Abstract
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a very aggressive and infiltrative brain tumor with a high mortality rate. There are radiomic models with handcrafted features to estimate glioblastoma prognosis. In this work, we evaluate to what extent of combining genomic with radiomic features makes an impact on the prognosis of overall survival (OS) in patients with GBM. We apply a hypercolumn-based convolutional network to segment tumor regions from magnetic resonance images (MRI), extract radiomic features (geometric, shape, histogram), and fuse with gene expression profiling data to predict survival rate for each patient. Several state-of-the-art regression models such as linear regression, support vector machine, and neural network are exploited to conduct prognosis analysis. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset of MRI and gene expression profiling is used in the study to observe the model performance in radiomic, genomic, and radiogenomic features. The results demonstrate that genomic data are correlated with the GBM OS prediction, and the radiogenomic model outperforms both radiomic and genomic models. We further illustrate the most significant genes, such as IL1B, KLHL4, ATP1A2, IQGAP2, and TMSL8, which contribute highly to prognosis analysis.

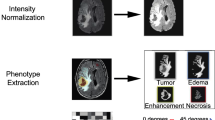
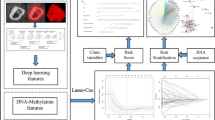
Our Proposed fully automated "Radiogenomic"" approach for survival prediction overview. It fuses geometric, intensity, volumetric, genomic and clinical information to predict OS.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alex V, Safwan M, Krishnamurthi G (2017) Automatic segmentation and overall survival prediction in gliomas using fully convolutional neural network and texture analysis. In: International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop. Springer, pp 216–225
Bai Y, Zhang QG, Wang XH (2014) Downregulation of tes by hypermethylation in glioblastoma reduces cell apoptosis and predicts poor clinical outcome. European Journal of Medical Research 19(1):66
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby J, Freymann J, Farahani K, Davatzikos C (2017) Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the tcga-gbm collection. The Cancer Imaging Archive, pp 286
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby JS, Freymann JB, Farahani K, Davatzikos C (2017) Advancing the cancer genome atlas glioma mri collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Scientific Data 4:170117
Bansal A, Chen X, Russell B, Gupta A, Ramanan D (2017) Pixelnet: Representation of the pixels, by the pixels, and for the pixels. arXiv:170206506
Bauer S, Wiest R, Nolte LP, Reyes M (2013) A survey of mri-based medical image analysis for brain tumor studies. Physics in Medicine & Biology 58(13):R97
Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O (2016) 3d u-net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, pp 424–432
DeCarlo LT (1997) On the meaning and use of kurtosis. Psychological Methods 2(3):292
Diehn M, Nardini C, Wang DS, McGovern S, Jayaraman M, Liang Y, Aldape K, Cha S, Kuo MD (2008) Identification of noninvasive imaging surrogates for brain tumor gene-expression modules. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(13):5213–5218
Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup NE, Kruchko C (2012) Cbtrus statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005–2009. Neuro-oncology 14(suppl_5):v1–v49
Ellingson BM (2015) Radiogenomics and imaging phenotypes in glioblastoma: novel observations and correlation with molecular characteristics. Curr Neurol Neurosci Reports 15(1): 506
Farag A, Ali A, Graham J, Farag A, Elshazly S, Falk R (2011) Evaluation of geometric feature descriptors for detection and classification of lung nodules in low dose ct scans of the chest. In: 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: from nano to macro. IEEE, Piscataway, pp 169– 172
Gevaert O, Mitchell LA, Achrol AS, Xu J, Echegaray S, Steinberg GK, Cheshier SH, Napel S, Zaharchuk G, Plevritis SK (2014) Glioblastoma multiforme: exploratory radiogenomic analysis by using quantitative image features. Radiology 273(1):168– 174
Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, Vapnik V (2002) Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Machine Learning 46(1-3):389–422
Hammoud MA, Sawaya R, Shi W, Thall PF, Leeds NE (1996) Prognostic significance of preoperative mri scans in glioblastoma multiforme. J Neuro-oncology 27(1):65–73
Islam M, Ren H (2017) Multi-modal pixelnet for brain tumor segmentation. In: International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop. Springer, New York, pp 298–308
Islam M, Jose VJM, Ren H (2018) Glioma prognosis: Segmentation of the tumor and survival prediction using shape, geometric and clinical information. In: International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop. Springer, New York, pp 142–153
Islam M, Li Y, Ren H (2019) Learning where to look while tracking instruments in robot-assisted surgery. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, New York, pp 412–420
Jungo A, McKinley R, Meier R, Knecht U, Vera L, Pérez-Beteta J, Molina-García D, Pérez-García VM, Wiest R, Reyes M (2017) Towards uncertainty-assisted brain tumor segmentation and survival prediction. In: International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop. Springer, New York, pp 474–485
Kim YW, Koul D, Kim SH, Lucio-Eterovic AK, Freire PR, Yao J, Wang J, Almeida JS, Aldape K, Yung WA (2013) Identification of prognostic gene signatures of glioblastoma: a study based on tcga data analysis. Neuro-oncology 15(7):829– 839
