Abstract
Purpose
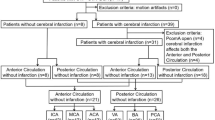
To externally validate the performance of automated stenosis detection on head and neck CT angiography (CTA) and investigate the impact factors using an independent bi-center dataset with digital subtraction angiography (DSA) as the ground truth.
Material and methods
Patients who underwent head and neck CTA and DSA between January 2019 and December 2021 were retrospectively included. The degree of stenosis was automatically evaluated using CerebralDoc based on CTA. The performance of CerebralDoc across levels (per-patient, per-region, per-vessel, and per-segment) and thresholds (≥ 50%, ≥ 70%, and = 100%) was evaluated. Logistic regression was performed to identify independent factors associated with false negative results.
Results
296 patients were analyzed. Specificity across levels and thresholds was high, exceeding 92%. The area under the curve ranged from poor (0.615, 95% CI: 0.544, 0.686; at the region-based analysis for stenosis ≥ 70%) to excellent (0.945, 95% CI: 0.905, 0.985; at the patient-based analysis for stenosis ≥ 50%). Sensitivity ranged from 0.714 (95% CI: 0.675, 0.750) at the segment-based analysis for stenosis ≥ 70% to 0.895 (95% CI: 0.849, 0.919) at the patient-based analysis for stenosis ≥ 50%. The multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that false negative results were primarily more likely to specific stenosis locations (particularly the M2 segment and skull base segment of the internal carotid artery) and occlusion.
Conclusions
CerebralDoc has the potential to automated stenosis detection on head and neck CTA, but further efforts are needed to optimize its performance.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available to be shared upon publication by correspondence with KL (likunhua@hospital.cqmu.edu.cn).
Abbreviations
- AI:
-
Artificial intelligence
- AS:
-
Arterial stenosis
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CTA:
-
CT angiography
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- PACS:
-
Picture archiving and communication system
References
Gutierrez J, Turan TN, Hoh BL et al (2022) Intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(21)00376-8
Bonati LH, Jansen O, de Borst GJ et al (2022) Management of atherosclerotic extracranial carotid artery stenosis. Lancet Neurol 21(3):273–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(21)00359-8
Li J, Wu H, Hang H et al (2022) Carotid vulnerable plaque coexisting with cerebral small vessel disease and acute ischemic stroke: a Chinese atherosclerosis risk evaluation study. Eur Radiol 32(9):6080–6089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-022-08757-9
Wu S, Wu B, Liu M et al (2019) Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol 18(4):394–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(18)30500-3
Nardi V, Benson J, Bois MC et al (2022) Carotid plaques from symptomatic patients with mild stenosis is associated with intraplaque hemorrhage. Hypertension 79(1):271–282. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.121.18128
Howard DPJ, Gaziano L, Rothwell PM (2021) Risk of stroke in relation to degree of asymptomatic carotid stenosis: a population-based cohort study, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 20(3):193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(20)30484-1
Libby P (2021) The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature 592(7855):524–533. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03392-8
Wardlaw JM, Mair G, von Kummer R et al (2022) Accuracy of automated computer-aided diagnosis for stroke imaging: a critical evaluation of current evidence. Stroke. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.121.036204
Torres C, Lum C, Puac-Polanco P et al (2021) Differentiating carotid free-floating thrombus from atheromatous plaque using intraluminal filling defect length on CTA: a validation study. Neurology 97(8):e785–e793. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000012368
Luijten SPR, Wolff L, Duvekot MHC et al (2022) Diagnostic performance of an algorithm for automated large vessel occlusion detection on CT angiography. J Neurointerv Surg 14(8):794–798. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-017842
Fu F, Shan Y, Yang G et al (2023) Deep learning for head and neck CT angiography: stenosis and plaque classification. Radiology. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.220996
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T et al (2019) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/American stroke association. Stroke 50(12):e344–e418. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
Nam JG, Hwang EJ, Kim J et al (2023) AI improves nodule detection on chest radiographs in a health screening population: a randomized controlled trial. Radiology. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.221894
Lauritzen AD, Rodríguez-Ruiz A, von Euler-Chelpin MC et al (2022) An artificial intelligence-based mammography screening protocol for breast cancer: outcome and radiologist workload. Radiology. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.210948
Yang J, Xie M, Hu C et al (2021) Deep learning for detecting cerebral aneurysms with CT angiography. Radiology 298(1):155–163. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020192154
Venkadesh KV, Setio AAA, Schreuder A et al (2021) Deep learning for malignancy risk estimation of pulmonary nodules detected at low-dose screening CT. Radiology. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2021204433
Chen W, Liu X, Li K et al (2021) A deep-learning model for identifying fresh vertebral compression fractures on digital radiography. Eur Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-08247-4
Chilamkurthy S, Ghosh R, Tanamala S et al (2018) Deep learning algorithms for detection of critical findings in head CT scans: a retrospective study. Lancet 392(10162):2388–2396. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31645-3
Zreik M, van Hamersvelt R, Wolterink J et al (2019) A recurrent CNN for automatic detection and classification of coronary artery plaque and stenosis in coronary CT angiography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(7):1588–1598. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2018.2883807
Stib MT, Vasquez J, Dong MP et al (2020) Detecting large vessel occlusion at multiphase CT angiography by using a deep convolutional neural network. Radiology 297(3):640–649. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020200334
