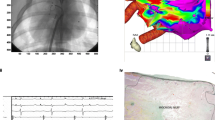
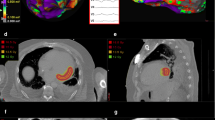
Abstract
Aim
Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy (SABR) is used in non-oncologic indications, recently even for cardiac arrhythmias. Thus, aim of this analysis is to review preclinical, early clinical evidences and future direction of the latter new treatment approach.
Method
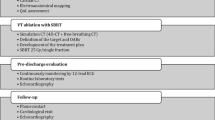
A collection of available data regarding SABR and cardiac arrhythmias was made, by Pubmed research and 2 independent researchers, including preclinical and clinical data. A review of ongoing trials was conducted on ClinicalTrials.gov.
Results
Preclinical research conducted in animal models showed that a safe and effective noninvasive treatment approach for cardiac arrhythmias could be represented by SABR with a median time of response around 2–3 months. The treatment dose plays a crucial role: the atrioventricular node would seem more radiosensitive than the other cardiac electric zones. Clinical data, such as published case series, case reports and early prospective studies, have already suggested the feasibility, efficacy and safety of SABR (25 Gy in one session) for refractory ventricular arrhythmias.
Conclusion
Considering the ongoing trials of SABR and new technological improvements in radiotherapy (e.g. hybrid magnetic resonance) and in arrhythmias noninvasive mapping systems, the future analyses will improve the reliability of those preliminary results.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD et al (2016) ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 37(27):2129–2200
Zecchin M, Severgnini M, Fiorentino A et al (2018) Management of patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIED) undergoing radiotherapy: a consensus document from Associazione Italiana Aritmologia e Cardiostimolazione (AIAC), Associazione Italiana Radioterapia Oncologica (AIRO), Associazione Italiana Fisica Medica (AIFM). Int J Cardiol 15(255):175–183
Ernst S (2017) Catheter ablation: general principles and advances. Card Electrophysiol Clin 9(2):311–317
Romero J, Shivkumar K, Di Biase L et al (2019) Mastering the art of epicardial access in cardiac electrophysiology. Heart Rhythm 16(11):1738–1749
Leksell L (1951) The stereotactic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand 102:316–319
Mazzola R, Fersino S, Alongi P et al (2018) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver oligometastases: predictive factors of local response by 18F-FDG-PET/CT. Br J Radiol 91(1088):20180058
Mazzola R, Fersino S, Aiello D et al (2018) Linac-based stereotactic body radiation therapy for unresectable locally advanced pancreatic cancer: risk-adapted dose prescription and image-guided delivery. Strahlenther Onkol 194(9):835–842
Alongi F, Mazzola R, Fiorentino A et al (2019) Phase II study of accelerated Linac-based SBRT in five consecutive fractions for localized prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 195(2):113–120
Franco P, De Bari B, Ciammella P (2014) The role of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy in oncological and non-oncological clinical settings: highlights from the 7th meeting of AIRO–Young Members Working Group (AIRO Giovani). Tumori 100(6):214–219
Graeff C, Bert C (2018) Noninvasive cardiac arrhythmia ablation with particle beams. Med Phys 45(11):e1024–e1035
Song CW, Cho LC, Yuan J et al (2013) Radiobiology of stereotactic body radiation therapy/stereotactic radiosurgery and the linear-quadratic model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87(1):18–19
Shimohigashi Y, Doi Y, Kouno Y et al (2019) Image quality evaluation of in-treatment four-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography in volumetric-modulated arc therapy for stereotactic body radiation therapy. Phys Med 68:10–16
Constantinescu A, Lehmann H, Packer D, Bert C, Durante M, Graeff C (2016) Treatment planning studies in patient data with scanned carbon ion beams for catheter-free ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 27:335–344
Bert C, Durante M (2011) Motion in radiotherapy: particle therapy. Phys Med Biol 56:R113–R144
