Abstract
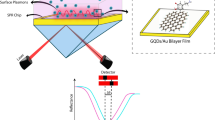
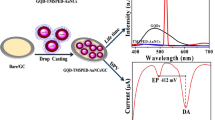
In this study, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique has been utilized to characterize the optical properties of chitosan-graphene quantum dots (CS-GQDs) thin film and dopamine (DA). Theoretical fitting of SPR dips yielded refractive indices of DA solutions and CS-GQDs thin films, as well as the thickness of the thin film. For DA solution, n and k values were the same as deionized water for all concentrations. The values of n and k for CS-GQDs thin film were 1.6990 and 0.1302 respectively before contacting DA. The experimental SPR reflectance curves obtained using CS-GQDs thin film were shifted continuously to the right with increasing DA concentrations. After adsorption of DA molecules, both n and thickness of the CS-GQDs thin film increased, while the value of k decreased. This, in turns, enhanced the SPR sensitivity towards DA. The obtained results underscore the appropriate and sufficient potential of the used technique to measure refractive index variations in real-time when very low concentration was used (1 fM) with refractive index sensitivity of 10.186°/RIU.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Javaheri S, Babaeipour M, Boochani A, Naderi S (2018) Electronic and optical properties of V doped A1N nanosheet : DFT calculations, Chinese. J Phys 56:2698–2709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2018.10.021
Singh S (2002) Refractive index measurement and its applications. Phys Scr 65:167–180. https://doi.org/10.1238/Physica.Regular.065a00167
Mistrik J, Kasap S, Ruda H, Koughia C (2017) Optical properties of electronic materials: fundamentals and characterization. In: Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48933-9
Yang R, Shi M, Wei Q, Wu F, Xue M, Zhou Y (2019) A first-principles study of the properties of P-43m-Si3×2 (X=N, P and As), Chinese. J Phys 59:535–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2019.04.007
Ibrahim J, Al Masri M, Verrier I, Kampfe T, Veillas C, Celle F, Cioulachtjian S, Lefèvre F, Jourlin Y (2019) Surface plasmon resonance based temperature sensors in liquid environment. Sensors 19:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153354
Addanki S, Amiri IS, Yupapin P (2018) Review of optical fibers-introduction and applications in fiber lasers. Results Phys 10:743–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.07.028
Phillips KS, Cheng QJ (2008) Surface plasmon resonance. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-375-6_46
Wang Y, Knoll W, Dostalek J (2012) Bacterial pathogen surface plasmon resonance biosensor advanced by long range surface plasmons and magnetic nanoparticle assays. Anal Chem 84:8345–8350. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac301904x
Hong LH, Yahaya A, Munajat Y (2015) Simulation of surface plasmon resonance sensor. AIP Conf Proc 1674:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4928832
Yanase Y, Sakamoto K, Kobayashi K, Hide M (2016) Diagnosis of immediate-type allergy using surface plasmon resonance. Opt Mater Express 6:1339. https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.6.001339
Mukhtar WM, Murat NF, Samsuri ND, Dasuki KA (2018) Maximizing the response of SPR signal: a vital role of light excitation wavelength. AIP Conf Proc 2016. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5055506
Xia G, Zhou C, Jin S, Huang C, Xing J, Liu Z (2019) Sensitivity enhancement of two-dimensional materials based on genetic optimization in surface plasmon resonance. Sensors (Switzerland) 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051198
Sadafi MM, Karami H, Hosseini M (2021) A tunable hybrid graphene-metal metamaterial absorber for sensing in the THz regime. Curr Appl Phys 31:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2021.07.020
SalmanOgli A, Nasseri B, Kohneh Shahri MY, Piskin E (2016) Plasmon – plasmon interaction effect on effective medium electrical conductivity (an effective agent for photothermal therapy). Curr Appl Phys 16:1498–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2016.08.021
