Abstract
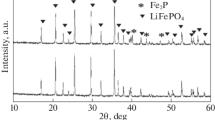
Nano-Li2FeSiO4/C composites were prepared from three kinds of nano-SiO2 (their particle sizes are 15 ± 5, 30 ± 5, and 50 ± 5 nm, respectively) by a traditional solid-state reaction method. The as-prepared materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), elementary analyzer, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis, galvanostatic charge–discharge test, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. XRD results reveal that nano-Li2FeSiO4 composites fabricated from nano-SiO2 (smaller than 30 nm) have less impurity. SEM results indicate that the particle size of nano-Li2FeSiO4 composites is nearly accord with the particle size of nano-SiO2. BET analysis indicates that the specific surface areas of LFS15, LFS30, and LFS50 are 35.10, 35.27, and 26.68 m2 g, respectively, and the main pore size distribution of LFS15, LFS30, and LFS50 are 1.5, 5.5, and 10 nm, respectively. Electrochemical measurements indicate that nano-Li2FeSiO4 composites prepared from nano-SiO2 of 30 ± 5 nm have the best electrochemical performance among the three samples.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Islam MS, Dominko R, Masquelier C, Sirisopanaporn C, Armstrong AR, Bruce PG (2011) Silicate cathodes for lithium batteries: alternatives to phosphates. J Mater Chem 21:9811–9818
Zhang QT, Zhao YL, Su C, Li MY (2011) Nano/Micro Lithium Transitionmetal (Fe, Mn, Co and Ni) Silicate Cathode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries. Recent Pat Nanotech 5:225–233
Ellis BL, Lee KT, Nazar LF (2010) Positive electrode materials for li-ion and li-batteries. Chem Mater 22:691–714
Aravindan V, Karthikeyan K, Ravi S, Amaresh S, Kim WS, Lee YS (2010) Adipic acid assisted sol–gel synthesis of Li2MnSiO4 nanoparticles with improved lithium storage properties. J Mater Chem 20:7340–7343
Aravindan V, Karthikeyan K, Kang KS, Yoon WS, Kim WS, Lee YS (2011) Influence of carbon towards improved lithium storage properties of Li2MnSiO4 cathodes. J Mater Chem 21:2470–2475
Lyness C, Delobel B, Armstrong AR, Bruce PG (2007) The lithium intercalation compound Li2CoSiO4 and its behaviour as a positive electrode for lithium batteries. Chem Commun 46:4890–4892
Nytén A, Abouimrane A, Armand M, Gustafsson T, Thomas JO (2005) Electrochemical performance of Li2FeSiO4 as a new Li-battery cathode material. Electrochem Commun 7:156–160
Dominko R, Conte DE, Hanzel D, Gaberscek M, Jamnik J (2008) Impact of synthesis conditions on the structure and performance of Li2FeSiO4. J Power Sources 178:842–847
Armstrong AR, Kuganathan N, Islam MS, Bruce PG (2011) Structure and lithium transport pathways in Li2FeSiO4 cathodes for lithium batteries. J Am Chem Soc 133:13031–13035
Zaghib K, Salah AA, Ravet N, Mauger A, Gendron F, Julien CM (2006) Structural, magnetic and electrochemical properties of lithium iron orthosilicate. J Power Sources 160:1381–1386
Zhang S, Deng C, Yang S (2009) Preparation of nano-Li2FeSiO4 as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochem Solid-State Let 12:A136–A139
Li LM, Guo HJ, Li XH, Wang ZX, Peng WJ, Xiang KX, Cao X (2009) Effects of roasting temperature and modification on properties of Li2FeSiO4/C cathode. J Power Sources 189:45–50
Gong ZL, Li YX, He GN, Li J, Yang Y (2008) Nanostructured Li2FeSiO4 electrode material synthesized through hydrothermal-assisted sol–gel process. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 11:A60–A63
Fan XY, Li Y, Wang JJ, Gou L, Zhao P, Li DL, Huang L, Sun SG (2010) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of porous Li2FeSiO4/C cathode material for long-life lithium-ion batteries. J Alloy Compd 493:77–80
