Abstract
Purpose
The mandibular ramus is regarded as a relatively safe zone for a sagittal splitting osteotomy or for harvesting bone during implant treatment. The only important anatomical structure is the mandibular canal. The mandible has some anatomical variants that need to be recognized, such as a bifid mandibular canal, a retromolar canal, and rarely a temporal crest canal (TCC). In this study, cadaver mandibles were used to evaluate the TCC in the mandibular ramus using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
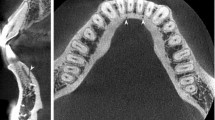
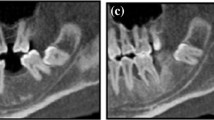
Altogether, 90 sites on 48 mandibles from Japanese cadavers were examined in this study. The CBCT volumetric images were acquired for areas of 79 mm\(\varphi \times \) 71 mm. Three-dimensional observation of the images was undertaken to estimate the frequency, position of the orifices, and canal continuity. The cadaver mandibles in which the TCCs were observed were dissected from the inner surface to confirm the contents.
Results
Five TCCs (5.6 %) were observed in 90 observation areas. At least one TCC was confirmed in four (8.3 %) of 48 mandibles. Two types of TCC were recognized. Dissection revealed that they contained neurovascular bundles.
Conclusion
Three-dimensional diagnosis is essential prior to surgical procedures in the mandibular ramus because unexpected blood vessels may be present that may cause bleeding or complications during the surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naitoh M, Hiraiwa Y, Aimiya H, Ariji E (2009) Observation of bifid mandibular canal using cone-beam computerized tomography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implant 24:155–159
Kuribayashi A, Watanabe H, Imaizumi A, Tantanapornkul W, Katakami K, Kurabayashi T (2010) Bifid mandibular canals: cone beam computed tomography evaluation. Dentmaxillofac Radiol 39:235–239
Kawai T, Asaumi R, Sato I, Kumazawa Y, Yosue T (2012) Observation of the retromolar foramen and canal of the mandible: a CBCT and macroscopic study. Oral Radiol 28:10–14
Imada TS, Fernandes LM, Centurion BS, de Oliveira-Santos C, Honório HM, Rubira-Bullen IR (2012) Accessory mental foramina: prevalence, position and diameter assessed by cone-beam computed tomography and digital panoramic radiographs. Clin Oral Implants Res. doi:10.1111/clr.12066. [Epub ahead of print]
Naitoh M, Hiraiwa Y, Aimiya H, Gotoh K, Ariji E (2009) Accessory mental foramen assessment using cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107:289–294
Naitoh M, Nakahara K, Suenaga Y, Gotoh K, Kondo S, Ariji E (2009) Variations of the bony canal in the mandibular ramus using cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Radiol 26:36–40
Rouas P, Nancy J, Bar D (2007) Identification of double mandibular canals: literature review and three case reports with CT scans and cone beam CT. Dentmaxillofac Radiol 36:34–38
Claeys V, Wackens G (2005) Bifid mandibular canal: literature review and case report. Dentmaxillofac Radiol 34:55–58
Ossenberg NS (1986) Temporal crest canal: case report and statistics on a rare mandibular variant. Oral Surg 62:10–12
Ossenberg NS (1987) Retromolar foramen of the human mandible. Am J Phys Anthropol 73:119–128
Liebgott B (2011) The anatomical basis of dentistry, 3rd edn. Mosby Elsevier, Maryland Heights
Turner W (1864) On some variations in the arrangement of the nerves of the human body. Nat Hist Rev 4:612–617
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Munetaka Naitoh and Eiichiro Ariji (Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, School of Dentistry, Aichi-Gakuin University) for their assistance.
Conflict of interest T. Kawai, R. Asaumi, Y. Kumazawa, I. Sato, and T. Yosue declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors presented the contents of this study at the CARS 2012 Congress in Pisa, Italy. We thank the judges for giving us 1st prize in the category of CMI poster awards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawai, T., Asaumi, R., Kumazawa, Y. et al. Observation of the temporal crest canal in the mandibular ramus by cone beam computed tomography and macroscopic study. Int J CARS 9, 295–299 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0931-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0931-6