Gomaa M, Salah A, Abdel Fattah G (2022) Utilizing dip-coated graphene/nanogold to enhance SPR-based fiber optic sensor. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 128:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05196-z
Kumar R, Pal S, Pal N, Mishra V, Prajapati YK (2021) High-performance bimetallic surface plasmon resonance biochemical sensor using a black phosphorus–MXene hybrid structure. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 127:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04408-w
Wong CL, Olivo M (2014) Surface plasmon resonance imaging sensors : a review. 809–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9662-3
Lei J, Ji B, Lin J (2016) A high-performance light absorber based on a metamaterial nanopyramid array, Chinese. J Phys 54:940–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2016.09.003
Naz G, Butt FK, Bajwa SZ, Khan WS, Irfan M, Irfan M (2019) Au / Cu 2 O core / shell nanostructures with efficient photoresponses, Chinese. J Phys 59:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2019.03.008
Ben H, Hocini A, Temmar MN, Khedrouche D (2019) Design of mid infrared high sensitive metal-insulator-metal plasmonic sensor, Chinese. J Phys 61:86–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2019.07.006
Zhijian L, Qing Z, Yaonan W, Suxia X (2019) Fano resonance in asymmetric gold nano-dimers with square and rectangular sections, Chinese. J Phys 59:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2019.01.018
Jiang Q, Boyu J, Peng L, Xiaowei S, Haiyan T, Yinping D, Xun G, Zuoqiang H, Jingquan L (2018) Investigation of ultrafast plasmon control in silver block by PEEM, Chinese. J Phys 56:340–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2017.11.015
Pan M, Lee K, Wang L, Wei P (2017) Biosensors and bioelectronics chip-based digital surface plasmon resonance sensing platform for ultrasensitive biomolecular detection. Biosens Bioelectron 91:580–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.003
Caucheteur C, Guo T, Albert J (2015) Review of plasmonic fiber optic biochemical sensors : improving the limit of detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 3883–3897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8411-6
Huang Y, Wu D, Chuang C, Nie B, Cui H, Yun W (2015) Theoretical analysis of tapered fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensor for voltage sensitivity. Opt Fiber Technol 22:42–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2015.01.004
Arghir I, Spasic D, Verlinden BE, Delport F, Lammertyn J (2015) Improved surface plasmon resonance biosensing using silanized optical fibers. Sensors Actuators B Chem 216:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.04.069
Zhao J, Cao S, Liao C, Wang Y, Wang G, Xu X, Fu C, Xu G, Lian J, Wang Y (2016) Surface plasmon resonance refractive sensor based on silver-coated side-polished fiber. Sensors Actuators B Chem 230:206–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.02.020
Chang YF, Wang WH, Hong YW, Yuan RY, Chen KH, Huang YW, Lu PL, Chen YH, Chen YMA, Su LC, Wang SF (2018) Simple strategy for rapid and sensitive detection of avian influenza A H7N9 virus based on intensity-modulated SPR biosensor and new generated antibody. Anal Chem 90:1861–1869. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03934
Fen YW, Yunus WMM, Yusof NA (2012) Surface plasmon resonance optical sensor for detection of Pb 2 + based on immobilized p-tert-butylcalix [4 ] arene-tetrakis in chitosan thin film as an active layer. Sensors Actuators B Chem 171–172:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.03.070
Ali M, Karaaslan M, Sabah C (2018) Metamaterial-based fluid sensor for identifying different types of fuel oil samples, Chinese. J Phys 56:1872–1878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2018.08.018
Zubaidah S, Chao CC, Chau YC, Hanif A, Raziq M, Kooh R, Kumara NTRN, Chiang H (2021) Plasmonic refractive index sensor based on the combination of rectangular and circular resonators including baffles, Chinese. J Phys 71:286–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2021.02.006
Horchani R (2018) Refractive index sensing using a linear graded plasmonic chain of metal nano-particles, Chinese. J Phys 56:1247–1251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2018.03.038