Verma V, Mishra MV, Mehta MP (2016) A systematic review of the cost and cost-effectiveness studies of proton radiotherapy. Cancer 122(10):1483–1501
Sharma A, Wong D, Weidlich G et al (2010) Noninvasive stereotactic radiosurgery (CyberHeart) for creation of ablation lesions in the atrium. Heart Rhythm 7(6):802–810
Blanck O, Bode F, Gebhard M et al (2014) Dose-escalation study for cardiac radiosurgery in a porcine model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 89(3):590–598
Bode F, Blanck O, Gebhard M et al (2015) Pulmonary vein isolation by radiosurgery: implications for non-invasive treatment of atrial fibrillation. Europace 17(12):1868–1874
Lehmann HI, Richter D, Prokesch H et al (2015) Atrioventricular node ablation in Langendorff-perfused porcine hearts using carbon ion particle therapy: methods and an in vivo feasibility investigation for catheter-free ablation of cardiac arrhythmias. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 8:429–438
Lehmann HI, Deisher AJ, Takami M et al (2017) External arrhythmia ablation using photon beams: ablation of the atrioventricular junction in an intact animal model. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 10:e004304
Refaat MM, Ballout JA, Zakka P et al (2017) Swine atrioventricular node ablation using stereotactic radiosurgery: methods and in vivo feasibility investigation for catheter-free ablation of cardiac arrhythmias. J Am Heart Assoc 6(11):e007193
Cuculich PS, Schill MR, Kashani R et al (2017) Noninvasive cardiac radiation for ablation of ventricular tachycardia. N Engl J Med 377(24):2325–2336
Loo BW Jr, Soltys SG, Wang L et al (2015) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the treatment of refractory cardiac ventricular arrhythmia. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 8:748–750
Jumeau R, Ozsahin M, Schwitter J et al (2018) Rescue procedure for an electrical storm using robotic non-invasive cardiac radio-ablation. Radiother Oncol 128(2):189–191
Stöhr EJ, Shave RE, Baggish AL, Weiner RB (2016) Left ventricular twist mechanics in the context of normal physiology and cardiovascular disease: a review of studies using speckle tracking echocardiography. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 311(3):H633–H644
Robinson CG, Samson PP, Moore KMS et al (2019) Phase I/II trial of electrophysiology-guided noninvasive cardiac radioablation for ventricular tachycardia. Circulation 139:313–321
Cvek J, Neuwirth R, Knybel L et al (2014) Cardiac radiosurgery for malignant ventricular tachycardia. Cureus 6:e190
Zei PC, Mak R (2019) Noninvasive stereotactic radioablation for ventricular tachycardia ENCORE-VT (EP-guided noninvasive cardiac radioablation): is the sequel as good as the original? Circulation 139:322–324
Cochet H, Komatsu Y, Sacher F, Jadidi AS, Scherr D, Riffaud M, Derval N et al (2013) Integration of merged delayed-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and multidetector computed tomography for the guidance of ventricular tachycardia ablation: a pilot study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 24(4):419–426
Ipsen S, Blanck O, Oborn B et al (2014) Radiotherapy beyond cancer: target localization in real-time MRI and treatment planning for cardiac radiosurgery. Med Phys 41(12):120702
Franzone P, Fiorentino A, Barra S, Cante D, Masini L, Cazzulo E, Todisco L, Gabriele P, Garibaldi E, Merlotti A, Redda MG, Alongi F, Corvò R (2016) Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT): practical recommendations of Italian Association of Radiation Oncology (AIRO). Radiol Med 121(12):958–965
Mayinger M, Kovacs B, Tanadini-Lang S et al (2020) First magnetic resonance imaging-guided cardiac radioablation of sustained ventricular tachycardia. Radiother Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2020.01.008
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiorentino, A., Gregucci, F., Bonaparte, I. et al. Stereotactic Ablative radiation therapy (SABR) for cardiac arrhythmia: A new therapeutic option?. Radiol med 126, 155–162 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01218-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01218-7