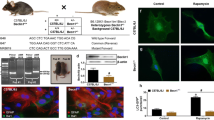
Abstract
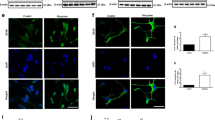
Previously we showed that Beclin1 has a regulatory role in the secretion of inflammatory molecules in glia after exposure to morphine and Tat (an HIV protein). Here we show increased secretion of neuronal growth factors and increased neuronal survival in Beclin1-deficient glia. However, without glia co-culture, neurons deficient in Beclin1 showed greater death and enhanced dendritic beading when compared to wild-type neurons, suggesting that glial-secreted growth factors compensate for the damage reduced autophagy causes neurons. To assess if our ex vivo results correlated with in vivo studies, we used a wild-type (Becn1+/+) and Beclin1-deficient (Becn1+/+) mouse model and intracranially infused the mice with Tat and subcutaneously administered morphine pellets. After morphine implantation, significantly impaired locomotor activities were detected in both Becn1+/+ and Becn1+/- mice, irrespective of Tat infusion. After induction of pain, morphine-induced antinociception was detected. Interestingly, co-exposure to morphine and Tat increased sensitivity to pain in Becn1+/+ mice, but not in similarly treated Becn1+/- mice. Brain homogenates from Becn1+/+ mice exposed to Tat, alone and in combination with morphine, showed increased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduced expression of growth factors when compared to similarly treated Becn1+/- mice. Likewise, increased neuronal loss was detected when both Tat and morphine were administered to Becn1+/+ mice, but not in similarly treated Becn1+/- mice. Overall, our findings show that there is a Beclin1-driven interaction between Tat and morphine in glia and neurons. Moreover, reduced glial-Beclin1 may provide a layer of protection to neurons under stressful conditions, such as when exposed to morphine and Tat.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Sharing
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Alirezaei M, Kiosses WB, Flynn CT, Brady NR, Fox HS (2008) Disruption of neuronal autophagy by infected microglia results in neurodegeneration. PLoS One 3:e2906
Alirezaei M, Kiosses WB, Fox HS (2008) Decreased neuronal autophagy in HIV dementia: a mechanism of indirect neurotoxicity. Autophagy 4:963–966
Antinori A, Arendt G, Becker JT, Brew BJ, Byrd DA, Cherner M, Clifford DB, Cinque P, Epstein LG, Goodkin K, Gisslen M, Grant I, Heaton RK, Joseph J, Marder K, Marra CM, McArthur JC, Nunn M, Price RW, Pulliam L, Robertson KR, Sacktor N, Valcour V, Wojna VE (2007) Updated research nosology for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology 69:1789–1799
Arendt G, Hefter H, Hilperath F, von Giesen HJ, Strohmeyer G, Freund HJ (1994) Motor analysis predicts progression in HIV-associated brain disease. J Neurol Sci 123:180–185
Bansal AK, Mactutus CF, Nath A, Maragos W, Hauser KF, Booze RM (2000) Neurotoxicity of HIV-1 proteins gp120 and Tat in the rat striatum. Brain Res 879:42–49
Bach LA (2018) IGF-binding proteins. J Mol Endocrinol 61:T11-t28
Bains M, Florez-McClure ML, Heidenreich KA (2009) Insulin-like growth factor-I prevents the accumulation of autophagic vesicles and cell death in Purkinje neurons by increasing the rate of autophagosome-to-lysosome fusion and degradation. J Biol Chem 284:20398–20407
Berger JR, Nath A (1997) HIV dementia and the basal ganglia. Intervirology 40:122–131
Berliocchi L, Russo R, Maiarù M, Levato A, Bagetta G, Corasaniti MT (2011) Autophagy impairment in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 7:83–83
Berliocchi L, Maiarù M, Varano GP, Russo R, Corasaniti MT, Bagetta G, Tassorelli C (2015) Spinal autophagy is differently modulated in distinct mouse models of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 11:3–3