Haque T, Rouf HK (2021) DNA hybridization detection using graphene-MoSe2–Ag heterostructure-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 127:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04888-w
Islam MR, Iftekher ANM, Hasan KR, Nayen MJ, Bin Islam S, Islam R, Khan RL, Moazzam E, Tasnim Z (2021) Surface plasmon resonance based highly sensitive gold coated PCF biosensor. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 127:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04162-5
Chung JW, Kim SD, Bernhardt R, Pyun JC (2005) Application of SPR biosensor for medical diagnostics of human hepatitis B virus (hHBV). Sensors Actuators, B Chem 111–112:416–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2005.03.055
Uzun L, Say R, Ünal S, Denizli A (2009) Production of surface plasmon resonance based assay kit for hepatitis diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2878–2884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.02.021
Uludag Y, Tothill IE (2012) Cancer biomarker detection in serum samples using surface plasmon resonance and quartz crystal microbalance sensors with nanoparticle signal amplification. Anal Chem 84:5898–904. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac300278p
Ertürk G, Özen H, Tümer MA, Mattiasson B, Denizli A (2016) Microcontact imprinting based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor for real-time and ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen (PSA) from clinical samples. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 224:823–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.10.093
He L, Pagneux Q, Larroulet I, Serrano AY, Pesquera A, Zurutuza A, Mandler D, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S (2017) Label-free femtomolar cancer biomarker detection in human serum using graphene-coated surface plasmon resonance chips. Biosens Bioelectron 89:606–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.01.076
Liang RP, Yao GH, Fan LX, Qiu JD (2012) Magnetic Fe 3O 4@Au composite-enhanced surface plasmon resonance for ultrasensitive detection of magnetic nanoparticle-enriched α-fetoprotein. Anal Chim Acta 737:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.05.043
Osman B, Uzun L, Beşirli N, Denizli A (2013) Microcontact imprinted surface plasmon resonance sensor for myoglobin detection. Mater Sci Eng C 33:3609–3614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2013.04.041
Sener G, Uzun L, Say R, Denizli A (2011) Use of molecular imprinted nanoparticles as biorecognition element on surface plasmon resonance sensor. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 160:791–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2011.08.064
Bocková M, Chadtová Song X, Gedeonová E, Levová K, Kalousová M, Zima T, Homola J (2016) Surface plasmon resonance biosensor for detection of pregnancy associated plasma protein A2 in clinical samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:7265–7269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9664-z
Le Brun AP, Soliakov A, Shah DSH, Holt SA, McGill A, Lakey JH (2015) Engineered self-assembling monolayers for label free detection of influenza nucleoprotein. Biomed Microdevices 17:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-9951-z
Zeng C, Huang X, Xu J, Li G, Ma J, Ji HF, Zhu S, Chen H (2013) Rapid and sensitive detection of maize chlorotic mottle virus using surface plasmon resonance-based biosensor. Anal Biochem 440:18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2013.04.026
Cairns TM, Ditto NT, Atanasiu D, Lou H, Brooks BD, Saw WT, Eisenberg RJ, Cohen GH (2019) Surface plasmon resonance reveals direct binding of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gH/gL to gD and locates a gH/gL binding site on gD. J Virol 93:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00289-19
Omidniaee A, Karimi S, Farmani A (2021) Surface plasmon resonance-based SiO2 Kretschmann configuration biosensor for the detection of blood glucose. Silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01081-9
