Abstract
Objective
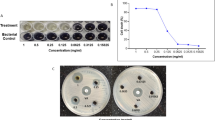
To investigate the bactericidal effects of Jinghua Weikang Capsule (荆花胃康胶丸) and its major component Chenopodium ambrosioides L. on antibiotic-resistant Helicobacter pylori.
Methods
Four clinical antibiotic-resistant H. pylori strains were isolated and incubated in liquid medium containing Jinghua Weikang Capsule or Chenopodium ambrosioides L. By means of time-kill curve method, the average colony counts and bactericidal rate were calculated at time points of 0, 4, 8 and 24 h after the incubation and the time-kill curves were charted.
Results
Both Jinghua Weikang Capsule and Chenopodium ambrosioides L. at a concentration of 0.64 g/L showed obvious bactericidal effect against antibiotic-resistant H. pylori after 4 h of incubation.
Conclusion
Jinghua Weikang Capsule and Chenopodium ambrosioides L. are considered to be active against antibiotic-resistant H. pylori in vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miwa H, Sakaki N, Sugano K, Sekine H, Higuchi K, Uemura N, et al. Recurrent peptic ulcers in patients following successful Helicobacter pylori eradication: a multicenter study of 4940 patients. Helicobacter 2004;9:9–16.
Nervi G, Liatopoulou S, Cavallaro LG, Gnocchi A, Dal-Bo N, Rugge M, et al. Does Helicobacter pylori infection eradication modify peptic ulcer prevalence? A 10 years’ endoscopical survey. World J Gastroenterol 2006;12:2398–2401.
Fischbach W, Goebeler-Kolve ME, Dragosics B, Greiner A, Stolte M. Long term outcome of patients with gastric marginal zone B cell lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) following exclusive Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: experience from a large prospective series. Gut 2004;53:34–37.
Konturek PC, Konturek SJ, Brzozowski T. Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancerogenesis. J Physiol Pharmacol 2009;60:3–21.
Huang XT, Zhang XZ, Li N, Cheng H. In vitro activity of Jinghuaweikang capsules against clinical isolates of antibiotic-resistant Helicobacter pylori. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Dig (Chin) 2010;18:290–293.
Zhang WD, Hu FL, Xiao SD, Xu ZM. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in China. Modern Dig Intervent (Chin) 2010;15:265–270.
Wong BC, Lam SK, Wong WM, Chen JS, Zheng TT, Feng RE, et al. China Gastric Cancer Study Group. Helicobacter pylori eradication to prevent gastric cancer in a highrisk region of China: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004;291:187–194.
Liang X, Liu WZ, Lu H, Xu WW, Xiao SD. Helicobacter pylori: in vitro induction of resistance to antibiotics and surveillance of its resistant prevalence. Chin J Dig Dis (Chin) 2003;23:146–149.
Federman DG, Kirsner RS, Moriarty JP, Concato J. The effect of antibiotic therapy for patients infected with Helicobacter pylori who have chronic urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol 2003;49:861–864.
Mégraud F. H pylori antibiotic resistance: prevalence, importance, and advances in testing. Gut 2004;53:1374–1384.
Cheng H, Hu FL, Xie Y, Hu PJ, Wang JY, Lv NH, et al. Chinese Helicobacter Pylori Research Group, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics and its influence on the treatment outcome in China: a multicenter clinical study. Chin J Gastroenterol (Chin) 2007;12:525–530.
Cao CY, Shan YJ, Li SC, Jin H, Tang HW. The antibioticresistance analysis of 200 Helicobacter pylori isolates. Zhejiang Prev Med (Chin) 2008;20:21–23.
Li XR, Li FQ, Xue YC, Shi DX, Ma J. Current status of the essential oil extraction process of Chinese medicine. Chin J Manag Chin Med (Chin) 2006;14:66–67.
Dou Y, Wang XD, Liang H, Liu SJ, Dong SH, Wang J. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of Jinghua Weikang Capsules and famotidine in treatment of Hp related peptic ulcer. Chin J New Drugs (Chin) 2004;13:650–652.
Jiang HQ, Zhang RX, Lu XP, Liu GF. Clinical observation of Jinghua Weikang therapy in patients with chronic gastritis. Tianjin Phamacy (Chin) 2004;16:31–33.
Zhang BF, Han YS, Yang J. Clinical observation of Jinghua Weikang Capsule in patients with peptic ulcer. Tianjin J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2004;21:201.
Miu H. Observation of effects of Jinghua Weikang Capsules on chronic gastritis and eradication of Helicobacteria pylori. Clin J Med Offic (Chin) 2010;38:563–564.
Fan Z, Wen Q. Effect of Jinghua Weikang Capsules on gastric ulcers. Chin Gen Pract (Chin) 2009;12:429–430.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Capital Medical Development and Research Foundation (No. SF-2007-III-01) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 8107295)
These authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Liu, Y., Zhang, Xz. et al. In vitro bactericidal activity of jinghua weikang capsule (荆花胃康胶丸) and its individual herb Chenopodium Ambrosioides L. against antibiotic-resistant Helicobacter Pylori . Chin. J. Integr. Med. 19, 54–57 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1248-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1248-y