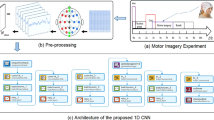
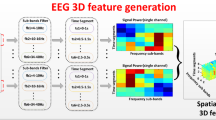
Abstract
Recently, deep learning-based methods have achieved meaningful results in the Motor imagery electroencephalogram (MI EEG) classification. However, because of the low signal-to-noise ratio and the various characteristics of brain activities among subjects, these methods lack a subject adaptive feature extraction mechanism. Another issue is that they neglect important spatial topological information and the global temporal variation trend of MI EEG signals. These issues limit the classification accuracy. Here, we propose an end-to-end 3D CNN to extract multiscale spatial and temporal dependent features for improving the accuracy performance of 4-class MI EEG classification. The proposed method adaptively assigns higher weights to motor-related spatial channels and temporal sampling cues than the motor-unrelated ones across all brain regions, which can prevent influences caused by biological and environmental artifacts. Experimental evaluation reveals that the proposed method achieved an average classification accuracy of 93.06% and 97.05% on two commonly used datasets, demonstrating excellent performance and robustness for different subjects compared to other state-of-the-art methods.In order to verify the real-time performance in actual applications, the proposed method is applied to control the robot based on MI EEG signals. The proposed approach effectively addresses the issues of existing methods, improves the classification accuracy and the performance of BCI system, and has great application prospects.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin SU, Alsulaiman M, Muhammad G, Mekhtiche MA, Hossain MS (2019) Deep learning for eeg motor imagery classification based on multi-layer cnns feature fusion. Futur Gener Comput Syst 101:542–554
Ang KK, Chin ZY, Wang C, Guan C, Zhang H (2012) Filter bank common spatial pattern algorithm on bci competition iv datasets 2a and 2b. Front Neurosci 6:39
Baig MZ, Aslam N, Shum HP (2020) Filtering techniques for channel selection in motor imagery eeg applications: a survey. Artif Intell Rev 53(2):1207–1232
Bashivan P, Rish I, Yeasin M, Codella N (2015) Learning representations from eeg with deep recurrent-convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06448
Bjorck N, Gomes CP, Selman B, Weinberger KQ (2018) In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 7694–7705
Dai G, Zhou J, Huang J, Wang N (2020) Hs-cnn: a cnn with hybrid convolution scale for eeg motor imagery classification. J Neural Eng 17(1):016025
Dong E, Zhou K, Tong J, Du S (2020) A novel hybrid kernel function relevance vector machine for multi-task motor imagery eeg classification. Biomed Signal Process Control 60:101991
Fawaz HI, Lucas B, Forestier G, Pelletier C, Schmidt DF, Weber J, Webb GI, Idoumghar L, Muller PA, Petitjean F (2020) Inceptiontime: finding alexnet for time series classification. Data Min Knowl Disc 34(6):1936–1962
Gaur P, Gupta H, Chowdhury A, McCreadie K, Pachori RB, Wang H (2021) A sliding window common spatial pattern for enhancing motor imagery classification in eeg-bci. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 70:1–9
Glorot X, Bengio Y (2010) In: Proceedings of the thirteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics, pp. 249–256
Gong A, Liu J, Chen S, Fu Y (2018) Time-frequency cross mutual information analysis of the brain functional networks underlying multiclass motor imagery. J Mot Behav 50(3):254–267
Gramfort A, Luessi M, Larson E, Engemann DA, Strohmeier D, Brodbeck C, Goj R, Jas M, Brooks T, Parkkonen L et al (2013) Meg and eeg data analysis with mne-python. Front Neurosci 7:267
Hong X, Zheng Q, Liu L, Chen P, Ma K, Gao Z, Zheng Y (2021) Dynamic joint domain adaptation network for motor imagery classification. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 29:556–565
Ingolfsson TM, Hersche M, Wang X, Kobayashi N, Cavigelli L, Benini L (2020) In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC) (IEEE), pp. 2958–2965
Kwon OY, Lee MH, Guan C, Lee SW (2019) Subject-independent brain-computer interfaces based on deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(10):3839–3852
Lawhern VJ, Solon AJ, Waytowich NR, Gordon SM, Hung CP, Lance BJ (2018) Eegnet: a compact convolutional neural network for eeg-based brain-computer interfaces. J Neural Eng 15(5):056013
Lei B, Liu X, Liang S, Hang W, Wang Q, Choi KS, Qin J (2019) Walking imagery evaluation in brain computer interfaces via a multi-view multi-level deep polynomial network. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 27(3):497–506
Li Y, Zhang XR, Zhang B, Lei MY, Cui WG, Guo YZ (2019) A channel-projection mixed-scale convolutional neural network for motor imagery eeg decoding. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 27(6):1170–1180
Li D, Xu J, Wang J, Fang X, Ying J (2020) A multi-scale fusion convolutional neural network based on attention mechanism for the visualization analysis of eeg signals decoding. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 28(12):2615–2626
Li X, Chen S, Hu X, Yang J (2019) In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2682–2690