Kamal Eddin FB, Fen YW, Omar NAS, Liew JYC, Daniyal WMEMM (2021) Femtomolar detection of dopamine using surface plasmon resonance sensor based on chitosan / graphene quantum dots thin film. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 120202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120202
Kamal Eddin FB, Fen YW (2020) Recent advances in electrochemical and optical sensing of dopamine. Sensors 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041039
Kamal Eddin FB, Fen YW (2020) The principle of nanomaterials based surface plasmon resonance biosensors and its potential for dopamine detection. Molecules 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122769
Omar NAS, Fen YW, Abdullah J, Mustapha Kamil Y, Daniyal WMEMM, Sadrolhosseini AR, Mahdi MA (2020) Sensitive detection of dengue virus type 2 E-proteins signals using self-assembled monolayers/reduced graphene oxide-PAMAM dendrimer thin film-SPR optical sensor. Sci Rep 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59388-3
Omar NAS, Fen YW, Abdullah J, Zaid MHM, Daniyal WMEMM, Mahdi MA (2019) Sensitive surface plasmon resonance performance of cadmium sulfide quantum dots-amine functionalized graphene oxide based thin film towards dengue virus E-protein. Opt Laser Technol 114:204–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.01.038
Omar NAS, Fen YW (2017) Recent development of SPR spectroscopy as potential method for diagnosis of dengue virus E-protein. Sens Rev. SR-07–2017–0130. https://doi.org/10.1108/SR-07-2017-0130
Omar NAS, Fen YW, Saleviter S, Mohd W, Mustaqim E, Daniyal M, Ain N, Anas A (2019) Development of a graphene-based surface plasmon resonance optical sensor chip for potential biomedical application. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121928
Rosddi NNM, Fen YW, Omar NAS, Anas NAA, Hashim HS, Ramdzan NSM, Fauzi NIM, Anuar MF, Daniyal WMEMM (2021) Glucose detection by gold modified carboxyl-functionalized graphene quantum dots-based surface plasmon resonance. Optik 239:166779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166779
Situ C, Mooney MH, Elliott CT, Buijs J (2010) Advances in surface plasmon resonance biosensor technology towards high-throughput, food-safety analysis. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem 29:1305–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2010.09.003
Zainuddin NH, Fen YW, Alwahib AA, Yaacob MH, Bidin N, Omar NAS, Mahdi MA (2018) Detection of adulterated honey by surface plasmon resonance optical sensor. Optik (Stuttg) 168:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.04.048
Fen YW, Yunus WMM, Talib ZA (2013) Analysis of Pb ( II ) ion sensing by crosslinked chitosan thin film using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Opt-Int J Light Electron Opt 124:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2011.11.035
Daniyal WMEMM, Fen YW, Fauzi NIM, Hashim HS, Ramdzan NSM, Omar NAS (2020) Recent advances in surface plasmon resonance optical sensors for potential application in environmental monitoring. Sensors Mater 32:4191–4200
Ramdzan NSM, Fen YW, Anas NAA, Omar NAS, Saleviter S (2020) Development of biopolymer and conducting polymer-based optical sensors for heavy metal ion detection. Molecules 25:26
Hashim HS, Fen YW, Omar NAS, Abdullah J, Daniyal WMEMM, Saleviter S (2020) Detection of phenol by incorporation of gold modified-enzyme based graphene oxide thin film with surface plasmon resonance technique. Opt Express 28:9738
Fauzi NIM, YW Fen, Omar NAS, Saleviter S, Daniyal WMEMM, Hashim HS, Nasrullah M (2020) Nanostructured chitosan/maghemite composites thin film for potential optical detection of mercury ion by surface plasmon resonance investigation. Polymers 12:1497
Daniyal WMEMM, Fen YW, Abdullah J, Sadrolhosseini AR, Saleviter S, Omar NAS (2018) Exploration of surface plasmon resonance for sensing copper ion based on nanocrystalline cellulose-modified thin film. Opt Express 26:34880
Anas NAA, Fen YW, Omar NAS, Ramdzan NSM, Daniyal WMEMM, Saleviter S, Zainudin AA (2019) Optical properties of chitosan/hydroxyl-functionalized graphene quantum dots thin film for potential optical detection of ferric (III) ion. Opt Laser Technol 120:105724