Bogulavsky JJ, Gregus AM, Kim PT, Costa AC, Rajadhyaksha AM, Inturrisi CE (2009) Deletion of the glutamate receptor 5 subunit of kainate receptors affects the development of morphine tolerance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:579–587
Boven LA, Middel J, Portegies P, Verhoef J, Jansen GH, Nottet HS (1999) Overexpression of nerve growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in AIDS dementia complex. J Neuroimmunol 97:154–162
Bodor GS (2016) Quantitative, Multidrug Pain Medication Testing by Liquid Chromatography: Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Methods Mol Biol 1383:223–240
Bokhari SM, Yao H, Bethel-Brown C, Fuwang P, Williams R, Dhillon NK, Hegde R, Kumar A, Buch SJ (2009) Morphine enhances Tat-induced activation in murine microglia. J Neurovirol 15:219–228
Bruce-Keller AJ, Turchan-Cholewo J, Smart EJ, Geurin T, Chauhan A, Reid R, Xu R, Nath A, Knapp PE, Hauser KF (2008) Morphine causes rapid increases in glial activation and neuronal injury in the striatum of inducible HIV-1 Tat transgenic mice. Glia 56:1414–1427
Bruce-Keller AJ, Chauhan A, Dimayuga FO, Gee J, Keller JN, Nath A (2003) Synaptic transport of human immunodeficiency virus-Tat protein causes neurotoxicity and gliosis in rat brain. J Neurosci 23:8417–8422
Cao L, Glazyrin A, Kumar S, Kumar A (2017) Role of Autophagy in HIV Pathogenesis and Drug Abuse. Mol Neurobiol 54:5855–5867
Corvin AP, Molinos I, Little G, Donohoe G, Gill M, Morris DW, Tropea D (2012) Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) and its active peptide (1–3)IGF1 enhance the expression of synaptic markers in neuronal circuits through different cellular mechanisms. Neurosci Lett 520:51–56
Chang SL, Connaghan KP, Wei Y, Li MD (2014) NeuroHIV and use of addictive substances. Int Rev Neurobiol 118:403–440
Chao CC, Hu S, Peterson PK (1995) Glia, cytokines, and neurotoxicity. Crit Rev Neurobiol 9:189–205
Chefer VI, Shippenberg TS (2009) Augmentation of Morphine-Induced Sensitization but Reduction in Morphine Tolerance and Reward in Delta-Opioid Receptor Knockout Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:887–898
Chen H, Hu Y, Xie K, Chen Y, Wang H, Bian Y, Wang Y, Dong A, Yu Y (2018) Effect of autophagy on allodynia, hyperalgesia and astrocyte activation in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Int J Mol Med 42:2009–2019
D’Aversa TG, Yu KO, Berman JW (2004) Expression of chemokines by human fetal microglia after treatment with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protein Tat. J Neurovirol 10:86–97
Dever SM, Rodriguez M, Lapierre J, Costin BN, El-Hage N (2015) Differing roles of autophagy in HIV-associated neurocognitive impairment and encephalitis with implications for morphine co-exposure. Front Microbiol 6:653–653
Dolder PC, Liechti ME, Rentsch KM (2015) Development and validation of a rapid turboflow LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of LSD and 2-oxo-3-hydroxy LSD in serum and urine samples of emergency toxicological cases. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:1577–1584
El-Hage N, Bruce-Keller AJ, Yakovleva T, Bazov I, Bakalkin G, Knapp PE, Hauser KF (2008) Morphine exacerbates HIV-1 Tat-induced cytokine production in astrocytes through convergent effects on [Ca(2+)](i), NF-kappaB trafficking and transcription. PLoS One 3:e4093–e4093
El-Hage N, Wu G, Wang J, Ambati J, Knapp PE, Reed JL, Bruce-Keller AJ, Hauser KF (2006) HIV-1 Tat and opiate-induced changes in astrocytes promote chemotaxis of microglia through the expression of MCP-1 and alternative chemokines. Glia 53:132–146
El-Hage N, Rodriguez M, Dever SM, Masvekar RR, Gewirtz DA, Shacka JJ (2015) HIV-1 and morphine regulation of autophagy in microglia: limited interactions in the context of HIV-1 infection and opioid abuse. J Virol 89:1024–1035
