Abstract
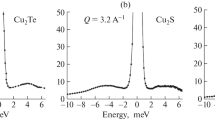
The paper reports the results of a neutron scattering study of \( {\hbox{C}}{{\hbox{u}}_{{2 - \delta }}}{\hbox{Se}} \) superionic compounds. The crystallographic model fitted to the diffraction data shows the occupation of 8c and 32f sites by Cu atoms. Observed diffuse background is related to correlated thermal vibrations of Se and Cu atoms, with Se↔Cu (8c,32f) and Cu (8c)↔Cu (8c) correlations being most important. The quasi-elastic neutron experiments show the decrease of the self-diffusion coefficient with the deviation from the stoichiometry due to the longer residence time of Cu ions between diffusion hops. Combination of neutron diffraction, diffuse scattering and quasi-elastic scattering experimental data suggests that the Cu atoms diffuse between the nearest 8c sites through the 32f sites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korzhuev MA, Bankina VF, Gruznov BF, Bushmarina GS (1989) Electrophysical properties of superionic Cu2-xSe. Sov Phys Semicond 23:959–962
Yakshibaev RA, Konev VN, Balapanov MK (1984) Ion conductivity and diffusion in superionic conductor \( \alpha {\hbox{ - C}}{{\hbox{u}}_{{2 - \delta }}}{\hbox{Se}} \). Sov Phys Solid State 26:2189–2191
Korzhuev MA (1989) Mixed conduction and ultrafast chemical diffusion in superionic Cu2-xSe. Sov Phys Solid State 31:1666–1670
Kashida S, Akai X-ray J (1988) diffraction and electron microscopy studies of the room temperature structure of Cu2Se. J Phys C Solid State Phys 21:5329–5336
Milat O, Vučić Z, Ruščić B (1987) Superstructural ordering in low-temperature phase of superionic Cu2Se. Solid State Ionics 23:37–47
Frangis N, Manolikas C, Amelinckx S (1991) Vacancy-ordered superstructures in Cu2Se. Phys Status Solidi A 126:9–22
Heyding RD, Murray RM (1976) The crystal structures of Cu1.8Se, Cu3Se2, α- and γ-CuSe, CuSe2 and Cu3Se2 II. Can J Chem 54:841–848
Skomorokhov AN, Trots DM, Knapp M, Bickulova NN, Fuess H (2006) Structural behaviour of \( \beta {\hbox{ - C}}{{\hbox{u}}_{{2 - \delta }}}{\hbox{Se}} \) (δ = 0, 0.15, 0.25) in dependence on temperature studied by synchrotron powder diffraction. J Alloys Compd 421:64–71
Sakuma T (1995) Structural and dynamic properties of solid state ionics. Bull Electrochem 11:57–80
Yamamoto K, Kashida S (1991) X-ray study of average structures of Cu2Se and Cu1.8S in the room temperature and the high temperature phases. J Solid State Chem 93:202–211
Yamamoto K, Kashida S (1991) X-ray study of the cation distribution in Cu2Se, Cu1.8Se and Cu1.8S; analysis by the maximum entropy method. Solid State Ionics 48:241–248
Oliveria M, McMullan RK, Wuensch BJ (1988) Single crystal neutron diffraction analysis of the cation distribution in the high-temperature phases α-Cu2-xS, α-Cu2-xSe, and α-Ag2Se. Solid State Ionics 28–30:1332–1337
Boyce JB, Hayes TM, Mikkelsen JC (1981) EXAFS investigation of mobile ion density: CuI and Cu2Se contrasted. Solid State Ionics 5:497–500
Danilkin SA (2009) An investigation of the structural dynamics in the fast ionic conductor \( {\hbox{C}}{{\hbox{u}}_{{2 - \delta }}}{\hbox{Se}} \) using neutron scattering. J Alloys Compd 467:509–513
Hempelmann R (2000) Quasielastic neutron scattering and solid state diffusion. Clarendon, Oxford
ANSTO (2010). Available at: http://www.ansto.gov.au/research/bragg_institute/facilities/instruments/echidna. Accessed 28 Oct 2010
Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (2010) http://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/user/neutrons/instrumentation/neutron-instruments/v3/. Accessed 28 Oct 2010
Ruffle B (2000) User manual for FITMO2, BENSC, Berlin
Richard D, Ferrand M, Kearley GJ (1996) Analysis and visualisation of neutron-scattering data. J Neutron Res 4:33–39
Larson AC, Von Dreele RB (2000) General structure analysis system (GSAS), Los Alamos National Laboratory Report LAUR 86-74
Polyakov VI (2001) Visualization of conduction channels and the dynamics of ion transport in superionic conductors. Phys Solid State 43:655–662
Chahid A, McGreevy RL (1998) Structure and ionic conduction in CuI: diffuse neutron scattering and RMC modeling. J Phys Condens Matter 10:2597–2609
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Australian Research Council-Discovery Projects (DP0984525). The authors acknowledge for the provision of beam time from ANSTO (Australia) and Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (Germany).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danilkin, S.A., Avdeev, M., Sakuma, T. et al. Neutron scattering study of short-range correlations and ionic diffusion in copper selenide. Ionics 17, 75–80 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-010-0489-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-010-0489-z