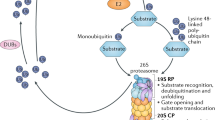
Abstract
Background
The 26S proteasome is at the heart of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, which is the key cellular pathway for the regulated degradation of proteins and enforcement of protein quality control. The 26S proteasome is an unusually large and complicated protease comprising a 28-subunit core particle (CP) capped by one or two 19-subunit regulatory particles (RP). Multiple activities within the RP process incoming ubiquitinated substrates for eventual degradation by the barrel-shaped CP. The large size and elaborate architecture of the proteasome have made it an exceptional model for understanding mechanistic themes in macromolecular assembly.
Objective
In the present work, we highlight the most recent mechanistic insights into proteasome assembly, with particular emphasis on intrinsic and extrinsic factors regulating proteasome biogenesis. We also describe new and exciting questions arising about how proteasome assembly is regulated and deregulated in normal and diseased cells.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search using the PubMed search engine was performed, and key findings yielding mechanistic insight into proteasome assembly were included in this review.
Results
Key recent studies have revealed that proteasome biogenesis is dependent upon intrinsic features of the subunits themselves as well as extrinsic factors, many of which function as dedicated chaperones.
Conclusion
Cells rely on a diverse set of mechanistic strategies to ensure the rapid, efficient, and faithful assembly of proteasomes from their cognate subunits. Importantly, physiological as well as pathological changes to proteasome assembly are emerging as exciting paradigms to alter protein degradation in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A K, Xing C, De Martino G N, Mizrachi D, Hernandez M D, Sousa A B, Martínez de Villarreal L, dos Santos H G, Garg A (2010). PSMB8 encoding the beta5i proteasome subunit is mutated in joint contractures, muscle atrophy, microcytic anemia, and panniculitisinduced lipodystrophy syndrome. Am J Hum Genet, 87(6): 866–872
Akahane T, Sahara K, Yashiroda H, Tanaka K, Murata S (2013). Involvement of Bag6 and the TRC pathway in proteasome assembly. Nat Commun, 4: 2234
Arendt C S, Hochstrasser M (1997). Identification of the yeast 20S proteasome catalytic centers and subunit interactions required for active-site formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94(14): 7156–7161
Arendt C S, Hochstrasser M (1999). Eukaryotic 20S proteasome catalytic subunit propeptides prevent active site inactivation by Nterminal acetylation and promote particle assembly. EMBO J, 18(13): 3575–3585
Arima K, Kinoshita A, Mishima H, Kanazawa N, Kaneko T, Mizushima T, Ichinose K, Nakamura H, Tsujino A, Kawakami A, Matsunaka M, Kasagi S, Kawano S, Kumagai S, Ohmura K, Mimori T, Hirano M, Ueno S, Tanaka K, Tanaka M, Toyoshima I, Sugino H, Yamakawa A, Tanaka K, Niikawa N, Furukawa F, Murata S, Eguchi K, Ida H, Yoshiura K (2011). Proteasome assembly defect due to a proteasome subunit beta type 8 (PSMB8) mutation causes the autoinflammatory disorder, Nakajo-Nishimura syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108(36): 14914–14919
Asano S, Fukuda Y, Beck F, Aufderheide A, Forster F, Danev R, Baumeister W (2015). Proteasomes. A molecular census of 26S proteasomes in intact neurons. Science, 347(6220): 439–442
Aufderheide A, Beck F, Stengel F, Hartwig M, Schweitzer A, Pfeifer G, Goldberg A L, Sakata E, Baumeister W, Förster F (2015). Structural characterization of the interaction of Ubp6 with the 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 112(28): 8626–8631
Bader M, Benjamin S, Wapinski O L, Smith D M, Goldberg A L, Steller H (2011). A conserved f box regulatory complex controls proteasome activity in Drosophila. Cell, 145(3): 371–382
Bai M, Zhao X, Sahara K, Ohte Y, Hirano Y, Kaneko T, Yashiroda H, Murata S (2014). Assembly mechanisms of specialized core particles of the proteasome. Biomolecules, 4(3): 662–677
Barrault M B, Richet N, Godard C, Murciano B, Le Tallec B, Rousseau E, Legrand P, Charbonnier J B, Le Du M H, Guerois R, Ochsenbein F, Peyroche A (2012). Dual functions of the Hsm3 protein in chaperoning and scaffolding regulatory particle subunits during the proteasome assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109(17): E1001–E1010
Barthelme D, Chen J Z, Grabenstatter J, Baker T A, Sauer R T (2014). Architecture and assembly of the archaeal Cdc48 20S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 111(17): E1687–E1694
Barthelme D, Jauregui R, Sauer RT (2015). An ALS disease mutation in Cdc48/p97 impairs 20S proteasome binding and proteolytic communication. Protein Sci, 24:1521–1527
Barthelme D, Sauer R T (2012a). Identification of the Cdc48 20S proteasome as an ancient AAA + proteolytic machine. Science, 337(6096): 843–846
Barthelme D, Sauer RT (2012b). Identification of the Cdc48 20S proteasome as an ancient AAA + proteolytic machine. Science, 337(6096): 843–846
Barthelme D, Sauer R T (2013). Bipartite determinants mediate an evolutionarily conserved interaction between Cdc48 and the 20S peptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 110(9): 3327–3332
Bashore C, Dambacher CM, Goodall E A, Matyskiela ME, Lander G C, Martin A (2015). Ubp6 deubiquitinase controls conformational dynamics and substrate degradation of the 26S proteasome. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 22(9): 712–719
Basler M, Kirk C J, Groettrup M (2013). The immunoproteasome in antigen processing and other immunological functions. Curr Opin Immunol, 25(1): 74–80
Beck F, Unverdorben P, Bohn S, Schweitzer A, Pfeifer G, Sakata E, Nickell S, Plitzko J M, Villa E, Baumeister W, Forster F (2012). Near-atomic resolution structural model of the yeast 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109(37): 14870–14875
