Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of ancient Chinese medical formula Xiayuxue Decoction (下瘀血汤, XYXD) on activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and defenestration of sinusoidal endothelial cells (SECs) in CCl4-induced fibrotic liver of mice.
Methods
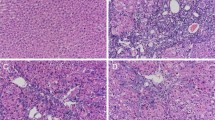
High performance liquid chromatography was used to identify the main components of XYXD and control the quality of extraction. C57BL/6 mice were induced liver fibrosis by CCl4 exposure and administered with XYXD for 6 weeks simultaneously. Liver tissue was investigated by hematoxylin-eosin and Sirius-red staining. Sinusoidal fenestrations were observed by scanning electronic microscopy and fluorescent immunohistochemistry of PECAM-1 (CD31). Whole liver lysates were detected of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and type-I collagen by Western blot. Primary rat HSCs-T6 cells were analyzed by detecting α-SMA, F-actin, DNA fragmentation through confocal microscopy, Western blot, terminal-deoxynucleoitidyl transferase mediated nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay and cellomics arrayscan, respectively.
Results
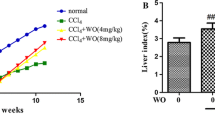
Amygdalin and emodin in XYXD were identified. XYXD (993 mg/kg) inhibited Sirius red positive area up to 70.1% (P<0.01), as well as protein levels of α-SMA and type-I collagen by 42.0% and 18.5% (P<0.05) respectively. In vitro, XYXD (12.5 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL) suppressed the activation of HSCs and reversed the myofibroblastic HSCs into quiescent, demonstrated as inhibition of fluorescent F-actin by 32.3% and 46.6% (P<0.05). Besides, XYXD induced the apoptosis of HSC-T6 cells by 20.0% (P<0.05) and 49.5% (P<0.01), evidenced by enhanced TUNEL positivity. Moreover, ultrastructural observation suggested XYXD inhibited defenestration of SECs, which was confirmed by 31.1% reduction of protein level of CD31 (P<0.05).
Conclusions
XYXD inhibited both HSCs activation and SECs defenestration which accompany chronic liver injuries. These data may help to understand the underlying mechanisms of XYXD for prevetion of chronic liver diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner DA, Rippe RA, Rhodes K, Trotter JF, Breindl M. fibrogenesis and type I collagen gene regulation. J Lab Clin Med 1994;124:755–760.
Rockey DC, Boyles JK, Gabbiani G, Friedman SL. Rat hepatic lipocytes express smooth muscle actin upon activation in vivo and in culture. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 1992;24:193–203.
Mitsuru S, Shinsuke S, Haruki S. Hepatic stellate cells: unique characteristics in cell biology and phenotype. Cell Struct Funct 2003;28:105–112.
Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. Hepatic stellate cells and the reversal of fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;21:S84–S87.
Issa R, Williams E, Trim N, Kendall T, Arthur MJ, Reichen J, et al. Apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells: involvment in resolution of biliary fibrosis and regulation by soluble growth factors. Gut 2001;48:548–557.
Braet F, Wisse E. Structural and functional aspects of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrae: a review. Comp Hepatol 2002;1:1–17.
DeLeve LD, Wang X, Hu L, McCuskey MK, McCuskey RS. Rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype is maintained by paracrine and autocrine regulation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2004;287:757–763.
Wisse E, De Zanger RB, Charels K, van Der Smissen P, McCuskey RS. The liver sieve: considerations concerning the structure and function of endothelial fenestrae, the sinusoidal wall and the space of Disse. Hepatology 1985;5:683–692.
Mu YP, Liu P, Liu Y, Liu Y, Li FH, Chen GF, et al. Inhibiting action of Xiayuxue Decoction on hepatic fibrosis at progressive stage in rats and study on the prescription and syndrome. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2006;47:215–218.
Hou ZX. Treating 49 cases of endometriosis with Jiawei Xiayuexue Decoction. Shaanxi J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2010;26:19–20.
Zhao LN. Treating 52 cases of ascites with cirrhosis by modified Xiayuexue Decoction. Hebei J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2009;31:386–386.
Lin Y, Liu P. Modified “Xiayuxue Decoction” for intrahepatic cholestasis following gallbladder operation. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2008;3:14–15.
Liu GM, Guo XX, Xiong SQ. Clinical observation of treatment of angina with coronary artery disease by Xiayuexue Decoction. Zhejiang J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2007;42:574–575.
Schäfer S, Zerbe O, Gressner AM. The synthesis of proteoglycans in fat-storing cells of rat liver. Hepatology 1987;7:680–687.
Dong CJ, Chen XR. Treating 120 cases of early or intermediate hepatocirrhosis with Jiawei Xiayuxue Decoction. Zhejiang J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;36:339–339.
Du GL, Liu P, Wang L, Wang CS, Long AH, Mu YP. Relationship between traditional medical formulae and syndrome based pharmacological study of Xiayuxue Decoction against porcine serum induced liver fibrosis in rats. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formul (Chin) 2007;13:30–32.
Lotersztajn S, Julien B, Teixeira-Clerc F, Grenard P, Mallat A. Hepatic fibrosis: molecular mechanisms and drug targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2005;45:605–628.
Dominique T, Vijay S. Intrahepatic angiogenesis and sinusoidal remodeling in chronic liver disease: new targets for the treatment of portal hypertension? J Hepatol 2010;53:976–980.
De Minicis S, Seki E, Uchinami H, Kluwe J, Zhang Y, Brenner DA, et al. Gene expression profiles during hepatic stellate cell activation in culture and in vivo. Gastroenterology 2007;132:1937–1946.
Maher JJ, McGuire RF. Extracellular matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosis in vivo. J Clin Invest 1990;86:1641–1648.
Choi SS, Omenetti A, Witek RP, Moylan CA, Syn WK, Jung Y, et al. Hedgehog pathway activation and epithelialto-mesenchymal transitions during myofibroblastic transformation of rat hepatic cells in culture and cirrhosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2009;297:1093–1106.
Van AL, D’Souza SC. Rho GTPases and signaling networks. Genes 1997;11:2295–2322.
Nobes CD, Lauritzen I, Mattei MG, Paris S, Hall A, Chardin P. A new member of the Rho family, Rnd1, promotes disassembly of actin filament structures and loss of cell adhesion. J Cell Biol 1998;141:187–197.
Couvelard A, Scoazec JY, Feldmann G. Expression of cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion proteins by sinusoidal endothelial cells in the normal and cirrhotic human liver. Am J Pathol 1993;143:738–752.
Wack KE, Ross MA, Zegarra V, Sysko LR, Watkins SC, Stolz DB. Sinusoidal ultrastructure evaluated during the revascularization of regenerating rat liver. Hepatology 2001;33:363–378.
Katrin N, Thomas W, Andreas R, Ramadori G. Plateletendothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 gene expression in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells during liver injury and repair. J Hepatol 2000;32:921–932.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 20110490750), Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (No. Y0302), E-institute of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. E03008), Innovative Research Team in Universities, Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, Key Disciplines of Liver and Gallbladder Diseases and Key Laboratory of Chronic Liver Disease of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of China, National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2006CB504801), National S&T Major Project (No. 2009ZX09311-003)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Lj., Sun, My., Ning, Bb. et al. Xiayuxue Decoction (下瘀血汤) attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation and sinusoidal endothelium defenestration in CCl4-induced fibrotic liver of mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 20, 516–523 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1862-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1862-y