Abstract
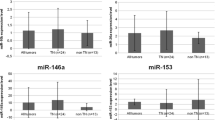
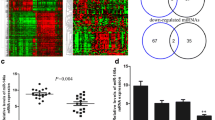
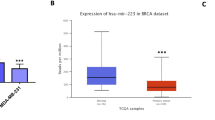
Breast cancer is the first common cancer among women worldwide. One of the major signaling pathways playing a role in the onset and progression of this disease is PI3K/Akt/mTOR, which can be inhibited by PTEN. miRNAs are small non-coding molecules that regulate the expression of their targets by inhibition or suppression, and thus, their dysregulated expression results in the development of cancer. Using various software applications predicting miRNAs and evaluating GEO microarray data, miR-144 was selected as an inhibitor of PTEN. The expression of miR-144 and PTEN was evaluated in 18 triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) clinical samples and cell lines including 4T1, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, SK-BR-3, and MCF-7 in comparison with normal cells. PTEN and miR-144 expression analysis revealed their elevated expression in MCF-7 cells. MDA-MB-468, SK-BR-3, and MDA-MB-231 cells showed decreased levels of PTEN and increased levels of miR-144. In contrast, 4T1 cells had an increased expression of PTEN and decreased expression of miR-144. In clinical samples, miR-144 was up-regulated in 22% of the cases and PTEN was down-regulated in 78% of the cases. The results showed that the expression of PTEN and miR-144 was inversely correlated in metastatic breast cancer cell lines. However, in TNBC clinical samples, there was no correlation between the expression of miR-144 and PTEN. Literature shows that there are other influencing factors affecting the expression of miRNAs. Therefore, care should be taken in interpreting the results of gene expression studies and its relation with cancer diagnosis/prognosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C, Leslie C (2010) Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol 11:R90
Cai H, Xue Y, Wang P, Wang Z, Li Z, Hu Y, Li Z, Shang X, Liu Y (2015) The long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates blood-tumor barrier permeability by targeting miR-144. Oncotarget 6:19759–19779
Cairns P, Okami K, Halachmi S, Halachmi N, Esteller M, Herman JG, Jen J, Isaacs WB, Bova GS, Sidransky D (1997) Frequent inactivation of PTEN/MMAC1 in primary prostate cancer. Cancer Res 57:4997–5000
Chang CW, Wu HC, Terry MB, Santella RM (2015) microRNA expression in prospectively collected blood as a potential biomarker of breast Cancer risk in the BCFR. Anticancer Res 35:3969–3977
Chou CH, Chang NW, Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Lin YL, Lee WH, Yang CD, Hong HC, Wei TY, Tu SJ, Tsai TR, Ho SY, Jian TY, Wu HY, Chen PR, Lin NC, Huang HT, Yang TL, Pai CY, Tai CS, Chen WL, Huang CY, Liu CC, Weng SL, Liao KW, Hsu WL, Huang HD (2016) miRTarBase 2016: updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D239–D247
DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, Jemal A (2014) Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 64:52–62
Dweep H, Gretz N, Sticht C (2014) miRWalk database for miRNA-target interactions. Methods Mol Biol 1182:289–305
Garofalo M, Croce CM (2011) microRNAs: master regulators as potential therapeutics in cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 51:25–43
Guo Y, Ying L, Tian Y, Yang P, Zhu Y, Wang Z, Qiu F, Lin J (2013) miR-144 downregulation increases bladder cancer cell proliferation by targeting EZH2 and regulating Wnt signaling. FEBS J 280:4531–4538
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Menard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:7065–7070
Jiang X, Shan A, Su Y, Cheng Y, Gu W, Wang W, Ning G, Cao Y (2015) miR-144/451 promote cell proliferation via targeting PTEN/AKT pathway in Insulinomas. Endocrinology 156:2429–2439
Keller A, Leidinger P, Vogel B, Backes C, ElSharawy A, Galata V, Mueller SC, Marquart S, Schrauder MG, Strick R, Bauer A, Wischhusen J, Beier M, Kohlhaas J, Katus HA, Hoheisel J, Franke A, Meder B, Meese E (2014) miRNAs can be generally associated with human pathologies as exemplified for miR-144. BMC Med 12:224