Beckwith R, Estrin E, Worden E J, Martin A (2013). Reconstitution of the 26S proteasome reveals functional asymmetries in its AAA + unfoldase. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 20(10): 1164–1172
Benaroudj N, Goldberg A L (2000). PAN, the proteasome-activating nucleotidase from archaebacteria, is a protein-unfolding molecular chaperone. Nat Cell Biol, 2(11): 833–839
Braun B C, Glickman M, Kraft R, Dahlmann B, Kloetzel P M, Finley D, Schmidt M (1999). The base of the proteasome regulatory particle exhibits chaperone-like activity. Nat Cell Biol, 1(4): 221–226
Burri L, Hockendorff J, Boehm U, Klamp T, Dohmen R J, Levy F (2000). Identification and characterization of a mammalian protein interacting with 20S proteasome precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 97(19): 10348–10353
Cascio P (2014). PA28alphabeta: the enigmatic magic ring of the proteasome? Biomolecules, 4(2): 566–584
Chen P, Hochstrasser M (1996). Autocatalytic subunit processing couples active site formation in the 20S proteasome to completion of assembly. Cell, 86(6): 961–972
Chu-Ping M, Slaughter C A, De Martino G N (1992). Purification and characterization of a protein inhibitor of the 20S proteasome (macropain). Biochim Biophys Acta, 1119(3): 303–311
Cohen-Kaplan V, Livneh I, Avni N, Fabre B, Ziv T, Kwon Y T, Ciechanover A (2016). p62- and ubiquitin-dependent stress-induced autophagy of the mammalian 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 113(47): E7490–E7499
Colot H V, Park G, Turner G E, Ringelberg C, Crew C M, Litvinkova L, Weiss R L, Borkovich K A, Dunlap J C (2006). A high-throughput gene knockout procedure for Neurospora reveals functions for multiple transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103(27): 10352–10357
da Fonseca P C, He J, Morris E P (2012). Molecular Model of the Human 26S Proteasome. Mol Cell, 46(1): 54–66
Dahlqvist J, Klar J, Tiwari N, Schuster J, Törmä H, Badhai J, Pujol R, van Steensel M A M, Brinkhuizen T, Gijezen L, Chaves A, Tadini G, Vahlquist A, Dahl N (2010). A single-nucleotide deletion in the POMP 5' UTR causes a transcriptional switch and altered epidermal proteasome distribution in KLICK genodermatosis. Am J Hum Genet, 86(4): 596–603
Dambacher C M, Worden E J, Herzik M A, Martin A, Lander G C (2016). Atomic structure of the 26S proteasome lid reveals the mechanism of deubiquitinase inhibition. eLife, 5: e13027
Dange T, Smith D, Noy T, Rommel P C, Jurzitza L, Cordero R J B, Legendre A, Finley D, Goldberg A L, Schmidt M (2011). Blm10 protein promotes proteasomal substrate turnover by an active gating mechanism. J Biol Chem, 286(50): 42830–42839
De M, Jayarapu K, Elenich L, Monaco J J, Colbert R A, Griffin T A (2003). Beta 2 subunit propeptides influence cooperative proteasome assembly. J Biol Chem, 278(8): 6153–6159
De La Mota-Peynado A, Lee S Y, Pierce B M, Wani P, Singh C R, Roelofs J (2013). The proteasome-associated protein Ecm29 inhibits proteasomal ATPase activity and in vivo protein degradation by the proteasome. J Biol Chem, 288(41): 29467–29481
De Martino G N, Proske R J, Moomaw C R, Strong A A, Song X, Hisamatsu H, Tanaka K, Slaughter C A (1996). Identification, purification, and characterization of a PA700-dependent activator of the proteasome. J Biol Chem, 271(6): 3112–3118
Ding W X, Ni H M, Gao W, Yoshimori T, Stolz D B, Ron D, Yin X M (2007). Linking of autophagy to ubiquitin-proteasome system is important for the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and cell viability. Am J Pathol, 171(2): 513–524
Driscoll J, Brown M G, Finley D, Monaco J J (1993). MHC-linked LMP gene products specifically alter peptidase activities of the proteasome. Nature, 365(6443): 262–264
Enenkel C, Lehmann A, Kloetzel PM (1998). Subcellular distribution of proteasomes implicates a major location of protein degradation in the nuclear envelope-ER network in yeast. EMBO J, 17(21): 6144–6154
Estrin E, Lopez-Blanco J R, Chacon P, Martin A (2013). Formation of an Intricate Helical Bundle Dictates the Assembly of the 26S Proteasome Lid. Structure, 21(9): 1624–1635
Fehlker M, Wendler P, Lehmann A, Enenkel C (2003). Blm3 is part of nascent proteasomes and is involved in a late stage of nuclear proteasome assembly. EMBO Rep, 4(10): 959–963
Finley D (2009). Recognition and processing of ubiquitin-protein conjugates by the proteasome. Annu Rev Biochem, 78(1): 477–513
Forouzan D, Ammelburg M, Hobel C F, Stroh L J, Sessler N, Martin J, Lupas A N (2012). The archaeal proteasome is regulated by a network of AAA ATPases. J Biol Chem, 287(46): 39254–39262
Forster A, Masters E I, Whitby F G, Robinson H, Hill C P (2005). The 1.9 A structure of a proteasome-11S activator complex and implications for proteasome-PAN/PA700 interactions. Mol Cell, 18(5): 589–599
Fort P, Kajava A V, Delsuc F, Coux O (2015). Evolution of proteasome regulators in eukaryotes. Genome Biol Evol, 7(5): 1363–1379
Frentzel S, Pesold-Hurt B, Seelig A, Kloetzel P M (1994). 20 S proteasomes are assembled via distinct precursor complexes. Processing of LMP2 and LMP7 proproteins takes place in 13–16 S preproteasome complexes. J Mol Biol, 236(4): 975–981
Fricke B, Heink S, Steffen J, Kloetzel P M, Kruger E (2007). The proteasome maturation protein POMP facilitates major steps of 20S proteasome formation at the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO Rep, 8(12): 1170–1175
Fukunaga K, Kudo T, Toh-e A, Tanaka K, Saeki Y (2010). Dissection of the assembly pathway of the proteasome lid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 396(4): 1048–1053
Funakoshi M, Tomko R J, Kobayashi H, Hochstrasser M (2009). Multiple assembly chaperones govern biogenesis of the proteasome regulatory particle base. Cell, 137(5): 887–899
Gaczynska M, Rock K L, Goldberg A L (1993). Gamma-interferon and expression of MHC genes regulate peptide hydrolysis by proteasomes. Nature, 365(6443): 264–267
