Abstract
Objective
To explore the effect of Renshen Yangrong Decoction (人参养荣汤, RYD) in protecting bone marrow from radiation injury.
Methods
One hundred and eighty Kuming mice were subjected to the three tests for anti-radiation injury effect evaluation, i.e. the test of peripheral white blood cell (WBC) count, the test of bone marrow nucleated cell count, and the bone marrow micronucleus test, using 60 mice for each test. The mice in each test were divided into 6 groups: the blank control group, the model control group, the positive control group treated by Shiyiwei Shenqi Tablet (十一味参芪片, 1.0 g/kg), and three RYD groups treated with high (42.0 g/kg), moderate (21.0 g/kg), and low (10.5 g/kg) doses of crude drugs of RYD, with 10 mice in each group. The treatment was given by gastrogavage perfusion continuously for 7–14 days before mice received 60Co-γ ray radiation and continued until the end of the experiment. The body weights of the mice were monitored, the changes in peripheral WBC and bone marrow nucleated cells were counted, and the variation in bone marrow micronucleated cells was observed on the respective appointed days.
Results
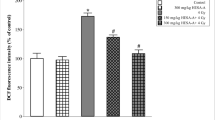
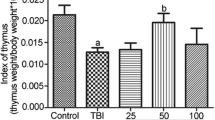
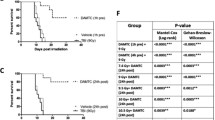
A significant decrease in body weight, peripheral WBC count, and bone marrow nucleated cell count, as well as marked changes in bone marrow micronucleated cells were observed in the mice after radiation, indicating that the radiation injury model was successfully established. As compared with the model control group, the decrease in body weight, peripheral WBC count, and bone marrow nucleated cell count, as well as the increase in bone marrow micronucleus cell count in the high dosage RYD treated group were obviously inhibited or lessened (P<0.05 or P<0.01).
Conclusion
RYD showed obvious protective effect in mice with bone marrow injury induced by radiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang YY, ed. Encyclopedia of Chinese medical sciences—Chinese formulae. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House;1992:192.
Zhang TZ, Xu GW, eds. Oncology. Vol 2. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Publishing House; 2005:2775.
Ministry of Health, P. R. China. Norms for health food inspection and evaluation. Beijing: Standards Press of China; 2003:167–207.
Committee of National Standardization, Ministry of Health, P. R. China. GB15919.1-2003. Evaluation and method on food safety toxicology. Beijing: Standards Press of China; 2004:17–48.
Luo J, Guo Y, Gou MH. Immunoregulation effect of ginseng tonic Decoction on mice. Chin J Modern Med (Chin) 2002;12(5):27–28.
Deng H, Tang F. Protective effect of Renshen Yangrong Decoction on membrane fluidity of mitochondrion in brain and liver subacute senile mice. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2006;26(Suppl):30–33.
Hu R, Deng H, Tang F. Effect of Renshen Yangrong Decoction on cerebral neuron form and density in aging mice. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2006;47:859–860.
Song QM, Tang F, Xie YC. Effect of Renshen Yangrong Decoction on antioxidation and viscera index in aging mice induced by D-galactose. Chin J Gerontol (Chin) 2003;23:386–387.
Lu XG, ed. Bone marrow cells and pathology. Beijing: Science Press; 2008:582.
Cao J, Lin Z, Yu ZP, eds. Principle and method of micronucleus test and its application in population monitoring and toxicology evaluation. Beijing: Military Medical Science Press; 2000:1–64.
Kliesch U. Micronucleus test and bone marrow chromosome analysis—a comparison of 2 methods in vivo for evaluating chemically induced chromosome alternations. Mutat Res 1980;80:321.
Sato N, Mizumoto K, Makamura M, Ueno H, Minamishima YA, Farber JL, et al. A possible role for centrosome overduplication in radiation-induced cell death. Oncogene 2000;19:5281
Zhang JT, ed. Modern pharmacological experimental method. Vol 2. Beijing: Beijing Medical University and China Union Medical University Publishing House; 1998:1886–1888.
Ding GR, Guo GZ. Research status on drugs for antiradiation injury. J Radiat Res Radiat Proc (Chin) 2007;25:321–325.
Wang N, Li YD, Liu K. Research survey on anti-radiation of Radix angelica sinensis and Radix Astragali and their effective components. Chin J Radiol Health (Chin) 2008;17:121.
Ge LB, Zhao KJ, Fei D. Experimental study on anti-fibrosis effects of Radix Astragali on rats induced by cervical radiation. Chin J Lab Diagn (Chin) 2009;13:881–882.
Huang LM, Sun CR, Wang L, Liu L. Optimization of effective anti-radiation Chinese medicine prescriptions with orthogonal t design. Chin J Pharmacol Clin (Chin) 2007;23:212–213.
Liu LM, Zhang YM, Lu SH, Sun YM, He GS. Regulation on function and maturation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells by Astragalus polysaccharide. Chin J Immunol 2010;26:712–715.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Scientific and Technologic Items of Traditional Chinese Medicine Administration of Beijing City (No. 2004 JingZhongZhong IV 15)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Yz., Lin, F., Zhuang, Gb. et al. Protective effect of Renshen Yangrong Decoction (人参养荣汤) on bone marrow against radiation injury in mouse. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 17, 453–458 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0634-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0634-1