Abstract
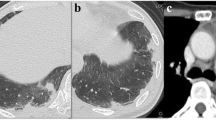
Computed tomography findings of pathologically proven pulmonary infarction associated with bronchogenic carcinoma are reported for two patients. In one case, the infarction was demonstrated as a well-defined pleura-based large nodule in the peripheral portion of the same lobe of the tumor. The nodule had a smooth, convex border and a linear strand from the apex of the lesion toward the hilum. The obstruction of the subsegmental pulmonary artery due to tumor invasion was considered the cause of pulmonary infarction. In the second case, the infarction was demonstrated as a rapidly appeared, pleura-based consolidation in the same lobe of the tumor with a blurred border. Obstruction of the pulmonary vein by a tumor might have played an important role in the development of the pulmonary infarction in association with a large pulmonary artery obstruction. We conclude that pulmonary infarction should be considered as a differential diagnosis when peripheral pulmonary nodules or masses are located in the same lobe as the primary cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanbury WJ, Cureton RJR, Simon G. Pulmonary infarcts associated with bronchogenic carcinoma. Thorax 1954;9:304–312.
Tsunoda H, Saida Y, Doi M, Kimura Y, Matsueda K, Kurosaki Y, et al. Pulmonary infarction associated with bronchogenic carcinoma. Nippon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi (Nippon Acta Radiol) 1989;49:1112–1121 (in Japanese).
Yoshida N, Sugita H, Nakajima Y, Nakano H, Kawabata Y. Relations between chest CT and pathologic findings in pulmonary infarction associated with lung cancer. Nippon Kyobu Shikkann Gakkai Zasshi 1995;33:1064–1072.
Held BT, Siegelman SS. Pulmonary infarction secondary to bronchogenic carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1974;120:145–150.
Marriott AE, Weisbrod G. Bronchogenic carcinoma associated with pulmonary infarction. Radiology 1982;145:593–597.
Nomori H, Horio H, Morinaga S, Suemasu K. Multiple pulmonary infarctions associated with lung cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;60:40–42.
Kadukura M, Kamio Y, Kitami A, Nakajima H, Fujisawa H, Kushihashi T, et al. Pulmonary adenocarcinoma complicated with pulmonary infarction presented as intrapulmonary metastases: a case report. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;12:189–193.
Ellis FH, Grindlay JH, Edwards JE, Minn R. The bronchial arteries. II. Their role in pulmonary embolism and infarction. Surgery 1952;31:167–179.
Dalen JE, Haffajee CI, Alpert JS 3rd, Howe JP, Ockene IS, Paraskos JA. Pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hemorrhage and pulmonary infarction. N Engl J Med 1977;296:1431–1435.
Tsao MS, Schraufnagel D, Wang NS. Pathogenesis of pulmonary infarction. Am J Med 1982;72:599–606.
Balakrishnan J, Meziane MA, Siegelman SS, Fishman EK. Pulmonary infarction: CT appearance with pathologic correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1989;13:941–945.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, M., Murakami, Y., Nitta, N. et al. Pulmonary infarction associated with bronchogenic carcinoma. Radiat Med 26, 76–80 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-007-0192-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-007-0192-9