Gerards W L, Enzlin J, Häner M, Hendriks ILA M, Aebi U, Bloemendal H, Boelens W (1997). The human alpha-type proteasomal subunit HsC8 forms a double ringlike structure, but does not assemble into proteasome-like particles with the beta-type subunits HsDelta or HsBPROS26. J Biol Chem, 272(15): 10080–10086
Gerards W L, de Jong W W, Bloemendal H, Boelens W (1998). The human proteasomal subunit HsC8 induces ring formation of other alpha-type subunits. J Mol Biol, 275(1): 113–121
Ghaemmaghami S, Huh W K, Bower K, Howson R W, Belle A, Dephoure N, O’Shea E K, Weissman J S (2003). Global analysis of protein expression in yeast. Nature, 425(6959): 737–741
Gille C, Goede A, Schlöetelburg C, Preißner R, Kloetzel P M, Göbel U B, Frömmel C (2003). A comprehensive view on proteasomal sequences: implications for the evolution of the proteasome. J Mol Biol, 326(5): 1437–1448
Gillette T G, Kumar B, Thompson D, Slaughter C A, De Martino G N (2008). Differential roles of the COOH termini of AAA subunits of PA700 (19 S regulator) in asymmetric assembly and activation of the 26 S proteasome. J Biol Chem, 283(46): 31813–31822
Gomes A V (2013). Genetics of proteasome diseases. Scientifica (Cairo), 2013: 637629
Gragnoli C, Cronsell J (2007). PSMD9 gene variants within NIDDM2 may rarely contribute to type 2 diabetes. J Cell Physiol, 212(3): 568–571
Griffin T A, Nandi D, Cruz M, Fehling H J, Kaer L V, Monaco J J, Colbert R A (1998). Immunoproteasome assembly: cooperative incorporation of interferon gamma (IFN-gamma)-inducible subunits. J Exp Med, 187(1): 97–104
Griffin T A, Slack J P, McCluskey T S, Monaco J J, Colbert R A (2000). Identification of proteassemblin, a mammalian homologue of the yeast protein, Ump1p, that is required for normal proteasome assembly. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun, 3(4): 212–217
Groettrup M, Standera S, Stohwasser R, Kloetzel P M (1997). The subunits MECL-1 and LMP2 are mutually required for incorporation into the 20S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94(17): 8970–8975
Groll M, Brandstetter H, Bartunik H, Bourenkow G, Huber R (2003). Investigations on the maturation and regulation of archaebacterial proteasomes. J Mol Biol, 327(1): 75–83
Groll M, Ditzel L, Löwe J, Stock D, Bochtler M, Bartunik H D, Huber R (1997). Structure of 20S proteasome from yeast at 2.4 A resolution. Nature, 386(6624): 463–471
Groll M, Glickman M H, Finley D, Bajorek M, Köhler A, Moroder L, Rubin D M, Huber R (2000). A gated channel into the proteasome core particle. Nat Struct Biol, 7(11): 1062–1067
Groll M, Heinemeyer W, Jager S, Ullrich T, Bochtler M, Wolf D H, Huber R (1999). The catalytic sites of 20S proteasomes and their role in subunit maturation: a mutational and crystallographic study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 96(20): 10976–10983
Haarer B, Aggeli D, Viggiano S, Burke D J, Amberg D C (2011). Novel interactions between actin and the proteasome revealed by complex haploinsufficiency. PLoS Genet, 7(9): e1002288
Hanssum A, Zhong Z, Rousseau A, Krzyzosiak A, Sigurdardottir A, Bertolotti A (2014). An inducible chaperone adapts proteasome assembly to stress. Mol Cell, 55(4): 566–577
Hatanaka A, Chen B, Sun J Q, Mano Y, Funakoshi M, Kobayashi H, Ju Y, Mizutani T, Shinmyozu K, Nakayama J, Miyamoto K, Uchida H, Oki M (2011). Fub1p, a novel protein isolated by boundary screening, binds the proteasome complex. Genes Genet Syst, 86(5): 305–314
Heinemeyer W, Fischer M, Krimmer T, Stachon U, Wolf D H (1997). The active sites of the eukaryotic 20 S proteasome and their involvement in subunit precursor processing. J Biol Chem, 272(40): 25200–25209
Heink S, Ludwig D, Kloetzel P M, Kruger E (2005). IFN-gammainduced immune adaptation of the proteasome system is an accelerated and transient response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102(26): 9241–9246
Hirano Y, Hayashi H, Iemura S, Hendil K B, Niwa S, Kishimoto T, Kasahara M, Natsume T, Tanaka K, Murata S (2006). Cooperation of multiple chaperones required for the assembly of mammalian 20S proteasomes. Mol Cell, 24(6): 977–984
Hirano Y, Hendil K B, Yashiroda H, Iemura S, Nagane R, Hioki Y, Natsume T, Tanaka K, Murata S (2005). A heterodimeric complex that promotes the assembly of mammalian 20S proteasomes. Nature, 437(7063): 1381–1385
Hirano Y, Kaneko T, Okamoto K, Bai M, Yashiroda H, Furuyama K, Kato K, Tanaka K, Murata S (2008). Dissecting beta-ring assembly pathway of the mammalian 20S proteasome. EMBO J, 27(16): 2204–2213
Hoang B, Benavides A, Shi Y, Frost P, Lichtenstein A (2009). Effect of autophagy on multiple myeloma cell viability. Mol Cancer Ther, 8(7): 1974–1984
Hoefer M M, Boneberg E M, Grotegut S, Kusch J, Illges H (2006). Possible tetramerisation of the proteasome maturation factor POMP/ proteassemblin/hUmp1 and its subcellular localisation. Int J Biol Macromol, 38(3-5): 259–267
Huang X, Luan B, Wu J, Shi Y (2016). An atomic structure of the human 26S proteasome. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 23(9): 778–785
Huber E M, Heinemeyer W, Li X, Arendt C S, Hochstrasser M, Groll M (2016). A unified mechanism for proteolysis and autocatalytic activation in the 20S proteasome. Nat Commun, 7: 10900
Huh WK, Falvo J V, Gerke L C, Carroll A S, Howson RW, Weissman J S, O’Shea E K (2003). Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature, 425(6959): 686–691
Ishii K, Noda M, Yagi H, Thammaporn R, Seetaha S, Satoh T, Kato K, Uchiyama S (2015). Disassembly of the self-assembled, double-ring structure of proteasome alpha7 homo-tetradecamer by alpha6. Sci Rep, 5: 18167
Isono E, Nishihara K, Saeki Y, Yashiroda H, Kamata N, Ge L, Ueda T, Kikuchi Y, Tanaka K, Nakano A, Toh-e A (2007). The assembly pathway of the 19S regulatory particle of the yeast 26S proteasome. Mol Biol Cell, 18(2): 569–580
Iwata A, Riley B E, Johnston J A, Kopito R R (2005). HDAC6 and microtubules are required for autophagic degradation of aggregated huntingtin. J Biol Chem, 280(48): 40282–40292