Lee DY, Jeyapalan Z, Fang L, Yang J, Zhang Y, Yee AY, Li M, Du WW, Shatseva T, Yang BB (2010) Expression of versican 3′-untranslated region modulates endogenous microRNA functions. PLoS One 5:e13599
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA (2007) Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 449:682–688
Madhavan D, Peng C, Wallwiener M, Zucknick M, Nees J, Schott S, Rudolph A, Riethdorf S, Trumpp A, Pantel K, Sohn C, Chang-Claude J, Schneeweiss A, Burwinkel B (2016) Circulating miRNAs with prognostic value in metastatic breast cancer and for early detection of metastasis. Carcinogenesis 37:461–470
Mohammadi-Yeganeh S, Paryan M, Mirab Samiee S, Soleimani M, Arefian E, Azadmanesh K, Mostafavi E, Mahdian R, Karimipoor M (2013) Development of a robust, low cost stem-loop real-time quantification PCR technique for miRNA expression analysis. Mol Biol Rep 40:3665–3674
Panigrahi AR, Pinder SE, Chan SY, Paish EC, Robertson JF, Ellis IO (2004) The role of PTEN and its signalling pathways, including AKT, in breast cancer; an assessment of relationships with other prognostic factors and with outcome. J Pathol 204:93–100
Phin S, Moore MW, Cotter PD (2013) Genomic rearrangements of PTEN in prostate Cancer. Front Oncol 3:240
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Zhang J, Carver B, Haveman WJ, Pandolfi PP (2010) A coding-independent function of gene and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature 465:1033–1038
Rasheed BK, Stenzel TT, McLendon RE, Parsons R, Friedman AH, Friedman HS, Bigner DD, Bigner SH (1997) PTEN gene mutations are seen in high-grade but not in low-grade gliomas. Cancer Res 57:4187–4190
Shah NR, Chen H (2014) MicroRNAs in pathogenesis of breast cancer: implications in diagnosis and treatment. World J Clin Oncol 5:48–60
Smith GL, Xu Y, Buchholz TA, Giordano SH, Jiang J, Shih YC, Smith BD (2012) Association between treatment with brachytherapy vs whole-breast irradiation and subsequent mastectomy, complications, and survival among older women with invasive breast cancer. Jama 307:1827–1837
Suva LJ, Washam C, Nicholas RW, Griffin RJ (2011) Bone metastasis: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7:208–218
Tamura M, Gu J, Tran H, Yamada KM (1999) PTEN gene and integrin signaling in cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1820–1828
Vlachos IS, Paraskevopoulou MD, Karagkouni D, Georgakilas G, Vergoulis T, Kanellos I, Anastasopoulos IL, Maniou S, Karathanou K, Kalfakakou D, Fevgas A, Dalamagas T, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2015) DIANA-TarBase v7.0: indexing more than half a million experimentally supported miRNA:mRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D153–D159
Xiao J, Tao T, Yin Y, Zhao L, Yang L, Hu L (2017) miR-144 may regulate the proliferation, migration and invasion of trophoblastic cells through targeting PTEN in preeclampsia. Biomed Pharmacother 94:341–353
Yang J, Ren Y, Wang L, Li B, Chen Y, Zhao W, Xu W, Li T, Dai F (2010) PTEN mutation spectrum in breast cancers and breast hyperplasia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136:1303–1311
Zhang LY, Ho-Fun Lee V, Wong AM, Kwong DL, Zhu YH, Dong SS, Kong KL, Chen J, Tsao SW, Guan XY, Fu L (2013) MicroRNA-144 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through repression of PTEN. Carcinogenesis 34:454–463
Acknowledgement
This study was funded by Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran [grant number: 5639]. The author would like to thank Stem Cell Technology Research Center, Tehran, Iran, for providing technical Support.
Funding
This study was funded by Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran [grant number: 5639].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kia, V., Sharif Beigli, M., Hosseini, V. et al. Is miR-144 an effective inhibitor of PTEN mRNA: a controversy in breast cancer. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 54, 621–628 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-018-0282-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-018-0282-2