Egervari K, Potter G, Guzman-Hernandez ML, Salmon P, Soto-Ribeiro M, Kastberger B, Balla T, Wehrle-Haller B, Kiss JZ (2016) Astrocytes spatially restrict VEGF signaling by polarized secretion and incorporation of VEGF into the actively assembling extracellular matrix. Glia 64:440–456
El-Hage N, Bruce-Keller AJ, Yakovleva T, Bazov I, Bakalkin G, Knapp PE, Hauser KF (2008) Morphine exacerbates HIV-1 Tat-induced cytokine production in astrocytes through convergent effects on [Ca(2+)](i), NF-kappaB trafficking and transcription. PLoS One 3:e4093
El-Hage N, Gurwell JA, Singh IN, Knapp PE, Nath A, Hauser KF (2005) Synergistic increases in intracellular Ca2+, and the release of MCP-1, RANTES, and IL-6 by astrocytes treated with opiates and HIV-1 Tat. Glia 50:91–106
El-Hage N, Wu G, Ambati J, Bruce-Keller AJ, Knapp PE, Hauser KF (2006) CCR2 mediates increases in glial activation caused by exposure to HIV-1 Tat and opiates. J Neuroimmunol 178:9–16
Ellis R, Langford D, Masliah E (2007) HIV and antiretroviral therapy in the brain: neuronal injury and repair. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:33–44
Frake RA, Ricketts T, Menzies FM, Rubinsztein DC (2015) Autophagy and neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest 125:65–74
Ferrara N (2002) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol 29:10–14
Feng YM, Jia YF, Su LY, Wang D, Lv L, Xu L, Yao YG (2013) Decreased mitochondrial DNA copy number in the hippocampus and peripheral blood during opiate addiction is mediated by autophagy and can be salvaged by melatonin. Autophagy 9:1395–1406
Fields J, Dumaop W, Eleuteri S, Campos S, Serger E, Trejo M, Kosberg K, Adame A, Spencer B, Rockenstein E, He JJ, Masliah E (2015) HIV-1 Tat alters neuronal autophagy by modulating autophagosome fusion to the lysosome: implications for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. J Neurosci 35:1921–1938
Fields J, Dumaop W, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Spencer B, Grant I, Ellis R, Letendre S, Patrick C, Adame A, Masliah E (2013) Age-dependent molecular alterations in the autophagy pathway in HIVE patients and in a gp120 tg mouse model: reversal with beclin-1 gene transfer. J Neurovirol 19:89–101
Fitting S, Xu R, Bull C, Buch SK, El-Hage N, Nath A, Knapp PE, Hauser KF (2010) Interactive comorbidity between opioid drug abuse and HIV-1 Tat: chronic exposure augments spine loss and sublethal dendritic pathology in striatal neurons. Am J Pathol 177:1397–1410
Fitting S, Zou S, El-Hage N, Suzuki M, Paris JJ, Schier CJ, Rodriguez JW, Rodriguez M, Knapp PE, Hauser KF (2014) Opiate addiction therapies and HIV-1 Tat: interactive effects on glial [Ca(2)(+)]i, oxyradical and neuroinflammatory chemokine production and correlative neurotoxicity. Curr HIV Res 12:424–434
Fitting S, Stevens DL, Khan FA, Scoggins KL, Enga RM, Beardsley PM, Knapp PE, Dewey WL, Hauser KF (2016) Morphine Tolerance and Physical Dependence Are Altered in Conditional HIV-1 Tat Transgenic Mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 356:96–105
Garza HH Jr, Prakash O, Carr DJ (1996) Aberrant regulation of cytokines in HIV-1 TAT72-transgenic mice. J Immunol 156:3631–3637
Gonek M, McLane VD, Stevens DL, Lippold K, Akbarali HI, Knapp PE, Dewey WL, Hauser KF, Paris JJ (2018) CCR5 mediates HIV-1 Tat-induced neuroinflammation and influences morphine tolerance, dependence, and reward. Brain Behav Immun 69:124–138
Gurwell JA, Nath A, Sun Q, Zhang J, Martin KM, Chen Y, Hauser KF (2001) Synergistic neurotoxicity of opioids and human immunodeficiency virus-1 Tat protein in striatal neurons in vitro. Neuroscience 102:555–563
Guerri C, Pascual M (2019) Impact of neuroimmune activation induced by alcohol or drug abuse on adolescent brain development. Int J Dev Neurosci 77:89–98