Jager S, Groll M, Huber R, Wolf D H, Heinemeyer W (1999). Proteasome beta-type subunits: unequal roles of propeptides in core particle maturation and a hierarchy of active site function. J Mol Biol, 291(4): 997–1013
Ju D, Xie Y (2004). Proteasomal degradation of RPN4 via two distinct mechanisms, ubiquitin-dependent and-independent. J Biol Chem, 279(23): 23851–23854
Kaganovich D, Kopito R, Frydman J (2008). Misfolded proteins partition between two distinct quality control compartments. Nature, 454(7208): 1088–1095
Kaneko T, Hamazaki J, Iemura S, Sasaki K, Furuyama K, Natsume T, Tanaka K, Murata S (2009). Assembly pathway of the Mammalian proteasome base subcomplex is mediated by multiple specific chaperones. Cell, 137(5): 914–925
Kim D U, Hayles J, Kim D, Wood V, Park H O, Won M, Yoo H S, Duhig T, Nam M, Palmer G, Han S, Jeffery L, Baek S T, Lee H, Shim Y S, Lee M, Kim L, Heo K S, Noh E J, Lee A R, Jang Y J, Chung K S, Choi S J, Park J Y, Park Y, Kim H M, Park S K, Park H J, Kang E J, Kim H B, Kang H S, Park H M, Kim K, Song K, Song K B, Nurse P, Hoe K L (2010a). Analysis of a genome-wide set of gene deletions in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nat Biotechnol, 28(6): 617–623
Kim S, Saeki Y, Fukunaga K, Suzuki A, Takagi K, Yamane T, Tanaka K, Mizushima T, Kato K (2010b). Crystal structure of yeast rpn14, a chaperone of the 19 S regulatory particle of the proteasome. J Biol Chem, 285(20): 15159–15166
Kim Y C, Snoberger A, Schupp J, Smith D M (2015). ATP binding to neighbouring subunits and intersubunit allosteric coupling underlie proteasomal ATPase function. Nat Commun, 6(8520):1
Kingsbury D J, Griffin T A, Colbert R A (2000). Novel propeptide function in 20 S proteasome assembly influences beta subunit composition. J Biol Chem, 275(31): 24156–24162
Kleijnen M F, Roelofs J, Park S, Hathaway N A, Glickman M, King R W, Finley D (2007). Stability of the proteasome can be regulated allosterically through engagement of its proteolytic active sites. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 14(12): 1180–1188
Kloetzel P M (2004). Generation of major histocompatibility complex class I antigens: functional interplay between proteasomes and TPPII. Nat Immunol, 5(7): 661–669
Kock M, NunesMM, Hemann M, Kube S, Jürgen Dohmen R, Herzog F, Ramos P C, Wendler P (2015). Proteasome assembly from 15S precursors involves major conformational changes and recycling of the Pba1-Pba2 chaperone. Nat Commun, 6: 6123
Koizumi S, Irie T, Hirayama S, Sakurai Y, Yashiroda H, Naguro I, Ichijo H, Hamazaki J, Murata S (2016). The aspartyl protease DDI2 activates Nrf1 to compensate for proteasome dysfunction. eLife, 5: e18357
Kragelund B B, Schenstrom S M, Rebula C A, Panse V G, Hartmann-Petersen R (2016). DSS1/Sem1, a multifunctional and intrinsically disordered protein. Trends Biochem Sci, 41(5): 446–459
Kriegenburg F, Seeger M, Saeki Y, Tanaka K, Lauridsen A M B, Hartmann-Petersen R, Hendil K B (2008). Mammalian 26S proteasomes remain intact during protein degradation. Cell, 135(2): 355–365
Kulak N A, Pichler G, Paron I, Nagaraj N, Mann M (2014). Minimal, encapsulated proteomic-sample processing applied to copy-number estimation in eukaryotic cells. Nat Methods, 11(3): 319–324
Kusmierczyk A R, Hochstrasser M (2008). Some assembly required: dedicated chaperones in eukaryotic proteasome biogenesis. Biol Chem, 389(9): 1143–1151
Kusmierczyk A R, Kunjappu MJ, Funakoshi M, HochstrasserM(2008). A multimeric assembly factor controls the formation of alternative 20S proteasomes. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 15(3): 237–244
Kusmierczyk A R, Kunjappu M J, Kim R Y, Hochstrasser M (2011). A conserved 20S proteasome assembly factor requires a C-terminal HbYX motif for proteasomal precursor binding. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 18(5): 622–629
Kwon Y D, Nagy I, Adams P D, Baumeister W, Jap B K (2004a). Crystal structures of the Rhodococcus proteasome with and without its propeptides: implications for the role of the pro-peptide in proteasome assembly. J Mol Biol, 335(1): 233–245
Kwon Y D, Nagy I, Adams P D, Baumeister W, Jap B K (2004b). Crystal structures of the Rhodococcus proteasome with and without its pro-peptides: implications for the role of the pro-peptide in proteasome assembly. J Mol Biol, 335(1): 233–245
Lander G C, Estrin E, Matyskiela M E, Bashore C, Nogales E, Martin A (2012). Complete subunit architecture of the proteasome regulatory particle. Nature, 482: 186–191
Lasker K, Forster F, Bohn S, Walzthoeni T, Villa E, Unverdorben P, Beck F, Aebersold R, Sali A, Baumeister W (2012). Molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome holocomplex determined by an integrative approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109(5): 1380–1387
Le Tallec B, Barrault M B, Courbeyrette R, Guerois R, Marsolier-Kergoat M C, Peyroche A (2007). 20S proteasome assembly is orchestrated by two distinct pairs of chaperones in yeast and in mammals. Mol Cell, 27(4): 660–674
Le Tallec B, Barrault M B, Guerois R, Carre T, Peyroche A (2009). Hsm3/S5b participates in the assembly pathway of the 19S regulatory particle of the proteasome. Mol Cell, 33(3): 389–399
Lee S C, Shaw B D (2007). A novel interaction between Nmyristoylation and the 26S proteasome during cell morphogenesis. Mol Microbiol, 63(4): 1039–1053
Lee S Y, De la Mota-Peynado A, Roelofs J (2011). Loss of Rpt5 protein interactions with the core particle and Nas2 protein causes the formation of faulty proteasomes that are inhibited by Ecm29 protein. J Biol Chem, 286(42): 36641–36651
Leggett D S, Hanna J, Borodovsky A, Crosas B, Schmidt M, Baker R T, Walz T, Ploegh H, Finley D (2002). Multiple associated proteins regulate proteasome structure and function. Mol Cell, 10(3): 495–507
Lehmann A, Janek K, Braun B, Kloetzel P M, Enenkel C (2002). 20 S proteasomes are imported as precursor complexes into the nucleus of yeast. J Mol Biol, 317(3): 401–413
