechanism of acupuncture on neuromodulation in the gut—a review. Neuromodulation 2011;14: 8–12; discussion 12.
Yin J, Chen JD. Gastrointestinal motility disorders and acupuncture. Auton Neurosci 2010;157: 31–37.
Zhu WL, Li Y, Wei HF, Ren XX, Sun J, Zhang LF, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture at different acupoints on neuropeptide and somatostatin in rat brain with irritable bowel syndrome. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18: 288–292.
Liu J, Huang H, Xu X, Chen JD. Effects and possible mechanisms of acupuncture at ST 36 on upper and lower abdominal symptoms induced by rectal distension in healthy volunteers. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2012;303:R209–R217.
Zhang CX, Qin YM, Guo BR. Clinical study on the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux by acupuncture. Chin J Integr Med 2010;16: 298–303.
Witt CM, Meissner K, Pach D, Thiele C, Ludtke R, Ghadiyali Z, et al. Stimulation of gastric slow waves with manual acupuncture at acupuncture points ST 36 and PC 6—a randomized single blind controlled trial. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2012;24: 438–445, e211-e432.
Chen J, Song GQ, Yin J, Koothan T, Chen JD. Electroacupuncture improves impaired gastric motility and slow waves induced by rectal distension in dogs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2008;295:G614–G620.
Shen GM, Zhou MQ, Xu GS, Xu Y, Yin G. Role of vasoactive intestinal peptide and nitric oxide in the modulation of electroacupucture on gastric motility in stressed rats. World J Gastroenterol 2006;12: 6156–6160.
Gao X, Qiao Y, Jia B, Jing X, Cheng B, Wen L, et al. NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic activity in dorsal motor nucleus of vagus mediates the enhancement of gastric motility by stimulating ST 36. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012;2012: 438460.
Bell FR. The relevance of the new knowledge of gastrointestinal hormones to veterinary science. Vet Res Commun 1978;2: 305–314.
Said SI, Mutt V. Polypeptide with broad biological activity: isolation from small intestine. Science 1970;169: 1217–1218.
Said SI, Mutt V. Potent peripheral and splanchnic vasodilator peptide from normal gut. Nature 1970;225: 863–864.
Cai GX, Liu BY, Yi J, Chen XM, Liu FL. Simotang enhances gastrointestinal motility, motilin and cholecystokinin expression in chronically stressed mice. World J Gastroenterol 2011;17: 1594–1599.
Lu X, Zhao X, Feng J, Liou AP, Anthony S, Pechhold S, et al. Postprandial inhibition of gastric ghrelin secretion by long-chain fatty acid through GPR120 in isolated gastric ghrelin cells and mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012;303:G367–G376.
Masuda Y, Tanaka T, Inomata N, Ohnuma N, Tanaka S, Itoh Z, et al. Ghrelin stimulates gastric acid secretion and motility in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000;276: 905–908.
Jensen RT. Involvement of cholecystokinin/gastrin-related peptides and their receptors in clinical gastrointestinal disorders. Pharmacol Toxicol 2002;91: 333–350.
Yin CS, Jeong HS, Park HJ, Baik Y, Yoon MH, Choi CB, et al. A proposed transpositional acupoint system in a mouse and rat model. Res Vet Sci 2008;84: 159–165.
Park JY, Park HJ, Choi YY, Kim MH, Kim SN, Yang WM. Effects of acupuncture on 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013;2013: 982095.
Than A, Kulkarni HJ, Hmone W, Tha SJ. Antidiarrhoeal efficacy of some Burmese indigenous drug formulations in experimental diarrhoea test models. J Crude Drug Res 1989;27: 195–200.
Lee CH, Kim DK, Yook TH, Sasaki M, Kitamura N. Effectiveness of electroacupuncture at Zusanli (ST 36) on the immunohistochemical density of enteroendocrine cells related to gastrointestinal function. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 2012;5: 63–71.
Shuai X, Xie P, Liu J, Xiang Y, Li J, Lan Y. Different effects of electroacupuncture on esophageal motility and serum hormones in cats with esophagitis. Dis Esophagus 2008;21: 170–175.