Ghazi-Khansari M, Zendehdel R, Pirali-Hamedani M, Amini M (2006) Determination of morphine in the plasma of addicts in using Zeolite Y extraction following high-performance liquid chromatography. Clin Chim Acta 364:235–238
Hauser KF, Fitting S, Dever SM, Podhaizer EM, Knapp PE (2012) Opiate drug use and the pathophysiology of neuroAIDS. Curr HIV Res 10:435–452
Hauser KF, Knapp PE (2014) Interactions of HIV and drugs of abuse: the importance of glia, neural progenitors, and host genetic factors. Int Rev Neurobiol 118:231–313
Harris H, Rubinsztein DC (2011) Control of autophagy as a therapy for neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 8:108–117
Hasbani MJ, Hyrc KL, Faddis BT, Romano C, Goldberg MP (1998) Distinct Roles for Sodium, Chloride, and Calcium in Excitotoxic Dendritic Injury and Recovery. Exp Neurol 154:241–258
Haney MJ, Zhao Y, Fay J, Duhyeong H, Wang M, Wang H, Li Z, Lee YZ, Karuppan MK, El-Hage N, Kabanov AV, Batrakova EV (2020) Genetically modified macrophages accomplish targeted gene delivery to the inflamed brain in transgenic Parkin Q311X(A) mice: importance of administration routes. Sci Rep 10:11818
Hamilton JA (2008) Colony-stimulating factors in inflammation and autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol 8:533–544
Hauser KF, El-Hage N, Stiene-Martin A, Maragos WF, Nath A, Persidsky Y, Volsky DJ, Knapp PE (2007) HIV-1 neuropathogenesis: glial mechanisms revealed through substance abuse. J Neurochem 100:567–586
Hahn YK, Masvekar RR, Xu R, Hauser KF, Knapp PE (2015) Chronic HIV-1 Tat and HIV reduce Rbfox3/NeuN: evidence for sex-related effects. Curr HIV Res 13:10–20
Hayashi Y, Koga Y, Zhang X, Peters C, Yanagawa Y, Wu Z, Yokoyama T, Nakanishi H (2014) Autophagy in superficial spinal dorsal horn accelerates the cathepsin B-dependent morphine antinociceptive tolerance. Neuroscience 275:384–394
Hefti F, Knusel B, Lapchak PA (1993) Protective effects of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor on basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in adult rats with partial fimbrial transections. Prog Brain Res 98:257–263
Hefti F (1994) Neurotrophic factor therapy for nervous system degenerative diseases. J Neurobiol 25:1418–1435
He C, Wei Y, Sun K, Li B, Dong X, Zou Z, Liu Y, Kinch LN, Khan S, Sinha S, Xavier RJ, Grishin NV, Xiao G, Eskelinen EL, Scherer PE, Whistler JL, Levine B (2013) Beclin 2 functions in autophagy, degradation of G protein-coupled receptors, and metabolism. Cell 154:1085–1099
Hollmann M, Heinemann S (1994) Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 17:31–108
Hu P, Thinschmidt JS, Caballero S, Adamson S, Cole L, Chan-Ling T, Grant MB (2015) Loss of survival factors and activation of inflammatory cascades in brain sympathetic centers in type 1 diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 308:E688–E698
Isackson PJ (1995) Trophic factor response to neuronal stimuli or injury. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5:350–357
Imai Y, Kohsaka S (2002) Intracellular signaling in M-CSF-induced microglia activation: role of Iba1. Glia 40:164–174
Ilyas G, Cingolani F, Zhao E, Tanaka K, Czaja MJ (2019) Decreased Macrophage Autophagy Promotes Liver Injury and Inflammation from Alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 43:1403–1413
Ikegaya Y, Kim JA, Baba M, Iwatsubo T, Nishiyama N, Matsuki N (2001) Rapid and reversible changes in dendrite morphology and synaptic efficacy following NMDA receptor activation: implication for a cellular defense against excitotoxicity. J Cell Sci 114:4083–4093
Katsuki H, Itsukaichi Y, Matsuki N (2000) Distinct signaling pathways involved in multiple effects of basic fibroblast growth factor on cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 885:240–250
Kaul M, Garden GA, Lipton SA (2001) Pathways to neuronal injury and apoptosis in HIV-associated dementia. Nature 410:988–994
