Abstract
Objective
To inquire the characteristic proteins in chronic myocardial ischemia by testing twodimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) map to explore the possible inherent pathological mechanism and the therapeutic intervention of qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome.
Methods
Ameroid constrictor ring was placed on the first interval of left anterior descending coronary artery to prepare chronic myocardial ischemia model on Chinese miniature swine. Animals were randomly divided into sham group and model group with 10 animals in each group, respectively. The dynamic symptoms observation of the four diagnostic information was collected from 0 to 12 weeks. Echocardiography was employed to evaluate cardiac function and the degree of myocardial ischemia, 2-DE and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) were used to carry out proteomics research on animals. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was applied to identify the relevant differential proteins on chronic myocardial ischemia with qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome.
Results
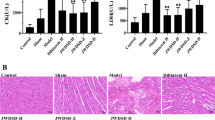
The preliminary study found that at the 12th week, chronic myocardial ischemia with qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome model was established stably. Compared with the sham group, there were 8 different proteins down-regulated, 22 proteins up-regulated significantly. After validated by MALDITOF-MS/MS, 11 protein spots were identified. Distinct proteins were mainly associated with energy metabolism and myocardial structural injury, including isocitrate dehydrogenase 3 (NAD+) alpha, NADH dehydrogenase (NAD) Fe-S protein 1, chain A (crystal structure of aldose reductase by binding domain reveals a new Nadph), heat shock protein 27 (HSP27), oxidoreductase (NAD-binding protein), antioxidant protein isoform, cardiac troponin T (cTnT), myosin (myosin light polypeptide), cardiac alpha tropomyosin, apolipoprotein A-I and albumin.
Conclusion
Down-regulated energy metabolism disorder mediated by NADH respiratory chain and myocardial injury may be the pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia with qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome. These proteins may be the potential diagnostic marker(s) for qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome, finally provided new clues for new therapeutic drug target of Chinese medicine
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He J, Gu DF, Wu XG, Kristi R, Duan XF, Ya CH, et al. Major causes of death among men and women in China. N Engl J Med 2005;353:1124–1134.
Jia ZH, Wang YJ, Wu YL, Li YS, Gao HL, Xi GC, et al. Entropy-based complex system partition method in extracting CHD angina pectoris syndrome elements and their distribution. Acad J Sec Milit Med Univ (Chin) 2007;28:775–777
Schwartz R, SHolmes DR. Pigs, dogs, Baboons and man: lessons for stenting from animal studies. J Interv Cardiol 1994;74:355–368.
Xu WY, Wang W, Guo SZ, Liu T, Liu L, Yu YX. Duplication of an animal model of myocardial ischemia with blood stasis syndrome in mini-swines. J Chin Integr Med (Chin) 2008;6:409–411.
Wang Y, Liu ZY, Li C, Li D, Ouyang YL, Yu JD, et al. Drug target prediction based on the herbs components: the study on the multi-targets pharmacological mechanism of Qishenkeli acting on the coronary heart disease. Evid Based Complem Altern Med 2012;4:1–10.
Guo SZ, Wang Wei, Liu T, Liu L, Tong YY, Xu WY, et al. Hemorheology and echocardiography evaluation of pig models with coronary heart disease (chronic myocardial ischemia) at the stage of blood stasis syndrome. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2007;25:702–706.
Wang J, Chen KJ, Weng WL, Qian ZH, Wang Y, Liu JG, et al. Research on diagnostic criteria of blood stasis symptom complex. Chin J Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Chin) 1988;8:585–589.
Shen ZY, Wang WJ. Reference criteria for differentiation of deficiency syndromes in traditional Chinese medicine. Chin J Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Chin) 1986;6:598.
Alonsozana GL, Christenson RH. The case for cardiac troponin T: marker for effective risk stratification of patients with acute cardiac ischemia. Clin Chem 1996;42:803–808.
Sinha MK, Roy D, Gaze DC. Role of “ischemia modified albumin”, a new biochemical marker of myocardial ischemia, in the early diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes. Emerg Med J 2004;21(1):29–34.
J Guay, H Lambert, G Gingras-Breton, JN Lavoie, J Huot, J Landry. Regulation of actin filament dynamics by p38 map kinase-mediated phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27. J Cell Science 1997;110:357–368.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Creation for Significant New Drugs (2012ZX09103-201-011), National Science and Technology Pillar Program (No. 2012BAI29B07), and Project of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (No. 2011-JYBZZ-JS055)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Chuo, Wj., Li, C. et al. Energy metabolism disorder and myocardial injury in chronic myocardial ischemia with Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome based on 2-DE proteomics. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 19, 616–620 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1230-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1230-8