Lehmann A, Niewienda A, Jechow K, Janek K, Enenkel C (2010). Ecm29 fulfils quality control functions in proteasome assembly. Mol Cell, 38(6): 879–888
Lehrbach N J, Ruvkun G (2016). Proteasome dysfunction triggers activation of SKN-1A/Nrf1 by the aspartic protease DDI-1. eLife, 5: e17721
Lek M, Karczewski K J, Minikel E V, Samocha K E, Banks E, Fennell T, O’Donnell-Luria A H, Ware J S, Hill A J, Cummings B B, Tukiainen T, Birnbaum D P, Kosmicki J A, Duncan L E, Estrada K, Zhao F, Zou J, Pierce-Hoffman E, Berghout J, Cooper D N, Deflaux N, De Pristo M, Do R, Flannick J, Fromer M, Gauthier L, Goldstein J, Gupta N, Howrigan D, Kiezun A, Kurki M I, Moonshine A L, Natarajan P, Orozco L, Peloso G M, Poplin R, Rivas M A, Ruano-Rubio V, Rose S A, Ruderfer D M, Shakir K, Stenson P D, Stevens C, Thomas B P, Tiao G, Tusie-Luna M T, Weisburd B, Won H H, Yu D, Altshuler D M, Ardissino D, Boehnke M, Danesh J, Donnelly S, Elosua R, Florez J C, Gabriel S B, Getz G, Glatt S J, Hultman C M, Kathiresan S, Laakso M, McCarroll S, McCarthy M I, McGovern D, McPherson R, Neale BM, Palotie A, Purcell SM, Saleheen D, Scharf J M, Sklar P, Sullivan P F, Tuomilehto J, Tsuang M T, Watkins H C, Wilson J G, Daly M J, MacArthur D G (2016). Analysis of proteincoding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature, 536(7616): 285–291
Li D, Dong Q, Tao Q, Gu J, Cui Y, Jiang X, Yuan J, Li W, Xu R, Jin Y, Li P, Weaver D T, Ma Q, Liu X, Cao C (2015). c-Abl regulates proteasome abundance by controlling the ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation of PSMA7 subunit. Cell Reports, 10(4): 484–496
Li J, Zou C, Bai Y, Wazer D E, Band V, Gao Q (2006). DSS1 is required for the stability of BRCA2. Oncogene, 25(8): 1186–1194
Li X, Kusmierczyk A R, Wong P, Emili A, Hochstrasser M (2007). beta- Subunit appendages promote 20S proteasome assembly by overcoming an Ump1-dependent checkpoint. EMBO J, 26(9): 2339–2349
Li X, Li Y, Arendt C S, Hochstrasser M (2016). Distinct elements in the proteasomal beta5 subunit propeptide required for autocatalytic processing and proteasome assembly. J Biol Chem, 291(4): 1991–2003
Li X, Thompson D, Kumar B, De Martino G N (2014). Molecular and cellular roles of PI31 (PSMF1) protein in regulation of proteasome function. J Biol Chem, 289(25): 17392–17405
Liu J, Yuan X, Liu J, Tian L, Quan J, Liu J, Chen X, Wang Y, Shi Z, Zhang J (2012). Validation of the association between PSMA6 -8 C/ G polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese Dongxiang and Han populations. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 98(2): 295–301
Lowe J, Stock D, Jap B, Zwickl P, Baumeister W, Huber R (1995). Crystal structure of the 20S proteasome from the archaeon T. acidophilum at 3.4 A resolution. Science, 268(5210): 533–539
Luan B, Huang X, Wu J, Mei Z, Wang Y, Xue X, Yan C, Wang J, Finley D J, Shi Y, Wang F (2016). Structure of an endogenous yeast 26S proteasome reveals two major conformational states. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 113(10): 2642–2647
Mannhaupt G, Schnall R, Karpov V, Vetter I, Feldmann H (1999). Rpn4p acts as a transcription factor by binding to PACE, a nonamer box found upstream of 26S proteasomal and other genes in yeast. FEBS Lett, 450(1-2): 27–34
Mao I, Liu J, Li X, Luo H (2008). REGgamma, a proteasome activator and beyond? Cellular and molecular life sciences. Cell Mol Life Sci, 65: 3971–3980
Marques A J, Glanemann C, Ramos P C, Dohmen R J (2007). The Cterminal extension of the beta7 subunit and activator complexes stabilize nascent 20 S proteasomes and promote their maturation. J Biol Chem, 282(48): 34869–34876
Marshall R S, Li F, Gemperline D C, Book A J, Vierstra R D (2015). Autophagic degradation of the 26S proteasome is mediated by the dual ATG8/ubiquitin receptor RPN10 in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell, 58(6): 1053–1066
Marshall R S, McLoughlin F, Vierstra R D (2016). Autophagic turnover of inactive 26S Proteasomes in yeast is directed by the ubiquitin receptor Cue5 and the Hsp42 chaperone. Cell Reports, 16(6): 1717–1732
Matyskiela M E, Lander G C, Martin A (2013). Conformational switching of the 26S proteasome enables substrate degradation. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 20(7): 781–788
Mayr J, Seemuller E, Muller S A, Engel A, Baumeister W (1998a). Late events in the assembly of 20S proteasomes. J Struct Biol, 124(2-3): 179–188
Mayr J, Seemuller E, Muller S A, Engel A, Baumeister W (1998b). Late events in the assembly of 20S proteasomes. J Struct Biol, 124(2-3): 179–188
Mayr J, Wang H R, Nederlof P, Baumeister W (1999). The import pathway of human and Thermoplasma 20S proteasomes into HeLa cell nuclei is different from that of classical NLS-bearing proteins. Biol Chem, 380(10): 1183–1192
Meiners S, Heyken D, Weller A, Ludwig A, Stangl K, Kloetzel P M, Kruger E (2003). Inhibition of proteasome activity induces concerted expression of proteasome genes and de novo formation of Mammalian proteasomes. J Biol Chem, 278(24): 21517–21525
Murata S, Sasaki K, Kishimoto T, Niwa S, Hayashi H, Takahama Y, Tanaka K (2007). Regulation of CD8+ T cell development by thymus-specific proteasomes. Science, 316(5829): 1349–1353
Nakamura Y, Umehara T, Tanaka A, Horikoshi M, Padmanabhan B, Yokoyama S (2007). Structural basis for the recognition between the regulatory particles Nas6 and Rpt3 of the yeast 26S proteasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 359(3): 503–509
Nandi D, Woodward E, Ginsburg D B, Monaco J J (1997). Intermediates in the formation of mouse 20S proteasomes: implications for the assembly of precursor beta subunits. EMBO J, 16(17): 5363–5375
Nederlof P M, Wang H R, Baumeister W (1995). Nuclear localization signals of human and Thermoplasma proteasomal alpha subunits are functional in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 92(26): 12060–12064
Pack C G, Yukii H, Toh-e A, Kudo T, Tsuchiya H, Kaiho A, Sakata E, Murata S, Yokosawa H, Sako Y, Baumeister W, Tanaka K, Saeki Y (2014). Quantitative live-cell imaging reveals spatio-temporal dynamics and cytoplasmic assembly of the 26S proteasome. Nat Commun, 5: 3396
