Abstract
Purpose
To assess atrophy differences among brain regions and time-dependent changes after whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT).
Materials and methods
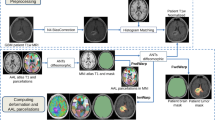
Twenty patients with lung cancer who underwent both WBRT and chemotherapy (WBRT group) and 18 patients with lung cancer who underwent only chemotherapy (control group) were recruited. Three-dimensional T1WI were analyzed to calculate volume reduction ratio after WBRT in various brain structures. The volume reduction ratio of the hippocampus was compared among following 3 periods: 0–3, 4–7, and 8–11 months after WBRT.
Results
The volume reduction ratio of the hippocampus was significantly higher in the WBRT group than in the control group (p < 0.05). In WBRT group, the volume reduction ratio of the hippocampus was significantly higher than that of the cortex and white matter (p < 0.05). There were significant differences in the volume reduction ratio between of 0–3 months and that of 4–7 months (p = 0.02) and between 4–7 months and that of 8–11 months (p = 0.01).
Conclusion
The hippocampus is more vulnerable to the radiation compared with other brain regions and may become atrophic even in the early stage after WBRT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roman DD, Sperduto PW. Neuropsychological effects of cranial radiation: current knowledge and future directions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31:983–98.
Shaw MG, Ball DL. Treatment of brain metastases in lung cancer: strategies to avoid/reduce late complications of whole brain radiation therapy. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2013;14:553–67.
Raber J, Rola R, LeFevour A, Morhardt D, Curley J, Mizumatsu S, et al. Radiation-induced cognitive impairments are associated with changes in indicators of hippocampal neurogenesis. Radiat Res. 2004;162:39–47.
Rola R, Raber J, Rizk A, Otsuka S, VandenBerg SR, Morhardt DR, et al. Radiation-induced impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis is associated with cognitive deficits in young mice. Exp Neurol. 2004;188:316–30.
Gondi V, Hermann BP, Mehta MP, Tome WA. Hippocampal dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign or low-grade adult brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85:348–54.
Redmond KJ, Mahone EM, Horska A. Association between radiation dose to neuronal progenitor cell niches and temporal lobes and performance on neuropsychological testing in children: a prospective study. Neuro Oncol. 2013;15(3):360–9.
Gondi V, Tome WA, Mehta MP. Why avoid the hippocampus? A comprehensive review. Radiother Oncol. 2010;97:370–6.
Oskan F, Ganswindt U, Schwarz SB, Manapov F, Belka C, et al. Hippocampus sparing in whole-brain radiotherapy. A review. Strahlenther Onkol. 2014;190(4):337–41.
Zhao R, Kong W, Shang J, Zhe H, Wang YY. Hippocampal-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy for lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2017;18(2):127–31.
Seibert TM, Karunamuni R, Bartsch H, Kaifi S, Krishnan AP, Dalia Y, et al. Radiation dose-dependent hippocampal atrophy detected with longitudinal volumetric magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;97:263–9.
Hong A, Hallock H, Valenzuela M, Lo S, Steel V, Paton E, et al. Change in the hippocampal volume after whole-brain radiation therapy with or without hippocampal avoidance technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;93:E82.
Lee YY, Nauert C, Glass JP. Treatment-related white matter changes in cancer patients. Cancer. 1986;57:1473–82.
Karunamuni R, Bartsch H, White NS, Moiseenko V, Carmona R, Marshall DC, et al. Dose-dependent cortical thinning after partial brain irradiation in high-grade glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016;94:297–304.
Reuter M, Fischl B. Avoiding asymmetry-induced bias in longitudinal image processing. Neuroimage. 2011;57:19–211.
Reuter M, Schmansky NJ, Rosas HD, Fischl B. Within-subject template estimation for unbiased longitudinal image analysis. Neuroimage. 2012;61:1402–18.
Schuff N, Woerner N, Boreta L, Kornfield T, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ, et al. Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative. MRI of hippocampal volume loss in early Alzheimer’s disease in relation to ApoE genotype and biomarkers. Brain. 2009;132:1067–77.
Martin P, Bender B, Focke NK. Post-processing of structural MRI for individualized diagnostics. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015;5:188–203.
Yazlovitskaya EM, Edwards E, Thotala D, Fu A, Osusky KL, Whetsell WO Jr, et al. Lithium treatment prevents neurocognitive deficit resulting from cranial irradiation. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11179–86.
