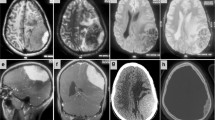
Abstract
IgG4-related disease is an emerging clinicopathologic entity. Hypophysitis, diffuse thickening of dura, and enlargement of the trigeminal nerve are well-known intracranial involvements of IgG4-related disease. This report of a case of systemic IgG4-related disease is the first to present neuroimaging of apparent supratentorial meningioma-like lesions and thickening and contrast enhancement of the walls of the intracranial internal carotid arteries. It is important to recognize IgG4-related intracranial pseudotumors so that patients do not undergo unnecessary surgical procedures.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamisawa T, Nakajima H, Egawa N, Funata N, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A. IgG4-related sclerosing disease incorporating sclerosing pancreatitis, cholangitis, sialadenitis and retroperitoneal fibrosis with lymphadenopathy. Pancreatology. 2006;6(1–2):132–7.
Shimatsu A, Oki Y, Fujisawa I, Sano T. Pituitary and stalk lesions (infundibulo-hypophysitis) associated with immunoglobulin G4-related systemic disease: an emerging clinical entity. Endocr J. 2009;56:1033–41.
Lindstrom KM, Cousar JB, Lopes MBS. IgG4-related meningeal disease: clinico-pathological features and proposal for diagnostic criteria. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;120:765–76.
Watanabe T, Fujiwara Y, Kawakami S, Hatta T, Hamano H, Kawa S, et al. Infraorbital nerve swelling associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Jpn J Radiol. 2011;29:194–201.
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22:21–30.
Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, Watanabe S, Shiratori K, Hayashi N. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:1561–8.
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–8.
Lui PC, Fan YS, Wong SS, Chan AN, Wong G, Chau TK, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumors of the central nervous system. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:1611–7.
Katsura M, Mori H, Kunimatsu A, Sasaki H, Abe O, Machida T, et al. Radiological features of IgG4-related disease in the head, neck, and brain. Neuroradiology. 2012;54:873–82.
Inoue D, Zen Y, Abo H, Gabata T, Demachi H, Yoshikawa J, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related periaortitis and periarteritis: CT findings in 17 patients. Radiology. 2011;261:625–33.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Research on Intractable Diseases (a Health and Labor Science Research Grant from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nishino, T., Toda, J., Nakatsuka, T. et al. IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumors mimicking multiple meningiomas. Jpn J Radiol 31, 405–407 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-013-0191-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-013-0191-y