Padmanabhan A, Vuong S A, Hochstrasser M (2016). Assembly of an evolutionarily conserved alternative proteasome isoform in human cells. Cell Reports, 14(12): 2962–2974
Pandey U B, Nie Z, Batlevi Y, McCray B A, Ritson G P, Nedelsky N B, Schwartz S L, DiProspero N A, Knight M A, Schuldiner O, Padmanabhan R, Hild M, Berry D L, Garza D, Hubbert C C, Yao T P, Baehrecke E H, Taylor J P (2007). HDAC6 rescues neurodegeneration and provides an essential link between autophagy and the UPS. Nature, 447(7146): 859–863
Panfair D, Ramamurthy A, Kusmierczyk A R (2015). Alpha-ring independent assembly of the 20S proteasome. Sci Rep, 5: 13130
Paraskevopoulos K, Kriegenburg F, TathamMH, Rösner H I, Medina B, Larsen I B, Brandstrup R, Hardwick K G, Hay R T, Kragelund B B, Hartmann-Petersen R, Gordon C (2014). Dss1 is a 26S proteasome ubiquitin receptor. Mol Cell, 56(3): 453–461
Park S, Kim W, Tian G, Gygi S P, Finley D (2011). Structural defects in the regulatory particle-core particle interface of the proteasome induce a novel proteasome stress response. J Biol Chem, 286(42): 36652–36666
Park S, Li X, Kim HM, Singh C R, Tian G, HoytMA, Lovell S, Battaile K P, Zolkiewski M, Coffino P, Roelofs J, Cheng Y, Finley D (2013). Reconfiguration of the proteasome during chaperone-mediated assembly. Nature, 497(7450): 512–516
Park S, Roelofs J, Kim W, Robert J, Schmidt M, Gygi S P, Finley D (2009). Hexameric assembly of the proteasomal ATPases is templated through their C termini. Nature, 459(7248): 866–870
Pathare G R, Nagy I, Sledz P, Anderson D J, Zhou H J, Pardon E, Steyaert J, Forster F, Bracher A, Baumeister W (2014). Crystal structure of the proteasomal deubiquitylation module Rpn8-Rpn11. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 111(8): 2984–2989
Peters L Z, Karmon O, David-Kadoch G, Hazan R, Yu T, Glickman M H, Ben-Aroya S (2015). The protein quality control machinery regulates its misassembled proteasome subunits. PLoS Genet, 11(4): e1005178
Radhakrishnan S K, den Besten W, Deshaies R J (2014). p97-dependent retrotranslocation and proteolytic processing govern formation of active Nrf1 upon proteasome inhibition. eLife, 3: e01856
Radhakrishnan S K, Lee C S, Young P, Beskow A, Chan J Y, Deshaies R J (2010). Transcription factor Nrf1 mediates the proteasome recovery pathway after proteasome inhibition in mammalian cells. Mol Cell, 38(1): 17–28
Ramos P C, Hockendorff J, Johnson E S, Varshavsky A, Dohmen R J (1998). Ump1p is required for proper maturation of the 20S proteasome and becomes its substrate upon completion of the assembly. Cell, 92(4): 489–499
Ramos P C, Marques A J, London M K, Dohmen R J (2004). Role of Cterminal extensions of subunits beta2 and beta7 in assembly and activity of eukaryotic proteasomes. J Biol Chem, 279(14): 14323–14330
Reits E A, Benham A M, Plougastel B, Neefjes J, Trowsdale J (1997). Dynamics of proteasome distribution in living cells. EMBO J, 16(20): 6087–6094
Roelofs J, Park S, Haas W, Tian G, McAllister F E, Huo Y, Lee B H, Zhang F, Shi Y, Gygi S P, Finley D (2009). Chaperone-mediated pathway of proteasome regulatory particle assembly. Nature, 459(7248): 861–865
Russell S J, Steger K A, Johnston S A (1999). Subcellular localization, stoichiometry, and protein levels of 26 S proteasome subunits in yeast. J Biol Chem, 274(31): 21943–21952
Sa-Moura B, Simões A M, Fraga J, Fernandes H, Abreu I A, Botelho H M, Gomes C M, Marques A J, Dohmen R J, Ramos P C, Macedo-Ribeiro S (2013). Biochemical and biophysical characterization of recombinant yeast proteasome maturation factor ump1. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 7(8): e201304006
Sadre-Bazzaz K, Whitby F G, Robinson H, Formosa T, Hill C P (2010). Structure of a Blm10 complex reveals common mechanisms for proteasome binding and gate opening. Mol Cell, 37(5): 728–735
Saeki Y, Toh E A, Kudo T, Kawamura H, Tanaka K (2009). Multiple proteasome-interacting proteins assist the assembly of the yeast 19S regulatory particle. Cell, 137(5): 900–913
Sakata E, Stengel F, Fukunaga K, Zhou M, Saeki Y, Förster F, Baumeister W, Tanaka K, Robinson C V (2011). The catalytic activity of Ubp6 enhances maturation of the proteasomal regulatory particle. Mol Cell, 42(5): 637–649
Satoh T, Saeki Y, Hiromoto T, Wang Y H, Uekusa Y, Yagi H, Yoshihara H, Yagi-Utsumi M, Mizushima T, Tanaka K, Kato K (2014). Structural basis for proteasome formation controlled by an assembly chaperone nas2. Structure, 22(5): 731–743
Savulescu A F, Shorer H, Kleifeld O, Cohen I, Gruber R, GlickmanMH, Harel A (2011). Nuclear import of an intact preassembled proteasome particle. Mol Biol Cell, 22(6): 880–891
Schmidt M, Haas W, Crosas B, Santamaria P G, Gygi S P, Walz T, Finley D (2005). The HEAT repeat protein Blm10 regulates the yeast proteasome by capping the core particle. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 12(4): 294–303
Schmidtke G, Kraft R, Kostka S, Henklein P, Frömmel C, Löwe J, Huber R, Kloetzel PM, Schmidt M(1996). Analysis of mammalian 20S proteasome biogenesis: the maturation of beta-subunits is an ordered two-step mechanism involving autocatalysis. EMBO J, 15: 6887–6898
Schmidtke G, Schmidt M, Kloetzel P M (1997). Maturation of mammalian 20 S proteasome: purification and characterization of 13 S and 16 S proteasome precursor complexes. J Mol Biol, 268(1): 95–106
Schweitzer A, Aufderheide A, Rudack T, Beck F, Pfeifer G, Plitzko JM, Sakata E, Schulten K, Förster F, Baumeister W (2016). Structure of the human 26S proteasome at a resolution of 3.9 A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 113(28): 7816–7821
Sha Z, Goldberg A L (2014). Proteasome-mediated processing of Nrf1 is essential for coordinate induction of all proteasome subunits and p97. Curr Biol, 24(14): 1573–1583
Sharon M, Taverner T, Ambroggio X I, Deshaies R J, Robinson C V (2006). Structural organization of the 19S proteasome lid: insights from MS of intact complexes. PLoS Biol, 4(8): e267