Bellinzona M, Gobbel GT, Shinohara C, Fike JR. Apoptosis is induced in the subependyma of young adult rats by ionizing irradiation. Neurosci Lett. 1996;208:163–6.
Snyder JS, Kee N, Wojtowicz JM. Effects of adult neurogenesis on synaptic plasticity in the rat dentate gyrus. J Neurophysiol. 2001;85:2423–31.
Monje ML, Mizumatsu S, Fike JR, Palmer TD. Irradiation induces neural precursor cell dysfunction. Nat Med. 2002;8:955–62.
Mizumatsu S, Monje ML, Morhardt DR, Rola R, Palmer TD, Fike JR. Extreme sensitivity of adult neurogenesis to low doses of X-irradiation. Cancer Res. 2003;63:4021–7.
Farjam R, Pramanik P, Aryal MP, Srinivasan A, Chapman CH, Tsien CI, et al. A radiation-induced hippocampal vascular injury surrogate marker predicts late neurocognitive dysfunction. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;93:908–15.
Ferrer I, Serrano T, Alcantara S, Tortosa A, Graus F. X-ray-induced cell death in the developing hippocampal complex involves neurons and requires protein synthesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993;52:370–8.
Nagai R, Tsunoda S, Hori Y, Asada H. Selective vulnerability to radiation in the hippocampal dentate granule cells. Surg Neurol. 2000;53:503–6.
Ramanan S, Kooshki M, Zhao W, Hsu FC, Robbins ME. PPARalpha ligands inhibit radiation-induced microglial inflammatory responses by negatively regulating NF-kappaB and AP-1 pathways. FreeRadic Biol Med. 2008;45:1695–704.
Lee WH, Sonntag WE, Mitschelen M, Yan H, Lee YW. Irradiation induces regionally specific alterations in proinflammatory environments in rat brain. Int J Radiat Biol. 2010;86:132–44.
Tofilon PJ, Fike JR. The radioresponse of the central nervous system: a dynamic process. Radiat Res. 2000;153:357–70.
Sasaki R, Matsumoto A, Itoh K, Kawabe T, Ota Y, Yamada K, et al. Target cells of apoptosis in the adult murine dentate gyrus and O4 immunoreactivity after ionizing radiation. Neurosci Lett. 2000;279:57–60.
Schultheiss TE, Stephens LC. Permanent radiation myelopathy. Br J Radiol. 1992;65:737–53.
Monje ML, Vogel H, Masek M, Ligon KL, Fisher PG, Palmer TD. Impaired human hippocampal neurogenesis after treatment for central nervous system malignancies. Ann Neurol. 2007;62:515–20.
Gebicke-Haerter PJ. Microglia in neurodegeneration: molecular aspects. Microsc Res Tech. 2001;54:47–58.
Joo KM, Jin J, Kang BG, Lee SJ, Kim KH, Yang H, et al. Trans-differentiation of neural stem cells: a therapeutic mechanism against the radiation induced brain damage. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e25936.
Nagel BJ, Palmer SL, Reddick WE, Glass JO, Helton KJ, et al. Abnormal hippocampal development in children with medulloblastoma treated with risk-adapted irradiation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:1575–82.
Olsson E, Eckerström C, Berg G, Borga M, Ekholm S, et al. Hippocampal volumes in patients exposed to low-dose radiation to the basal brain. A case-control study in long-term survivors from cancer in the head and neck region. Radiat Oncol. 2012;7:202.
Oehlke O, Wucherphennig D, Fels F, Frings L, Egger K, et al. Whole brain irradiation with hippocampal sparing and dose escalation on multiple brain metastases. Strablenther Onkol. 2015;38:439–49.
Lin SY, Yang CC, Wu YM, Tseng CK, Wei KC, et al. Evaluating the impact of hippocampal sparing during whole brain radiotherapy on neurocognitive functions: a preliminary report of a prospective phase II study. Biomed J. 2015;38(5):439–49.
Gondi V, Pugh SL, Tome WA, Caine C, Corn B, et al. Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): a phase II multi-institutional trial. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(34):3810–6.
Molly S, Soh C, Williams TL. Reversible delayed posthypoxic leukoencephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27:1763–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
All applicable institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
This study was approved by our institutional review board. Informed consent was obtained in the form of opt-out on the website.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Takeshita, Y., Watanabe, K., Kakeda, S. et al. Early volume reduction of the hippocampus after whole-brain radiation therapy: an automated brain structure segmentation study. Jpn J Radiol 38, 118–125 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-019-00895-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-019-00895-3