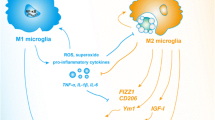
Abstract
Among the many products which influence microglial activation and resulting neuroinflammation, herbal medicine has recently drawn much attention due to its immunomodulatory and neuroprotective activities. The purpose of the current study was to investigate the effects of an extract of Panax notoginseng (NotoG™) on TLR ligand- and IFNγ-induced activation in N9 and EOC20 microglial cells lines. NotoG suppressed microglial activation as measured by reduced expression of accessory molecules (CD40 and CD86), decreased production of inflammatory mediators (IL-6 and TNFα), and diminished release of antibacterial products (nitric oxide). Furthermore, this immunosuppressive activity was neither dependent on the glucocorticoid receptor, nor the result of a single ginsenosides (Rb1, Rg1, or Re), which are the major active constituents of the whole extract. NotoG and select ginsenosides may therefore be of therapeutic benefit in treating or preventing neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis and parkinson’s disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloisi F (2001) Immune function of microglia. Glia 36:165–179
Aloisi F, De Simone R, Columba-Cabezas S, Penna G, Adorini L (2000) Functional maturation of adult mouse resting microglia into an APC is promoted by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interaction with Th1 cells. J Immunol 164:1705–1712
Aloisi F, Ambrosini E, Columba-Cabezas S, Magliozzi R, Serafini B (2001) Intracerebral regulation of immune responses. Ann Med 33:510–515
Amati L, Pepe M, Passeri ME, Mastronardi ML, Jirillo E, Covelli V (2006) Toll-like receptor signaling mechanisms involved in dendritic cell activation: potential therapeutic control of T cell polarization. Curr Pharm Des 12:4247–4254
Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan CS (1999) Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol 58:1685–1693
Barnes P, Powell-Griner E, McFann K, Nahin R (2004) Complemetary and alternative medicine use among adults: United States 2002. In: National Center for Health Statistics, p 343: Centers for disease control and prevention
Becher B, Durell BG, Miga AV, Hickey WF, Noelle RJ (2001) The clinical course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and inflammation is controlled by the expression of CD40 within the central nervous system. J Exp Med 193:967–974
Bhat NR, Zhang P, Lee JC, Hogan EL (1998) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. J Neurosci 18:1633–1641
Blumenthal M (2001) Asian ginseng: potential therapeutic uses. Adv Nurs Pract 9(26–28):33
Bu Y, Jin ZH, Park SY, Baek S, Rho S, Ha N, Park SK, Kim H (2005) Siberian ginseng reduces infarct volume in transient focal cerebral ischaemia in Sprague-Dawley rats. Phytother Res 19:167–169
Chan ED, Morris KR, Belisle JT, Hill P, Remigio LK, Brennan PJ, Riches DW (2001) Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase-NO* by lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by MEK1-ERK, MKK7-JNK, and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Infect Immun 69:2001–2010
Chen XC, Zhu YG, Zhu LA, Huang C, Chen Y, Chen LM, Fang F, Zhou YC, Zhao CH (2003) Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates dopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by suppressing oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol 473:1–7
Chung E, Lee KY, Lee YJ, Lee YH, Lee SK (1998) Ginsenoside Rg1 down-regulates glucocorticoid receptor and displays synergistic effects with cAMP. Steroids 63:421–424
Coleman JW (2002) Nitric oxide: a regulator of mast cell activation and mast cell-mediated inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol 129:4–10
Dalpke AH, Schafer MK, Frey M, Zimmermann S, Tebbe J, Weihe E, Heeg K (2002) Immunostimulatory CpG-DNA activates murine microglia. J Immunol 168:4854–4863
Delclaux C, Azoulay E (2003) Inflammatory response to infectious pulmonary injury. Eur Respir J Suppl 42:10s–14s
Dheen ST, Kaur C, Ling EA (2007) Microglial activation and its implications in the brain diseases. Curr Med Chem 14:1189–1197
Dijkstra IM, de Haas AH, Brouwer N, Boddeke HW, Biber K (2006) Challenge with innate and protein antigens induces CCR7 expression by microglia in vitro and in vivo. Glia 54:861–872
Esiri MM (2007) The interplay between inflammation and neurodegeneration in CNS disease. J Neuroimmunol 184:4–16
Glezer I, Simard AR, Rivest S (2007) Neuroprotective role of the innate immune system by microglia. Neuroscience 147:867–883
Jiang KY, Qian ZN (1995) Effects of Panax notoginseng saponins on posthypoxic cell damage of neurons in vitro. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 16:399–402
Joo SS, Won TJ, Lee DI (2005) Reciprocal activity of ginsenosides in the production of proinflammatory repertoire, and their potential roles in neuroprotection in vivo. Planta Med 71:476–481
Joo SS, Yoo YM, Ahn BW, Nam SY, Kim YB, Hwang KW, do Lee I (2008) Prevention of inflammation-mediated neurotoxicity by Rg3 and its role in microglial activation. Biol Pharm Bull 31:1392–1396
Lee MS, Kim YJ (2007) Signaling pathways downstream of pattern-recognition receptors and their cross talk. Annu Rev Biochem 76:447–480