Kam KC, GustafssonT TJO (2011) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of nanostructured Li2FeSiO4/C cathode material for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 192:356–359
Huang XB, Li X, Wang HY, Pan ZL, Qu MZ, Yu ZL (2010) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Li2FeSiO4/C as cathode material for lithium batteries. Solid State Ionics 181:1451–1455
Huang XB, Li X, Wang HY, Pan ZL, Qu MZ, Yu ZL (2010) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Li2FeSiO4/carbon/carbon nano-tubes for lithium ion battery. Electrochim Acta 55:7362–7366
Wu XZ, Jiang X, Huo QS, Zhang YX (2012) Facile synthesis of Li2FeSiO4/C composites with triblock copolymer P123 and their application as cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 80:50–55
Zheng ZM, Wang Y, Zhang A, Zhang TR, Cheng FY, Tao ZL, Chen J (2012) Porous Li2FeSiO4/C nanocomposite as the cathode material of lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 198:229–235
Shao B, Taniguchi I (2012) Synthesis of Li2FeSiO4/C nanocomposite cathodes for lithium batteries by a novel synthesis route and their electrochemical properties. J Power Sources 199:278–286
Qu L, Fang SH, Yang L, Hirano SI (2012) Li2FeSiO4/C cathode material synthesized by template-assisted sol–gel process with Fe2O3 microsphere. J Power Sources 217:243–247
Chen WH, Lan M, Zhu D, Wang C, Xue S, Yang CC, Li ZX, Zhang J, Mi LW, Chen WH, Lan M, Zhu D, Wang C, Xue S, Yang CC, Li ZX, Zhang J, Mi LW (2013) Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical performance of Li2FeSiO4/C for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv 3:408–412
Guo HJ, Cao X, Li XQ, Li LM, Li XH, Wang ZX, Peng WJ, Li QH (2010) Optimum synthesis of Li2Fe1−xMnxSiO4/C cathode for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 55:8036–8042
Deng C, Zhang S, Yang SY, Fu BL, Ma L (2011) Synthesis and characterization of Li2Fe0.97M0.03SiO4 ( M = Zn2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ )cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 196:386–392
Huang XB, Chen HH, Zhao SB, Chen YD, Yang JF, Ren YR, Wang HY, Qu MZ, Pang ZL, Yu ZL (2012) Synthesis and characterization of nano-Li1.95FeSiO4/C composite as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 60:239–243
Huang XB, Chen HH, Wang HY, Zhou SB, Chen YD, Liu BP, Yang JF, Zhou GN, Jiang QL, Qu MZ, Pang ZL, Yu ZL (2012) High-rate properties of Li1.95FeSiO4/C/CNTs composite as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 220:18–22
Xiao L, Guo YL, Qu DY, Deng BH, Liu HX, Tang DP (2013) Influence of particle sizes and morphologies on the electrochemical performances of spinel LiMn2O4 cathode materials. J Power Sources 225:286–292
Yoshida J, Stark M, Holzbock J, Hüsing N, Nakanishi S, Iba H, Abe H, Naito M (2013) Analysis of the size effect of LiMnPO4 particles on the battery properties by using STEM-EELS. J Power Sources 226:122–126
Delacourt C, Poizot P, Levasseur S, Masquelier C (2006) Size effects on carbon-free LiFePO4 powders. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 9:A352–A355
Acknowledgments
Financial supports from the Science and Technology Planning Project of Gansu Province (1212RJZA007) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, J., Qing, C., Zhang, Q. et al. Effect of the particle size on the electrochemical performance of nano-Li2FeSiO4/C composites. Ionics 20, 23–28 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-013-0965-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-013-0965-3