Kachelhoffer J, Mendel C, Dauchel J, Hohmatter D, Grenier JF. The effects of VIP on intestinal motility: study on ex vivo perfused isolated canine jejunal loops. Am J Dig Dis 1976;21: 957–962.
Harvey RF. Hormonal control of gastrointestinal motility. Am J Dig Dis 1975;20: 523–539.
Thomson AB, Wild G. Small bowel review: Part II. Can J Gastroenterol 1997;11: 607–618.
Ogawa A, Mochiki E, Yanai M, Morita H, Toyomasu Y, Ogata K, et al. Interdigestive migrating contractions are coregulated by ghrelin and motilin in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2012;302:R233–R241.
Sanger GJ, Holbrook JD, Andrews PL. The translational value of rodent gastrointestinal functions: a cautionary tale. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2011;32: 402–409.
Bassil AK, Dass NB, Murray CD, Muir A, Sanger GJ. Prokineticin-2, motilin, ghrelin and metoclopramide: prokinetic utility in mouse stomach and colon. Eur J Pharmacol 2005;524: 138–144.
Depoortere I, de Winter B, Thijs T, de Man J, Pelckmans P, Peeters T. Comparison of the gastroprokinetic effects of ghrelin, GHRP-6 and motilin in rats in vivo and in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 2005;515: 160–168.
Feng X, Peeters TL, Tang M. Motilin activates neurons in the rat amygdala and increases gastric motility. Peptides 2007;28: 625–631.
Jia YD, Liu CQ, Tang M, Jiang ZY. Expression of motilin in the hypothalamus and the effect of central erythromycin on gastric motility in diabetic rats. Neurosci Bull 2007;23: 75–82.
Fang P, Dong L, Luo JY. Effects of motilin on intracellular free calcium in cultured smooth muscle cells from the antrum of neonatal rats. Acta Physiol 2010;199: 53–61.
Schubert ML. Gastric secretion. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2004;20: 519–525.
Thomas PA, Akwari OE, Kelly KA. Hormonal control of gastrointestinal motility. World J Surg 1979;3: 545–552.
Qian Y, Zhao X, Kan J. Preventive effect of resistant starch on activated carbon-induced constipation in mice. Exp Ther Med 2013;6: 228–232.
Noguchi E, Ohsawa H, Tanaka H, Ikeda H, Aikawa Y. Electro-acupuncture stimulation effects on duodenal motility in anesthetized rats. Jpn J Physiol 2003;53: 1–7.
Sato A, Sato Y, Suzuki A, Uchida S. Neural mechanisms of the reflex inhibition and excitation of gastric motility elicited by acupuncture-like stimulation in anesthetized rats. Neurosci Res 1993;18: 53–62.
Gyires K. Neuropeptides and gastric mucosal homeostasis. Curr Top Med Chem 2004;4: 63–73.
Locatelli V, Bresciani E, Bulgarelli I, Rapetti D, Torsello A, Rindi G, et al. Ghrelin in gastroenteric pathophysiology. J Endocrinol Invest 2005;28: 843–848.
Takahashi T, Owyang C. Vagal control of nitric oxide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide release in the regulation of gastric relaxation in rat. J Physiol 1995;484: 481–492.
Gil K, Bugajski A, Thor P. Electrical vagus nerve stimulation decreases food consumption and weight gain in rats fed a high-fat diet. J Physiol Pharmacol 2011;62: 637–646.
Chey WY, Chang T. Neural hormonal regulation of exocrine pancreatic secretion. Pancreatology 2001;1: 320–335.
Becker HD, Borger HW, Schafmayer A. Effect of vagotomy on gastrointestinal hormones. World J Surg 1979;3: 615–622.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Lakshmi Rajagopal for English proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP, No. NRF- 2013R1A1A1005580)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, JH., Lee, DJ., Bae, CH. et al. Changes in small intestinal motility and related hormones by acupuncture stimulation at Zusanli (ST 36) in mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23, 215–220 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2609-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2609-8