Anas NAA, Fen YW, Omar NAS, Daniyal WMEMM, Ramdzan NSM, Saleviter S (2019) Development of graphene quantum dots-based optical sensor for toxic metal ion detection. Sensors 19:3850
Ramdzan NSM, Fen YW, Omar NAS, Anas NAA, Daniyal WMEMM, Saleviter S, Zainudin AA (2019) Optical and surface plasmon resonance sensing properties for chitosan/carboxyl-functionalized graphene quantum dots thin film. Optik 178:802–812
Fen YW, Yunus WMM (2013) Surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy as an alternative for sensing heavy metal ions: a review. Sens Rev 33:305–314
Daniyal WMEMM, Saleviter S, Fen YW (2018) Development of surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy for metal ion detection. Sens Mater 30:2023–2038
Zainudin AA, Fen YW, Yusof NA, Al-Rekabi SH, Mahdi MA, Omar NAS (2018) Incorporation of surface plasmon resonance with novel valinomycin doped chitosan-graphene oxide thin film for sensing potassium ion, Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc 191:111–115
Fen YW, Yunus WMM, Yusof NA, Ishak NS, Omar NAS, Zainudin AA (2015) Preparation, characterization and optical properties of ionophore doped chitosan biopolymer thin film and its potential application for sensing metal ion. Optik 126:4688–4692
Anas NAA, Fen YW, Yusof NA, Omar NAS, Daniyal WMEMM, Ramdzan NSM (2020) Highly sensitive surface plasmon resonance optical detection of ferric ion using CTAB/hydroxylated graphene quantum dots thin film. J Appl Phys 128:083105
Daniyal WMEMM, Fen YW, Abdullah J, Sadrolhosseini AR, Saleviter S, Omar NAS (2019) Label-free optical spectroscopy for characterizing binding properties of highly sensitive nanocrystalline cellulose-graphene oxide based nanocomposite towards nickel ion. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 212:25–31
Saleviter S, Fen YW, Daniyal WMEMM, Abdullah J, Sadrolhosseini AR, Omar NAS (2019) Design and analysis of surface plasmon resonance optical sensor for determining cobalt ion based on chitosan-graphene oxide decorated quantum dots-modified gold active layer. Opt Express 27:32294–32307
Hashim HS, Fen YW, Omar NAS, Fauzi NIM, Daniyal WMEMM (2021) Recent advances of priority phenolic compounds detection using phenol oxidases-based electrochemical and optical sensors. Measurement 184:109855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109855
Wei W, Nong J, Zhu Y, Zhang G, Wang N, Luo S, Chen N, Lan G, Chuang CJ, Huang Y (2018) Graphene/Au-enhanced plastic clad silica fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensor. Plasmonics 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0534-0
Arumugasamy SK, Govindaraju S, Yun K (2020) Electrochemical sensor for detecting dopamine using graphene quantum dots incorporated with multiwall carbon nanotubes. Appl Surf Sci 508:145294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145294
Ben Aoun S (2017) Subject Category : Subject Areas : Author for correspondence : Nanostructured carbon electrode modified with N-doped graphene quantum dots – chitosan nanocomposite : a sensitive electrochemical dopamine sensor. R Soc Open Sci 4:1–12
Weng S, Liang D, Qiu H, Liu Z, Lin Z, Zheng Z, Liu A, Chen W, Lin X (2015) Sensors and Actuators B : Chemical A unique turn-off fluorescent strategy for sensing dopamine based on formed polydopamine (pDA) using graphene quantum dots ( GQDs ) as fluorescent probe. Sensors Actuators B Chem 221:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.06.093
Zhou X, Ma P, Wang A, Yu C, Qian T, Wu S, Shen J (2014) Dopamine fluorescent sensors based on polypyrrole/graphene quantum dots core/shell hybrids. Biosens Bioelectron 64:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.09.038
Yan Y, Liu Q, Du X, Qian J, Mao H, Wang K (2015) Visible light photoelectrochemical sensor for ultrasensitive determination of dopamine based on synergistic effect of graphene quantum dots and TiO2 nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 853:258–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.10.021
Fen YW, Yunus WMM (2013) Utilization of chitosan-based sensor thin films for the detection of lead ion by surface plasmon resonance optical sensor. IEEE Sens J 13:1413–1418