Sharon M, Witt S, Glasmacher E, Baumeister W, Robinson C V (2007). Mass spectrometry reveals the missing links in the assembly pathway of the bacterial 20 S proteasome. J Biol Chem, 282(25): 18448–18457
Shi Y, Chen X, Elsasser S, Stocks B B, Tian G, Lee B H, Shi Y, Zhang N, de Poot S A H, Tuebing F, Sun S, Vannoy J, Tarasov S G, Engen J R, Finley D, Walters K J (2016). Rpn1 provides adjacent receptor sites for substrate binding and deubiquitination by the proteasome. Science
Shirozu R, Yashiroda H, Murata S (2015). Identification of minimum Rpn4-responsive elements in genes related to proteasome functions. FEBS Lett, 589(8): 933–940
Singh C R, Lovell S, Mehzabeen N, Chowdhury W Q, Geanes E S, Battaile K P, Roelofs J (2014). 1.15 A resolution structure of the proteasome-assembly chaperone Nas2 PDZ domain. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun, 70(4): 418–423
Sledz P, Unverdorben P, Beck F, Pfeifer G, Schweitzer A, Forster F, Baumeister W (2013). Structure of the 26S proteasome with ATPgammaS bound provides insights into the mechanism of nucleotidedependent substrate translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 110(18): 7264–7269
Smith D M, Chang S C, Park S, Finley D, Cheng Y, Goldberg A L (2007). Docking of the proteasomal ATPases’ carboxyl termini in the 20S proteasome’s alpha ring opens the gate for substrate entry. Mol Cell, 27(5): 731–744
Sokolova V, Li F, Polovin G, Park S (2015). Proteasome activation is mediated via a functional switch of the Rpt6 C-terminal tail following chaperone-dependent assembly. Sci Rep, 5: 14909
Stadtmueller B M, Hill C P (2011). Proteasome activators. Mol Cell, 41(1): 8–19
Stadtmueller B M, Kish-Trier E, Ferrell K, Petersen C N, Robinson H, Myszka D G, Eckert D M, Formosa T, Hill C P (2012). Structure of a proteasome Pba1-Pba2 complex: implications for proteasome assembly, activation, and biological function. J Biol Chem, 287(44): 37371–37382
Takagi K, Kim S, Yukii H, Ueno M, Morishita R, Endo Y, Kato K, Tanaka K, Saeki Y, Mizushima T (2012). Structural basis for specific recognition of Rpt1p, an ATPase subunit of 26S proteasome, by proteasome-dedicated chaperone Hsm3p. J Biol Chem, 287(15): 12172–12182
Takagi K, Saeki Y, Yashiroda H, Yagi H, Kaiho A, Murata S, Yamane T, Tanaka K, Mizushima T, Kato K (2014). Pba3-Pba4 heterodimer acts as a molecular matchmaker in proteasome alpha-ring formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 450(2): 1110–1114
Takeuchi J, Tamura T (2004). Recombinant ATPases of the yeast 26S proteasome activate protein degradation by the 20S proteasome. FEBS Lett, 565(1-3): 39–42
Tanaka K, Yoshimura T, Tamura T, Fujiwara T, Kumatori A, Ichihara A (1990). Possible mechanism of nuclear translocation of proteasomes. FEBS Lett, 271(1-2): 41–46
Thompson D, Hakala K, De Martino G N (2009). Subcomplexes of PA700, the 19S regulator of the 26 S proteasome, reveal relative roles of AAA subunits in 26 S proteasome assembly and activation and ATPase activity. J Biol Chem, 284(37): 24891–24903
Tian G, Park S, Lee M J, Huck B, McAllister F, Hill C P, Gygi S P, Finley D (2011). An asymmetric interface between the regulatory and core particles of the proteasome. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 18(11): 1259–1267
Tomko R J, Funakoshi M, Schneider K, Wang J, Hochstrasser M (2010). Heterohexameric ring arrangement of the eukaryotic proteasomal ATPases: implications for proteasome structure and assembly. Mol Cell, 38(3): 393–403
Tomko R J Jr, Hochstrasser M (2011). Incorporation of the Rpn12 subunit couples completion of proteasome regulatory particle lid assembly to lid-base joining. Mol Cell, 44(6): 907–917
Tomko R J, Hochstrasser M (2013). Molecular architecture and assembly of the eukaryotic proteasome. Annu Rev Biochem, 82(1): 415–445
Tomko R J, Hochstrasser M(2014). The intrinsically disordered Sem1 protein functions as a molecular tether during proteasome lid biogenesis. Mol Cell, 53(3): 433–443
Tomko R J Jr, Taylor D W, Chen Z A, Wang H W, Rappsilber J, Hochstrasser M (2015). A Single alpha helix drives extensive remodeling of the proteasome lid and completion of regulatory particle assembly. Cell, 163(2): 432–444
Uekusa Y, Okawa K, Yagi-Utsumi M, Serve O, Nakagawa Y, Mizushima T, Yagi H, Saeki Y, Tanaka K, Kato K (2014). Backbone (1)H, (1)(3)C and (1)(5)N assignments of yeast Ump1, an intrinsically disordered protein that functions as a proteasome assembly chaperone. Biomol NMR Assign, 8(2): 383–386
Unno M, Mizushima T, Morimoto Y, Tomisugi Y, Tanaka K, Yasuoka N, Tsukihara T (2002). The structure of the mammalian 20S proteasome at 2.75 A resolution. Structure, 10(5): 609–618
Unverdorben P, Beck F, led P, Schweitzer A, Pfeifer G, Plitzko J M, Baumeister W, Forster F (2014). Deep classification of a large cryo- EM dataset defines the conformational landscape of the 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 111(15): 5544–5549
Ustrell V, Hoffman L, Pratt G, Rechsteiner M (2002). PA200, a nuclear proteasome activator involved in DNA repair. EMBO J, 21(13): 3516–3525
Velichutina I, Connerly P L, Arendt C S, Li X, Hochstrasser M (2004). Plasticity in eucaryotic 20S proteasome ring assembly revealed by a subunit deletion in yeast. EMBO J, 23(3): 500–510
Verma R, et al (2002). Role of Rpn11 metalloprotease in deubiquitination and degradation by the 26S proteasome. Science, 298(5593): 611–615
Volker C, Lupas A N (2002). Molecular evolution of proteasomes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, 268: 1–22
Waite K A, De-La Mota-Peynado A, Vontz G, Roelofs J (2016). Starvation induces proteasome autophagy with different pathways for core and regulatory particles. J Biol Chem, 291(7): 3239–3253
Wang H R, Kania M, Baumeister W, Nederlof P M (1997). Import of human and Thermoplasma 20S proteasomes into nuclei of HeLa cells requires functional NLS sequences. Eur J Cell Biol, 73: 105–113