Kiriyama Y, Nochi H (2015) The Function of Autophagy in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16:26797–26812
Kim YJ, Kong Q, Yamamoto S, Kuramoto K, Huang M, Wang N, Hong JH, Xiao T, Levine B, Qiu X, Zhao Y, Miller RJ, Dong H, Meltzer HY, Xu M, He C (2021) An autophagy-related protein Becn2 regulates cocaine reward behaviors in the dopaminergic system. Sci Adv 7
Koek W, France CP, Javors MA (2012) Morphine-induced motor stimulation, motor incoordination, and hypothermia in adolescent and adult mice. Psychopharmacology 219:1027–1037
Komatsu M, Wang QJ, Holstein GR, Friedrich VL Jr, Iwata J, Kominami E, Chait BT, Tanaka K, Yue Z (2007) Essential role for autophagy protein Atg7 in the maintenance of axonal homeostasis and the prevention of axonal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:14489–14494
Klionsky DJ, Baehrecke EH, Brumell JH, Chu CT, Codogno P, Cuervo AM, Debnath J, Deretic V, Elazar Z, Eskelinen E-L, Finkbeiner S, Fueyo-Margareto J, Gewirtz D, Jäättelä M, Kroemer G, Levine B, Melia TJ, Mizushima N, Rubinsztein DC, Simonsen A, Thorburn A, Thumm M, Tooze SA (2011) A comprehensive glossary of autophagy-related molecules and processes (2nd edition). Autophagy 7:1273–1294
Klionsky DJ, Abdel-Aziz AK, Abdelfatah S, Abdellatif M, Abdoli A, Abel S, Abeliovich H, Abildgaard MH, Abudu YP, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adamopoulos IE, Adeli K, Adolph TE, Adornetto A, Aflaki E, Agam G, Agarwal A, Aggarwal BB, Agnello M, Agostinis P, Agrewala JN, Agrotis A, Aguilar PV, Ahmad ST, Ahmed ZM, Ahumada-Castro U, Aits S, Aizawa S, Akkoc Y, Akoumianaki T, Akpinar HA, Al-Abd AM, Al-Akra L, Al-Gharaibeh A, Alaoui-Jamali MA, Alberti S, Alcocer-Gómez E, Alessandri C, Ali M, Alim Al-Bari MA, Aliwaini S, Alizadeh J, Almacellas E, Almasan A, Alonso A, Alonso GD, Altan-Bonnet N, Altieri DC, Álvarez ÉMC, Alves S et al (2021) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition). Autophagy:1–382
Kramer-Hammerle S, Rothenaigner I, Wolff H, Bell JE, Brack-Werner R (2005) Cells of the central nervous system as targets and reservoirs of the human immunodeficiency virus. Virus Res 111:194–213
Lapierre J, Rodriguez M, Ojha CR, El-Hage N (2018) Critical Role of Beclin1 in HIV Tat and Morphine-Induced Inflammation and Calcium Release in Glial Cells from Autophagy Deficient Mouse. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 13:355–370
Lapierre J, Rodriguez M, Ojha CR, El-Hage N (2018) Critical Role of Beclin1 in HIV Tat and Morphine-Induced Inflammation and Calcium Release in Glial Cells from Autophagy Deficient Mouse. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol
Leonoudakis D, Braithwaite SP, Beattie MS, Beattie EC (2004) TNFalpha-induced AMPA-receptor trafficking in CNS neurons; relevance to excitotoxicity? Neuron Glia Biol 1:263–273
Liao D, Grigoriants OO, Wang W, Wiens K, Loh HH, Law PY (2007) Distinct effects of individual opioids on the morphology of spines depend upon the internalization of mu opioid receptors. Mol Cell Neurosci 35:456–469
Luo J, Elwood F, Britschgi M, Villeda S, Zhang H, Ding Z, Zhu L, Alabsi H, Getachew R, Narasimhan R, Wabl R, Fainberg N, James ML, Wong G, Relton J, Gambhir SS, Pollard JW, Wyss-Coray T (2013) Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) signaling in injured neurons facilitates protection and survival. J Exp Med 210:157–172
Malik S, Khalique H, Buch S, Seth P (2011) A growth factor attenuates HIV-1 Tat and morphine induced damage to human neurons: implication in HIV/AIDS-drug abuse cases. PLoS One 6:e18116
Maragos WF, Tillman P, Jones M, Bruce-Keller AJ, Roth S, Bell JE, Nath A (2003) Neuronal injury in hippocampus with human immunodeficiency virus transactivating protein, Tat. Neuroscience 117:43–53