Liu X, Lv L, Shen Y, Xiong P, Yang J, Liu J (2021) Multiscale space-time-frequency feature-guided multitask learning cnn for motor imagery eeg classification. J Neural Eng 18(2):026003
Lotte F, Bougrain L, Cichocki A, Clerc M, Congedo M, Rakotomamonjy A, Yger F (2018) A review of classification algorithms for eeg-based brain-computer interfaces: a 10 year update. J Neural Eng 15(3):031005
Ma X, Qiu S, Wei W, Wang S, He H (2019) Deep channel-correlation network for motor imagery decoding from same limb. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 28(1):297–306
Ma X, Wang D, Liu D, Yang J (2020) Dwt and cnn based multi-class motor imagery electroencephalographic signal recognition. J Neural Eng 17(1):016073
Maaten Lvd, Hinton G (2008) Visualizing data using t-sne. J Mach Learn Res 9(Nov):2579–2605
Miao Y, Jin J, Daly I, Zuo C, Wang X, Cichocki A, Jung TP (2021) Learning common time-frequency-spatial patterns for motor imagery classification. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 29:699–707
Musallam YK, AlFassam NI, Muhammad G, Amin SU, Alsulaiman M, Abdul W, Altaheri H, Bencherif MA, Algabri M (2021) Electroencephalography-based motor imagery classification using temporal convolutional network fusion. Biomed Signal Process Control 69:102826
Pang Y, Zhao X, Zhang L, Lu H (2020) In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9413–9422
Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G, Killeen T, Lin Z, Gimelshein N, Antiga L et al. (2019) In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp. 8026–8037
Penaloza CI, Nishio S (2018) Bmi control of a third arm for multitasking. Sci Robot 3(20):eaat1228
Sakhavi S, Guan C, Yan S (2018) Learning temporal information for brain-computer interface using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(11):5619–5629
Santurkar S, Tsipras D, Ilyas A, Madry A (2018) In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2483–2493
Schirrmeister RT, Springenberg JT, Fiederer LDJ, Glasstetter M, Eggensperger K, Tangermann M, Hutter F, Burgard W, Ball T (2017) Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for eeg decoding and visualization. Hum Brain Mapp 38(11):5391–5420
Sharma M, Pachori R, Rajendra A (2017) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. Pattern Recogn Lett 94:172–179
Sun B, Zhao X, Zhang H, Bai R, Li T (2021) Eeg motor imagery classification with sparse spectrotemporal decomposition and deep learning. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 18(2):541–551
Wu H, Li F, Li Y, Fu B, Shi G, Dong M, Niu Y (2019) A parallel multiscale filter bank convolutional neural networks for motor imagery eeg classification. Front Neurosci 13:1275
Xie X, Yu ZL, Lu H, Gu Z, Li Y (2016) Motor imagery classification based on bilinear sub-manifold learning of symmetric positive-definite matrices. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 25(6):504–516
Xu M, Yao J, Zhang Z, Li R, Yang B, Li C, Li J, Zhang J (2020) Learning eeg topographical representation for classification via convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit 105:107390
Zhang Y, Zhou G, Jin J, Wang X, Cichocki A (2015) Optimizing spatial patterns with sparse filter bands for motor-imagery based brain-computer interface. J Neurosci Methods 255:85–91
Zhang Y, Nam CS, Zhou G, Jin J, Wang X, Cichocki A (2018) Temporally constrained sparse group spatial patterns for motor imagery bci. IEEE Trans Cybern 49(9):3322–3332
Zhang J, Xie Y, Wu Q, Xia Y (2019) Medical image classification using synergic deep learning. Med Image Anal 54:10–19
Zhang D, Yao L, Chen K, Wang S, Chang X, Liu Y (2019) Making sense of spatio-temporal preserving representations for eeg-based human intention recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(7):3033–3044
Zhang L, Wang X, Yang D, Sanford T, Harmon S, Turkbey B, Wood BJ, Roth H, Myronenko A, Xu D et al (2020) Generalizing deep learning for medical image segmentation to unseen domains via deep stacked transformation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(7):2531–2540
Zhang H, Zhao X, Wu Z, Sun B, Li T (2021) Motor imagery recognition with automatic eeg channel selection and deep learning. J Neural Eng 18(1):016004
Zhang C, Kim YK, Eskandarian A (2021) Eeg-inception: an accurate and robust end-to-end neural network for eeg-based motor imagery classification. J Neural Eng 18(4):046014
Zhang X, Yao L, Wang X, Monaghan J, Mcalpine D, Zhang Y (2019) A survey on deep learning based brain computer interface: Recent advances and new frontiers. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.04149
Zhao X, Zhang H, Zhu G, You F, Kuang S, Sun L (2019) A multi-branch 3d convolutional neural network for eeg-based motor imagery classification. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 27(10):2164–2177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this research study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Wang, K., Liu, F. et al. 3D Convolution neural network with multiscale spatial and temporal cues for motor imagery EEG classification. Cogn Neurodyn 17, 1357–1380 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-022-09906-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-022-09906-y