Wang W, Chan J Y (2006). Nrf1 is targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane by an N-terminal transmembrane domain. Inhibition of nuclear translocation and transacting function. J Biol Chem, 281(28): 19676–19687
Wani P S, Rowland M A, Ondracek A, Deeds E J, Roelofs J (2015). Maturation of the proteasome core particle induces an affinity switch that controls regulatory particle association. Nat Commun, 6: 6384
Wani P S, Suppahia A, Capalla X, Ondracek A, Roelofs J (2016). Phosphorylation of the C-terminal tail of proteasome subunit alpha7 is required for binding of the proteasome quality control factor Ecm29. Sci Rep, 6: 27873
Weberruss MH, Savulescu A F, Jando J, Bissinger T, Harel A, Glickman M H, Enenkel C (2013). Blm10 facilitates nuclear import of proteasome core particles. EMBO J, 32(20): 2697–2707
Wei S J, Williams J G, Dang H, Darden T A, Betz B L, Humble M M, Chang F M, Trempus C S, Johnson K, Cannon R E, Tennant R W (2008). Identification of a specific motif of the DSS1 protein required for proteasome interaction and p53 protein degradation. J Mol Biol, 383(3): 693–712
Welk V, Coux O, Kleene V, Abeza C, Trümbach D, Eickelberg O, Meiners S (2016). Inhibition of proteasome activity induces formation of alternative proteasome complexes. J Biol Chem, 291(25): 13147–13159
Wendler P, Lehmann A, Janek K, Baumgart S, Enenkel C (2004). The bipartite nuclear localization sequence of Rpn2 is required for nuclear import of proteasomal base complexes via karyopherin alphabeta and proteasome functions. J Biol Chem, 279(36): 37751–37762
Whitby F G, Masters E I, Kramer L, Knowlton J R, Yao Y, Wang C C, Hill C P (2000). Structural basis for the activation of 20S proteasomes by 11S regulators. Nature, 408(6808): 115–120
Witt E, Zantopf D, Schmidt M, Kraft R, Kloetzel P M, Kruger E (2000). Characterisation of the newly identified human Ump1 homologue POMP and analysis of LMP7(beta 5i) incorporation into 20 S proteasomes. J Mol Biol, 301(1): 1–9
Wollenberg K, Swaffield J C (2001). Evolution of proteasomal ATPases. Mol Biol Evol, 18(6): 962–974
Worden E J, Padovani C, Martin A (2014). Structure of the Rpn11-Rpn8 dimer reveals mechanisms of substrate deubiquitination during proteasomal degradation. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 21(3): 220–227
Xie Y, Varshavsky A (2001). RPN4 is a ligand, substrate, and transcriptional regulator of the 26S proteasome: a negative feedback circuit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98(6): 3056–3061
Yao T, Cohen R E (2002). A cryptic protease couples deubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. Nature, 419(6905): 403–407
Yao Y, Toth C R, Huang L, Wong M L, Dias P, Burlingame A L, Coffino P, Wang C C (1999). alpha5 subunit in Trypanosoma brucei proteasome can self-assemble to form a cylinder of four stacked heptamer rings. Biochem J, 344(Pt 2): 349–358
Yashiroda H, Mizushima T, Okamoto K, Kameyama T, Hayashi H, Kishimoto T, Niwa S, Kasahara M, Kurimoto E, Sakata E, Takagi K, Suzuki A, Hirano Y, Murata S, Kato K, Yamane T, Tanaka K (2008). Crystal structure of a chaperone complex that contributes to the assembly of yeast 20S proteasomes. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 15(3): 228–236
Yashiroda H, Toda Y, Otsu S, Takagi K, Mizushima T, Murata S (2015). N-terminal alpha7 deletion of the proteasome 20S core particle substitutes for yeast PI31 function. Mol Cell Biol, 35(1): 141–152
Yu Y, Smith D M, Kim H M, Rodriguez V, Goldberg A L, Cheng Y (2010). Interactions of PAN’s C-termini with archaeal 20S proteasome and implications for the eukaryotic proteasome-ATPase interactions. EMBO J, 29(3): 692–702
Yu Z, Livnat-Levanon N, Kleifeld O, Mansour W, Nakasone M A, Castaneda C A, Dixon E K, Fushman D, Reis N, Pick E, GlickmanM H (2015). Base-CP proteasome can serve as a platform for stepwise lid formation. Biosci Rep, 35(3): e00194
Zaiss D M, Standera S, Kloetzel P M, Sijts A J (2002). PI31 is a modulator of proteasome formation and antigen processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99(22): 14344–14349
Zhang F, Hu M, Tian G, Zhang P, Finley D, Jeffrey P D, Shi Y (2009). Structural insights into the regulatory particle of the proteasome from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii. Mol Cell, 34(4): 473–484
Zhang Y, Lucocq J M, Yamamoto M, Hayes J D (2007). The NHB1 (Nterminal homology box 1) sequence in transcription factor Nrf1 is required to anchor it to the endoplasmic reticulum and also to enable its asparagine-glycosylation. Biochem J, 408(2): 161–172
Zhu K, Dunner K Jr, McConkey D J (2010). Proteasome inhibitors activate autophagy as a cytoprotective response in human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene, 29(3): 451–462
Zuhl F, Seemuller E, Golbik R, Baumeister W (1997). Dissecting the assembly pathway of the 20S proteasome. FEBS Lett, 418(1-2): 189–194
Zwickl P, Kleinz J, Baumeister W (1994). Critical elements in proteasome assembly. Nat Struct Biol, 1(11): 765–770
Zwickl P, Ng D, Woo K M, Klenk H P, Goldberg A L (1999). An archaebacterial ATPase, homologous to ATPases in the eukaryotic 26S proteasome, activates protein breakdown by 20 S proteasomes. J Biol Chem, 274(37): 26008–26014
Acknowledgements
The authors apologize to their colleagues whose work could not be discussed due to space limitations. This work was supported in part by start-up funds from the Florida State University College of Medicine (R. J.T.Jr.) and by a Research Support Funds Grant from Indiana University- Purdue University Indianapolis (A.R.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Howell, L.A., Tomko, R.J. & Kusmierczyk, A.R. Putting it all together: intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms governing proteasome biogenesis. Front. Biol. 12, 19–48 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-017-1439-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-017-1439-1