Elijovich L, Dornbos Iii D, Nickele C et al (2022) Automated emergent large vessel occlusion detection by artificial intelligence improves stroke workflow in a hub and spoke stroke system of care. J Neurointerv surg 14(7):704–708. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-017714
Dehkharghani S, Lansberg M, Venkatsubramanian C et al (2021) High-performance automated anterior circulation CT angiographic clot detection in acute stroke: a multireader comparison. Radiology 298(3):665–670. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2021202734
Amukotuwa SA, Straka M, Smith H et al (2019) Automated detection of intracranial large vessel occlusions on computed tomography angiography: a single center experience. Stroke 50(10):2790–2798. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.119.026259
Amukotuwa SA, Straka M, Dehkharghani S et al (2019) Fast automatic detection of large vessel occlusions on CT angiography. Stroke 50(12):3431–3438. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.119.027076
Slieker RC, van der Heijden A, Siddiqui MK et al (2021) Performance of prediction models for nephropathy in people with type 2 diabetes: systematic review and external validation study. BMJ 374:n2134. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n2134
Poorthuis MHF, Herings RAR, Dansey K et al (2021) External validation of risk prediction models to improve selection of patients for carotid endarterectomy. Stroke. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.120.032527
Mair G, White P, Bath PM et al (2022) Artificial Intelligence software to interpret brain computed tomography in patients with stroke: external validation of e-ASPECTS software. Ann Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26495
de Jong VMT, Rousset RZ, Antonio-Villa NE et al (2022) Clinical prediction models for mortality in patients with covid-19: external validation and individual participant data meta-analysis. BMJ 378:e069881. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj-2021-069881
Nguyen-Huynh MN, Wintermark M, English J et al (2008) How accurate is CT angiography in evaluating intracranial atherosclerotic disease? Stroke 39(4):1184–1188. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.107.502906
Budoff M, Dowe D, Jollis J et al (2008) Diagnostic performance of 64-multidetector row coronary computed tomographic angiography for evaluation of coronary artery stenosis in individuals without known coronary artery disease: results from the prospective multicenter accuracy (assessment by coronary computed tomographic angiography of individuals undergoing invasive coronary angiography) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 52(21):1724–1732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2008.07.031
Ranganathan P, Pramesh CS, Aggarwal R (2017) Common pitfalls in statistical analysis: logistic regression. Perspect Clin Res 8(3):148–151. https://doi.org/10.4103/picr.PICR_87_17
Matsoukas S, Morey J, Lock G et al (2023) AI software detection of large vessel occlusion stroke on CT angiography: a real-world prospective diagnostic test accuracy study. J Neurointerv Surg 15(1):52–56. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-018391
Sheth SA, Giancardo L, Colasurdo M et al (2022) Machine learning and acute stroke imaging. J Neurointerv Surg. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-018142
Leslie-Mazwi TM, Lev MH (2020) Towards artificial intelligence for clinical stroke care. Nat Rev Neurol 16(1):5–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0287-9
McKinney SM, Sieniek M, Godbole V et al (2020) International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature 577(7788):89–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1799-6
Murray NM, Unberath M, Hager GD et al (2020) Artificial intelligence to diagnose ischemic stroke and identify large vessel occlusions: a systematic review. J Neurointerv Surg 12(2):156–164. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-015135
Liebeskind DS, Wardlaw JM (2023) Imaging advances in stroke: use of advanced neurovascular imaging or disruptive innovation with artificial intelligence? Stroke. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.123.042308
Yahav-Dovrat A, Saban M, Merhav G et al (2021) Evaluation of artificial intelligence-powered identification of large-vessel occlusions in a comprehensive stroke center. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 42(2):247–254. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A6923
Fasen B, Heijboer RJJ, Hulsmans FH et al (2020) CT angiography in evaluating large-vessel occlusion in acute anterior circulation ischemic stroke: factors associated with diagnostic error in clinical practice. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 41(4):607–611. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A6469
Fu F, Wei J, Zhang M et al (2020) Rapid vessel segmentation and reconstruction of head and neck angiograms using 3D convolutional neural network. Nat Commun 11(1):4829. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18606-2
Choi CG, Lee DH, Lee JH et al (2007) Detection of intracranial atherosclerotic steno-occlusive disease with 3D time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography with sensitivity encoding at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(3):439–446
Funding
This work was supported by the Chongqing medical scientific research project (Joint project of Chongqing Health Commission and Science and Technology Bureau) under Grant No.2023MSXM014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. KL devised the study protocol and is the principal investigator. YY, XH, and DG participated in the study design. SN developed the methodology. XW acquired funding. KL, YY, XH, and XW conducted the data and statistical analyses. KL, DG, YY, and XH contributed to data interpretation. YY and XH drafted the initial manuscript, which was further revised by KL. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript. KL, DG, and XW have directly accessed and verified the underlying data reported in the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The research was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University.
Consent to participate
Ethics committee has confirmed that no consent to participate is required.
Consent to publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Huan, X., Guo, D. et al. Performance of deep learning-based autodetection of arterial stenosis on head and neck CT angiography: an independent external validation study. Radiol med 128, 1103–1115 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01683-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01683-w