Leung KW, Pon YL, Wong RN, Wong AS (2006) Ginsenoside-Rg1 induces vascular endothelial growth factor expression through the glucocorticoid receptor-related phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and beta-catenin/T-cell factor-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 281:36280–36288
Leung KW, Leung FP, Huang Y, Mak NK, Wong RN (2007a) Non-genomic effects of ginsenoside-Re in endothelial cells via glucocorticoid receptor. FEBS Lett 581:2423–2428
Leung KW, Yung KK, Mak NK, Chan YS, Fan TP, Wong RN (2007b) Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside-Rg1 in primary nigral neurons against rotenone toxicity. Neuropharmacology 52:827–835
Lin WM, Zhang YM, Moldzio R, Rausch WD (2007) Ginsenoside Rd attenuates neuroinflammation of dopaminergic cells in culture. J Neural Transm Suppl :105–112
Ling C, Li Y, Zhu X, Zhang C, Li M (2005) Ginsenosides may reverse the dexamethasone-induced down-regulation of glucocorticoid receptor. Gen Comp Endocrinol 140:203–209
Lopez MV, Cuadrado MP, Ruiz-Poveda OM, Del Fresno AM, Accame ME (2007) Neuroprotective effect of individual ginsenosides on astrocytes primary culture. Biochim Biophys Acta 1770:1308–1316
Mandel S, Packer L, Youdim MB, Weinreb O (2005) Proceedings from the “Third international conference on mechanism of action of nutraceuticals”. J Nutr Biochem 16:513–520
Muzio L, Martino G, Furlan R (2007) Multifaceted aspects of inflammation in multiple sclerosis: the role of microglia. J Neuroimmunol 191:39–44
Olson JK, Miller SD (2004) Microglia initiate central nervous system innate and adaptive immune responses through multiple TLRs. J Immunol 173:3916–3924
Olsson T, Jagodic M, Piehl F, Wallstrom E (2006) Genetics of autoimmune neuroinflammation. Curr Opin Immunol 18:643–649
Peterson LK, Fujinami RS (2007) Inflammation, demyelination, neurodegeneration and neuroprotection in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 184:37–44
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B (1998) Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 282:2085–2088
Ponomarev ED, Shriver LP, Maresz K, Dittel BN (2005) Microglial cell activation and proliferation precedes the onset of CNS autoimmunity. J Neurosci Res 81:374–389
Ponomarev ED, Shriver LP, Dittel BN (2006) CD40 expression by microglial cells is required for their completion of a two-step activation process during central nervous system autoimmune inflammation. J Immunol 176:1402–1410
Radad K, Gille G, Liu L, Rausch WD (2006) Use of ginseng in medicine with emphasis on neurodegenerative disorders. J Pharmacol Sci 100:175–186
Rausch WD, Liu S, Gille G, Radad K (2006) Neuroprotective effects of ginsenosides. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 66:369–375
Rhule A, Navarro S, Smith JR, Shepherd DM (2006) Panax notoginseng attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory mediators in RAW264.7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 106:121–128
Rock RB, Peterson PK (2006) Microglia as a pharmacological target in infectious and inflammatory diseases of the brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 1:117–126
Schell JB, Crane CA, Smith MF Jr, Roberts MR (2007) Differential ex vivo nitric oxide production by acutely isolated neonatal and adult microglia. J Neuroimmunol 189:75–87
Sengupta S, Toh SA, Sellers LA, Skepper JN, Koolwijk P, Leung HW, Yeung HW, Wong RN, Sasisekharan R, Fan TP (2004) Modulating angiogenesis: the yin and the yang in ginseng. Circulation 110:1219–1225
Suk K (2005) Regulation of neuroinflammation by herbal medicine and its implications for neurodegenerative diseases. A focus on traditional medicines and flavonoids. Neurosignals 14:23–33
Willenborg DO, Staykova M, Fordham S, O’Brien N, Linares D (2007) The contribution of nitric oxide and interferon gamma to the regulation of the neuro-inflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 191:16–25
Wu CF, Bi XL, Yang JY, Zhan JY, Dong YX, Wang JH, Wang JM, Zhang R, Li X (2007) Differential effects of ginsenosides on NO and TNF-alpha production by LPS-activated N9 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol 7:313–320
Xie Z, Wei M, Morgan TE, Fabrizio P, Han D, Finch CE, Longo VD (2002) Peroxynitrite mediates neurotoxicity of amyloid beta-peptide1-42- and lipopolysaccharide-activated microglia. J Neurosci 22:3484–3492
Zhang Z, Guo K, Schluesener HJ (2005) The immunostimulatory activity of CpG oligonucleotides on microglial N9 cells is affected by a polyguanosine motif. J Neuroimmunol 161:68–77
Zhu S, Zou K, Fushimi H, Cai S, Komatsu K (2004) Comparative study on triterpene saponins of Ginseng drugs. Planta Med 70:666–677
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by NIH grants COBRE P20 RR17670 from the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR) and NRSA fellowship ES-013044 (CAB). The authors wish to thank Pamela Shaw and the CEHS Fluorescence Core, as well as Dr. Darrell Jackson at UM for their expert technical assistance.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beamer, C.A., Shepherd, D.M. Inhibition of TLR Ligand- and Interferon Gamma-Induced Murine Microglial Activation by Panax Notoginseng. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7, 465–476 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9333-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9333-0