Ko C, Sohn G, Remmel TK (2013) Tree genera classification with geometric features from high-density airborne lidar. Can J Remote Sens 39(sup1):S73–S85
Lacroix M, Abi Said D, Fourney DR, Gokaslan ZL, Shi W, DeMonte F, Lang FF, McCutcheon IE, Hassenbusch SJ, Holland E et al (2001) A multivariate analysis of 416 patients with glioblastoma multiforme: prognosis, extent of resection, and survival. J Neurosurg 95(2):190–198
Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, van Stiphout RG, Granton P, Zegers CM, Gillies R, Boellard R, Dekker A et al (2012) Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Europ J Cancer 48(4):441–446
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3431–3440
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Farahani K, Kirby J, Burren Y, Porz N, Slotboom J, Wiest R et al (2015) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (brats). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(10):1993
Nadeau C, Ren H, Krupa A, Dupont PE (2015) Intensity-based visual servoing for instrument and tissue tracking in 3d ultrasound volumes. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 12(1):367–371. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2014.2343652
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2005) Epidemiology and etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathologica 109(1):93–108
Osman AF (2017) Automated brain tumor segmentation on magnetic resonance images and patient’s overall survival prediction using support vector machines. In: International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop. Springer, New York, pp 435– 449
Paszke A, Gross S, Chintala S, Chanan G, Yang E, DeVito Z, Lin Z, Desmaison A, Antiga L, Lerer A (2017) Automatic differentiation in pytorch. In: NIPS-W
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V, Vanderplas J, Passos A, Cournapeau D, Brucher M, Perrot M, Duchesnay E (2011) Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J Mach Learn. Res 12:2825–2830
Ren H, Vasilyev NV, Dupont PE (2011) Detection of curved robots using 3d ultrasound. In: IROS 2011, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2011.6094915, pp 2083– 2089
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, New York, pp 234–241
Saffari SE, Löve Á, Fredrikson M, Smedby Ö (2015) Regression models for analyzing radiological visual grading studies–an empirical comparison. BMC Med Imaging 15(1):49
Shboul ZA, Vidyaratne L, Alam M, Iftekharuddin KM (2017) Glioblastoma and survival prediction. In: International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop. Springer, New York, pp 358– 368
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:14091556
Srinivasan VB, Islam M, Zhang W, Ren H (2018) Finger movement classification from myoelectric signals using convolutional neural networks. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics(ROBIO). IEEE, Piscataway, pp 1070–1075
Tarassishin L, Casper D, Lee SC (2014) Aberrant expression of interleukin-1β and inflammasome activation in human malignant gliomas. PloS one 9(7)
Theiler J (1990) Estimating fractal dimension. JOSA A 7(6):1055–1073
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V, Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, Miller CR, Ding L, Golub T, Mesirov JP et al (2010) Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in pdgfra, idh1, egfr, and nf1. Cancer Cell 17(1):98–110
Yang D, Rao G, Martinez J, Veeraraghavan A, Rao A (2015) Evaluation of tumor-derived mri-texture features for discrimination of molecular subtypes and prediction of 12-month survival status in glioblastoma. Med Phys 42(11):6725–6735
Funding
This work is supported by the Singapore Academic Research Fund under Grant R-397-000-297-114, and NMRC Bedside and Bench under grant R-397-000-245-511 awarded to Dr. Hongliang Ren.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Initial 25 features selected for survival analysis:
-
Centroid coordinates of enhancement region
-
BBOX1
-
LRAP
-
TMSL8
-
CAV2
-
KLHL4
-
TUBA4A
-
PCDH9
-
SLC38A1
-
TSPAN13
-
IQGAP2
-
GBAS
-
RSAD2
-
MEST
-
ASPN
-
PLP1
-
C8orf4
-
RBP1
-
MOBKL2B
-
ECT2
-
IL1B
-
RPL39L
-
TES
-
ATP1A2
-
DDIT3
Initial 25 features selected for survival analysis:
-
Fractal dimensions of enhancement region
-
Centroid coordiantes of enhancement region
-
Second axis length of necrosis
-
BBOX1
-
LRAP
-
TMSL8
-
ALDH1L1
-
SCG2
-
PALMD
-
CAV2
-
MAPK4
-
KLHL4
-
COL3A1
-
DIRAS3
-
TUBA4A
-
GSTM3
-
PCDH9
-
SLC38A1
-
ARL4A
-
TSPAN13
-
EDNRA
-
NEFL
-
LIMS1
-
D4S234E
-
GABBR2
-
IQGAP2
-
RND3
-
GBAS
-
RSAD2
-
MEST
-
EYA4
-
ATP10B
-
C1QTNF3
-
ASPN
-
DCN
-
PLP1
-
C8orf4
-
RBP1
-
MOBKL2B
-
ECT2
-
GPC4
-
IL1B
-
RPL39L
-
REV3L
-
CCL20
-
TES
-
ECM2
-
DDIT3
-
FAM46A
Most important 33 features features contributed for survival analysis:
-
Fractal dimensions of enhancement region
-
Second axis length of necrosis
-
BBOX1
-
LRAP
-
TMSL8
-
CAV2
-
ALDH1L1
-
SCG2
-
PALMD
-
KLHL4
-
TUBA4A
-
PCDH9
-
SLC38A1
-
TSPAN13
-
IQGAP2
-
GBAS
-
Centroid coordinates of enhancement region
-
RSAD2
-
MEST
-
GABBR2
-
ASPN
-
PLP1
-
C8orf4
-
RBP1
-
MOBKL2B
-
ECT2
-
IL1B
-
RPL39L
-
TES
-
ATP1A2
-
DDIT3
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wijethilake, N., Islam, M. & Ren, H. Radiogenomics model for overall survival prediction of glioblastoma. Med Biol Eng Comput 58, 1767–1777 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-020-02179-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-020-02179-9