Mark RJ, Keller JN, Kruman I, Mattson MP (1997) Basic FGF attenuates amyloid beta-peptide-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and impairment of Na+/K+-ATPase activity in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 756:205–214
Menzies FM, Fleming A, Rubinsztein DC (2015) Compromised autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 16:345–357
Morgello S (2018) HIV neuropathology. Handb Clin Neurol 152:3–19
McLane VD, Bergquist I, Cormier J, Barlow DJ, Houseknecht KL, Bilsky EJ, Cao L (2017) Long-term morphine delivery via slow release morphine pellets or osmotic pumps: Plasma concentration, analgesia, and naloxone-precipitated withdrawal. Life Sci 185:1–7
Nath A, Conant K, Chen P, Scott C, Major EO (1999) Transient exposure to HIV-1 Tat protein results in cytokine production in macrophages and astrocytes. A hit and run phenomenon. J Biol Chem 274:17098–17102
Nath A (2015) Eradication of human immunodeficiency virus from brain reservoirs. J Neurovirol 21:227–234
Nath A (2002) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) proteins in neuropathogenesis of HIV dementia. J Infect Dis 186(Suppl 2):S193–S198
Nishiyama J, Miura E, Mizushima N, Watanabe M, Yuzaki M (2007) Aberrant membranes and double-membrane structures accumulate in the axons of Atg5-null Purkinje cells before neuronal death. Autophagy 3:591–596
Ozdinler PH, Macklis JD (2006) IGF-I specifically enhances axon outgrowth of corticospinal motor neurons. Nat Neurosci 9:1371–1381
Pan J, He L, Li X, Li M, Zhang X, Venesky J, Li Y, Peng Y (2017) Activating Autophagy in Hippocampal Cells Alleviates the Morphine-Induced Memory Impairment. Mol Neurobiol 54:1710–1724
Pechan PA, Chowdhury K, Gerdes W, Seifert W (1993) Glutamate induces the growth factors NGF, bFGF, the receptor FGF-R1 and c-fos mRNA expression in rat astrocyte culture. Neurosci Lett 153:111–114
Pullarkat PA, Dommersnes P, Fernández P, Joanny JF, Ott A (2006) Osmotically driven shape transformations in axons. Phys Rev Lett 96:048104
Philippon V, Vellutini C, Gambarelli D, Harkiss G, Arbuthnott G, Metzger D, Roubin R, Filippi P (1994) The basic domain of the lentiviral Tat protein is responsible for damages in mouse brain: involvement of cytokines. Virology 205:519–529
Ribatti D (2008) The discovery of the placental growth factor and its role in angiogenesis: a historical review. Angiogenesis 11:215–221
Rodriguez M, Lapierre J, Ojha CR, Estrada-Bueno H, Dever SM, Gewirtz DA, Kashanchi F, El-Hage N (2017) Importance of Autophagy in Mediating Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Morphine-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction and Inflammation in Human Astrocytes. Viruses 9:201
Rodriguez M, Kaushik A, Lapierre J, Dever SM, El-Hage N, Nair M (2017) Electro-Magnetic Nano-Particle Bound Beclin1 siRNA Crosses the Blood-Brain Barrier to Attenuate the Inflammatory Effects of HIV-1 Infection in Vitro. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology : the Official Journal of the Society on NeuroImmune Pharmacology 12:120–132
Rodriguez M, Lapierre J, Ojha CR, Kaushik A, Batrakova E, Kashanchi F, Dever SM, Nair M, El-Hage N (2017) Intranasal drug delivery of small interfering RNA targeting Beclin1 encapsulated with polyethylenimine (PEI) in mouse brain to achieve HIV attenuation. Sci Rep 7:1862
Rodriguez M, Kaushik A, Lapierre J, Dever SM, El-Hage N, Nair M (2017) Electro-Magnetic Nano-Particle Bound Beclin1 siRNA Crosses the Blood-Brain Barrier to Attenuate the Inflammatory Effects of HIV-1 Infection in Vitro. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 12:120–132
Robinson TE, Kolb B (1999) Morphine alters the structure of neurons in the nucleus accumbens and neocortex of rats. Synapse 33:160–162
Rubinsztein DC, Bento CF, Deretic V (2015) Therapeutic targeting of autophagy in neurodegenerative and infectious diseases. J Exp Med 212:979–990