Fen YW, Yunus WMM, Yusof NA (2011) Optical properties of cross-linked chitosan thin film for copper ion detection using surface plasmon resonance technique. Opt Appl 41:999–1013
Fen YW, Yunus WMM, Moksin MM, Talib ZA, Yusof NA (2011) Surface plasmon resonance optical sensor for mercury ion detection by crosslinked chitosan thin film. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 13:279–285
Fen YW, Yunus WMM, Talib ZA (2013) Analysis of Pb(II) ion sensing by crosslinked chitosan thin film using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Opt-Int J Light Electron Opt 124:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2011.11.035
Bahrami A, Sadrolhosseini AR, Mamdoohi G, Bahzad K, Abdi MM (2015) Surface plasmon sensor based on polypyrrole multiwalled carbon nanotube composite layer to detect Al (III) in aqueous solution. Dig J Nanomater Biostructures 10:535–541
Schasfoort RBM (2017) Handbook of surface plasmon resonance. Royal Society of Chemistry
Homola J (2006) Electromagnetic theory of surface plasmons. Springer Ser Chem Sens Biosens 3–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/5346_013
Bashkatov AN, Genina EA (2003) Water refractive index in dependence on temperature and wavelength: a simple approximation. Opt Technol Biophys Med IV 5068:393–395
Franca AS, Nollet LML (eds) (2017) Spectroscopic methods in food analysis (1st ed). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315152769
Fernandes SC, Vieira IC, Peralta RA, Neves A (2010) Development of a biomimetic chitosan film-coated gold electrode for determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid. Electrochim Acta 55:7152–7157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.06.062
Shalabney A, Abdulhalim I (2011) Sensitivity-enhancement methods for surface plasmon sensors. Laser Photonics Rev 5:571–606. https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.201000009
Fouad S, Sabri N, Jamal ZAZ, Poopalan P (2017) Surface plasmon resonance sensor sensitivity enhancement using gold-dielectric material. Int J Nanoelectron Mater 10:147–156
Daniyal WMEMM, Fen YW, Abdullah J, Sadrolhosseini AR, Mahdi MA (2021) Design and optimization of surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy for optical constant characterization and potential sensing application: theoretical and experimental approaches. Photonics 8:361
Usman F, Dennis JO, Seong KC, Ahmed AY, Ferrell TL, Fen YW, Sadrolhosseini AR, Ayodele OB, Meriaudeau F, Saidu A (2019) Enhanced sensitivity of surface plasmon resonance biosensor functionalized with doped polyaniline composites for the detection of low-concentration acetone vapour. J Sensors 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5786105
Mudgal N, Saharia A, Agarwal A, Singh G (2020) ZnO and Bi-metallic (Ag–Au) layers-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor with BaTiO3 and graphene for biosensing applications. IETE J Res 1:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2020.1844074
Acknowledgements
F.B.K.E. acknowledges the support received from OWSD and Sida (Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency), the laboratory facilities provided by the Institute of Advanced Technology, Department of Physics, Department of Chemistry, Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Education Malaysia through the Fundamental FRGS (FRGS/1/2019/STG02/UPM/02/1) and Universiti Putra Malaysia through Putra Grant (GP-IPB/2021/9700700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W.F. and F.B.K.E.; methodology, writing—original draft preparation, F.B.K.E.; supervision, validation, funding acquisition, Y.W.F.; writing—review and editing, Y.W.F. and F.B.K.E.; resources, Y.W.F., J.Y.C.L., and W.M.E.M.M.D.; software, Y.W.F., A.R.S., F.B.K.E., and W.M.E.M.M.D.; visualization, F.B.K.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eddin, F.B.K., Fen, Y.W., Sadrolhosseini, A.R. et al. Optical Property Analysis of Chitosan-Graphene Quantum Dots Thin Film and Dopamine Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy. Plasmonics 17, 1985–1997 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-022-01680-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-022-01680-1