Abstract
Purpose
To retrospectively evaluate high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) findings and clinical diagnoses of chronic interstitial pneumonia (IP) with a poor prognosis in young patients (≤50 years).
Materials and methods
HRCT images of 8 men and 7 women (mean age 34.8 years) obtained before lung transplantation or autopsy were reviewed. After reviewing whole lung specimens and pathologic diagnoses, all patients were clinically diagnosed according to the 2010 idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/usual interstitial pneumonia (IPF/UIP) consensus statement.
Results
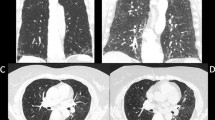
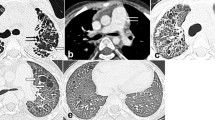
HRCT images revealed intralobular reticular opacity, air cysts, ground glass opacity, traction bronchiectasis, and interlobular septal thickening. Intralobular reticular opacity was the most extensive finding. Abnormal findings existed predominantly in both the peripheral and lower lung zones in only 1 patient. Classifications of HRCT patterns were “UIP” (n = 2), “inconsistent with UIP” (n = 11), and “indeterminate UIP” (n = 2). Multidisciplinary diagnoses were “IPF/UIP” (n = 1), “possible IPF/UIP” (n = 1), “IP with connective tissue disease” (n = 7), “fibrotic nonspecific IP” (n = 1), and “unclassified IP” (n = 5).
Conclusion
The most extensive HRCT finding was intralobular reticular opacity. Most HRCT images differed from typical IPF/UIP, and IPF/UIP was uncommon in young patients with chronic IP with a poor prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:788–824.
King TE Jr, Tooze JA, Schwarz MI, Brown KR, Cherniack RM. Predicting survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: scoring system and survival model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1171–81.
Nicholson AG, Colby TV, du Bois RM, Hansell DM, Wells AU. The prognostic significance of the histologic pattern of interstitial pneumonia in patients presenting with the clinical entity of cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:2213–7.
Nadrous HF, Myers JL, Decker PA, Ryu JH. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in patients younger than 50 years. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:37–40.
American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment: international consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and European Respiratory Society (ERS). Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:646–64.
Omote N, Taniguchi H, Kondoh Y, Watanabe N, Sakamoto K, Kimura T, et al. Lung-dominant connective tissue disease: clinical, radiologic, and histologic features. Chest. 2015;148:1438–46.
Fischer A, Antoniou KM, Brown KK, Cadranel J, Corte TJ, du Bois RM, et al. An official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society research statement: interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. Eur Respir J. 2015;46:976–87.
Hugh-Jones P, Lambert AV. A simple standard exercise test and its use for measuring exertion dyspnea. Br Med J. 1952;1:65–71.
Webb WR, Müller NL, Naidich DP. Illustrated glossary of high-resolution CT terms. In: High-resolution CT of the lung. 5th ed. Wolters Kluwer Health; 2015. p. 660–77.
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, Macmahon H, McLoud TC, Müller NL, Remy J. Fleischner Society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology. 2008;246:697–722.
Sumikawa H, Johkoh T, Ichikado K, Taniguchi H, Kondoh Y, Fujimoto K, et al. Usual interstitial pneumonia and chronic idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: analysis of CT appearance in 92 patients. Radiology. 2006;241:258–66.
Chung JH, Chawla A, Peljto AL, Cool CD, Groshong SD, Talbert JL, et al. CT scan findings of probable usual interstitial pneumonitis have a high predictive value for histologic usual interstitial pneumonitis. Chest. 2015;147:450–9.
Nishimura K, Kitaichi M, Izumi T, Nagai S, Kanaoka M, Itoh H. Usual interstitial pneumonia: histologic correlation with high-resolution CT. Radiology. 1992;182:337–42.
Akira M, Sakatani M, Ueda E. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: progression of honeycombing at thin-section CT. Radiology. 1993;189:687–91.
Hunninghake GW, Lynch DA, Galvin JR, Gross BH, Müller N, Schwartz DA, et al. Radiologic findings are strongly associated with a pathologic diagnosis of usual interstitial pneumonia. Chest. 2003;124:1215–23.
Lynch DA, Travis WD, Müller NL, Galvin JR, Hansell DM, Grenier PA, et al. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: CT features. Radiology. 2005;236:10–21.
Johkoh T, Müller NL, Cartier Y, Kavanagh PV, Hartman TE, Akira M, et al. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: diagnostic accuracy of thin-section CT in 129 patients. Radiology. 1999;211:555–60.
Song JW, Do KH, Kim MY, Jang SJ, Colby TV, Kim DS. Pathologic and radiologic differences between idiopathic and collagen vascular disease-related usual interstitial pneumonia. Chest. 2009;136:23–30.
Mino M, Noma S, Kobayashi Y, Iwata T. Serial changes of cystic air spaces in fibrosing alveolitis: a CT-pathological study. Clin Radiol. 1995;50:357–63.
Katzenstein AL, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:1301–15.
Marshall RP, Puddicombe A, Cookson WO, Laurent GJ. Adult familial cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis in the United Kingdom. Thorax. 2000;55:143–6.
Hodgson U, Laitinen T, Tukiainen P. Nationwide prevalence of sporadic and familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence of founder effect among multiplex families in Finland. Thorax. 2002;57:338–42.
Allam JS, Limper AH. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: is it a familial disease? Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006;12:312–7.
Nishiyama O, Taniguchi H, Kondoh Y, Kimura T, Katoh T, Oishi T, et al. Familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: serial high-resolution computed tomography findings in 9 patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2004;28:443–8.
Kono M, Nakamura Y, Enomoto N, Hashimoto D, Fujisawa T, Inui N, et al. Usual interstitial pneumonia preceding collagen vascular disease: a retrospective case control study of patients initially diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One. 2014;9:e94775.
Douglas WW, Tazelaar HD, Hartman TE, Hartman RP, Decker PA, Schroeder DR, et al. Polymyositis–dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1182–5.
Flaherty KR, Colby TV, Travis WD, Toews GB, Mumford J, Murray S, et al. Fibroblastic foci in usual interstitial pneumonia: idiopathic versus collagen vascular disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:1410–5.
Woodhead F, Wells AU, Desai SR. Pulmonary complications of connective tissue diseases. Clin Chest Med. 2008;29:149–64.
Akashi T, Takemura T, Ando N, Eishi Y, Kitagawa M, Takizawa T, et al. Histopathologic analysis of sixteen autopsy cases of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis and comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/usual interstitial pneumonia. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;131:405–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest or funding sources to disclose.
About this article
Cite this article
Uka, M., Iguchi, T., Kato, K. et al. Chronic interstitial pneumonia in young patients undergoing lung transplantation or autopsy: clinico-radiologic-pathologic observations from a single institution. Jpn J Radiol 34, 515–522 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-016-0551-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-016-0551-5