Sorrell ME, Hauser KF (2014) Ligand-gated purinergic receptors regulate HIV-1 Tat and morphine related neurotoxicity in primary mouse striatal neuron-glia co-cultures. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 9:233–244
Su LY, Luo R, Liu Q, Su JR, Yang LX, Ding YQ, Xu L, Yao YG (2017) Atg5- and Atg7-dependent autophagy in dopaminergic neurons regulates cellular and behavioral responses to morphine. Autophagy 13:1496–1511
Shehata M, Matsumura H, Okubo-Suzuki R, Ohkawa N, Inokuchi K (2012) Neuronal stimulation induces autophagy in hippocampal neurons that is involved in AMPA receptor degradation after chemical long-term depression. J Neurosci 32:10413–10422
Shi Y, Yuan S, Tang SJ (2019) Morphine and HIV-1 gp120 cooperatively promote pathogenesis in the spinal pain neural circuit. Mol Pain 15:1744806919868380
Szebenyi G, Dent EW, Callaway JL, Seys C, Lueth H, Kalil K (2001) Fibroblast growth factor-2 promotes axon branching of cortical neurons by influencing morphology and behavior of the primary growth cone. J Neurosci 21:3932–3941
Tan CC, Yu JT, Tan MS, Jiang T, Zhu XC, Tan L (2014) Autophagy in aging and neurodegenerative diseases: implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Neurobiol Aging 35:941–957
Vidal RL, Matus S, Bargsted L, Hetz C (2014) Targeting autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 35:583–591
Winslow AR, Rubinsztein DC (2008) Autophagy in neurodegeneration and development. Biochim Biophys Acta 1782:723–729
Wong E, Cuervo AM (2010) Autophagy gone awry in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Neurosci 13:805–811
Yang Y, Coleman M, Zhang L, Zheng X, Yue Z (2013) Autophagy in axonal and dendritic degeneration. Trends Neurosci 36:418–428
Yin Y, Yi M-H, Kim DW (2018) Impaired Autophagy of GABAergic Interneurons in Neuropathic Pain. Pain Res Manage 2018:9185368–9185368
Zou S, Fitting S, Hahn YK, Welch SP, El-Hage N, Hauser KF, Knapp PE (2011) Morphine potentiates neurodegenerative effects of HIV-1 Tat through actions at mu-opioid receptor-expressing glia. Brain 134:3616–3631
Zarrindast MR, Vahedy A, Heidari MR, Ghazi KM (1994) On the mechanism(s) of morphine-induced hypothermia. J Psychopharmacol 8:222–226
Zhao T, Adams MH, Zou SP, El-Hage N, Hauser KF, Knapp PE (2007) Silencing the PTEN gene is protective against neuronal death induced by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat. J Neurovirol 13:97–106
Zhao L, Zhu Y, Wang D, Chen M, Gao P, Xiao W, Rao G, Wang X, Jin H, Xu L, Sui N, Chen Q (2010) Morphine induces Beclin 1- and ATG5-dependent autophagy in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells and in the rat hippocampus. Autophagy 6:386–394
Zhou D, Masliah E, Spector SA (2011) Autophagy is increased in postmortem brains of persons with HIV-1-associated encephalitis. J Infect Dis 203:1647–1657
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Chet Raj Ojha for intellectual input. Funding for these studies were provided by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)-National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) grant DA036154 awarded to NEH and grant DA036154-S1 Diversity Supplement awarded to NEH to support JL. National Institute on Mental health (NIMH) grant MH118985 awarded to NEH and National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) T32GM132054-01 support to MP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lapierre, J., Karuppan, M.K.M., Perry, M. et al. Different Roles of Beclin1 in the Interaction Between Glia and Neurons after Exposure to Morphine and the HIV- Trans-Activator of Transcription (Tat) Protein. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 17, 470–486 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-021-10017-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-021-10017-4