Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) injection on pulmonary artery pressure and the expression of p38MAPK in lung tissue of rats subjected to chronic hypoxia.
Methods
Thirty adult male Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into three groups (ten in each group): rats in control group were exposed to normoxic condition and the rats in hypoxia group and PNS group were subjected to 4-week hypoxia, and PNS injection (50 mg·kg−1·d−1) was administrated intraperitoneally at 30 min in the PNS group daily before the rats were kept in the hypoxic chamber, while rats in the other two groups received equal dose of normal saline instead. After chronic hypoxia, mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) and mean carotid artery pressure (mCAP) were measured. The heart and lung tissues were harvested, and right ventricle (RV) and left ventricle plus ventricular septum (LV+S) were weighed to calculate the ratio of RV/(LV+S). The expression of p38MAPK mRNA was determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, the quantity of phosphorylated p38MAPK (p-p38MAPK) in rat lung tissues and pulmonary arterioles was determined by Western blot and immunohistochemistry.
Results
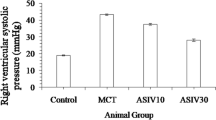
Compared with the control group, mPAP and the ratio of RV/(LV+S) in the hypoxia group were increased, the expression of p-p38MAPK in pulmonary arterioles and p38MAPK mRNA in the lung were higher (P<0.05). The changes of these parameters in the hypoxia group were significantly attenuated by PNS treatment (P<0.05).
Conclusion
PNS injection was shown to prevent hypoxic pulmonary hypertension at least partly by regulating p38MAPK pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Lu WJ, Yang K, Xu L, Lai N, Tian LC, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 decreases TRPC expression, storeoperated Ca2+ entry, and basal [Ca2+]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2013;304:C833–C843.
Kan W, Zhao KS, Jiang Y, Yan WS, Huang QB, Wang JZ, et al. Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in signal transduction of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression. Shock 2004;21:281–287.
Liu Z, Li S, Zhu JH, Huang CY. Expression of ERK and MKP-1 in vascular smooth muscle of spontaneously hypertensive rats with different ages. Chin J Pathophys (Chin) 2006;22:468–471.
Zhu YF, Dai AG, Hu RC. Effects of mitogen activated protein kinase on γ-glutamylcysteine synthase in lung of guinea pigs with bronchial asthma. Chin J Pathophys (Chin) 2007;23:1990–1995.
Wang Y, Huang S, Sah VP, Ross J, Brown JH, Han J, et al. Cardiac muscle cell hypertrophy and apoptosis induced by distinct members of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase family. J Biol Chem 1998;273:2161–2168.
Chu MP, Xu ZX, Zhang XL, Zhang J. Changes of expression of ICAM-1 in autoimmune myocarditis in mice and the interfering effect of panax notoginseng saponin. J Wenzhou Med Coll (Chin) 2007;37:203–205.
Ye HL, Wang F, Yu XW, Pan SY, Zheng XH, Guo LY, et al. Effect of Tianlong Kechuan Capsule on release of nitric oxide in rats with chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. China Med Herald (Chin) 2007;4(11):16–17.
Ono K, Han J. The p38 signal transduction pahtway: activation and function. Cell Signal 2000;12:1–13.
Zhang JF, Zhang DS. Study advancement in pharmalcological actions of total saponins of panax notoginseng. Med Recapitulatep (Chin) 2007;6:472–474.
Yue TL, Wang C, Gu JL, Ma XL, Kumar S, Lee JC, et al. Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase enhances ischemia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in cultured cardiac myocytes and exaggerates reperfusion injury in isolated perfused heart. Circ Res 2000;86:692–699.
Yin J, Chaufour X, McLachlan C, McGuire M, White G, King N, et al. Apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by cholesterol and its oxides in vitro and in vivo. Atherosclerosis 2000;148:365–374.
Seko Y, Tobe K, Ueki K, Kadowaki T, Yazaki Y. Hypoxia and hypoxia/reoxygenation activate Raf-1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, mitogen-activaed protein kinases, and S6 kinase in cultured rat cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 1996;78:82–90.
Rousseau S, Houle F, Landry J, Hout J. p38 MAP kinase activation by vascular endothelial growth factor mediates actin reorganization and cell migration in human endothelial cells. Oncogene 1997;15:2169–2177.
Veikkola T, Karkkainen M, Claesson-Welsh L, Alitalo K. Regulation of angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cancer Res 2000;60:203–212.
Zhou JY, Liu Y, Wu GS. The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in oxidative damage-induced cell death. Cancer Res 2006;66:4888–4894.
Nemoto S, Sheng Z, Lin A. Opposing effects of Jun kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases on cardiomyocytes hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biol 1998;18:3518–3526.
Robinson MJ, Cobb MH. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1997;9:180–186.
Ma WP, Yang YN, Zhou DB, Zhou WQ. The preventive effect of panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) on chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in rats. Chin J Pathophys (Chin) 2004;20:1074–1077.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Key Technology Development Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2006C33073) and the Key Projects of Traditional Chinese Medicine Development Plan of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2008ZA017, 2013ZZ011)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Zheng, Mx., Chen, He. et al. Effect of panax notoginseng saponins injection on the p38MAPK pathway in lung tissue in a rat model of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 21, 147–151 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1790-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1790-2