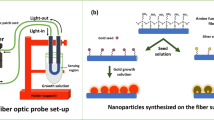
Abstract
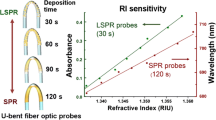
This study shows development of highly sensitive and stable localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR)-active U-bent glass and polymeric optical fiber (GOF and POF) sensor probes by a seed-mediated in situ growth technique. Here, the nickel/nickel oxide seeds (Ni/NiO, 3 to 5 nm size) were formed on the U-region of the fiber probe by sputter coating nickel under a low vacuum (3 Pa), and then, gold nanostructures (AuNSs) were grown over the Ni/NiO seeds. The evanescent wave absorbance (EWA) phenomenon in the U-bent fiber probe was exploited to monitor the growth kinetics of AuNSs in real-time. Experimental observations point to a potential galvanic replacement of Ni by Au. The newly formed AuNSs on U-bent GOF and POF probes gave rise to a LSPR-based refractive index sensitivity of 27.66 and 25.65 ΔA/ΔRIU with plasmonic peak at 600 and 570 nm, respectively. These plasmonic probes show an excellent chemical and mechanical stability, in addition to high surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) activity. This quick and facile technique is highly suitable for large-scale manufacture of reliable plasmonic fiber optic sensor probes for chemical and bio sensing applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Wang X, Wolfbeis OS (2020) Fiber-optic chemical sensors and biosensors (2015–2019). Anal Chem 92:397–430. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04708
Zhao Y, Tongjie, Xia F, Peng Y R (2019) Current status of optical fiber biosensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111505
Esfahani Monfared Y (2020) Overview of recent advances in the design of plasmonic fiber-optic biosensors. Biosensors 10:77. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10070077
Qu JH, Dillen A, Saeys W et al (2020) Advancements in SPR biosensing technology: an overview of recent trends in smart layers design, multiplexing concepts, continuous monitoring and in vivo sensing. Anal Chim Acta 1104:10–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.12.067
Sharma AK, Pandey AK, Kaur B (2018) A review of advancements (2007–2017) in plasmonics-based optical fiber sensors. Opt Fiber Technol 43:20–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2018.03.008
Estevez MC, Otte MA, Sepulveda B, Lechuga LM (2014) Trends and challenges of refractometric nanoplasmonic biosensors: a review. Anal Chim Acta 806:55–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.10.048
Caucheteur C, Guo T, Albert J (2015) Review of plasmonic fiber optic biochemical sensors: improving the limit of detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:3883–3897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8411-6
Rivero PJ, Goicoechea J, Arregui FJ (2017) Localized surface plasmon resonance for optical fiber-sensing applications. In: Nanoplasmonics - Fundam Appl InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/67544
Bilro L, Alberto N, Pinto JL, Nogueira R (2012) Optical sensors based on plastic fibers. Sensors 12:12184–12207. https://doi.org/10.3390/s120912184
Liang G, Luo Z, Liu K et al (2016) Fiber optic surface plasmon resonance-based biosensor technique: fabrication, advancement, and application. Crit Rev Anal Chem 46:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2015.1045119
Miliutina E, Guselnikova O, Chufistova S et al (2019) Fast and all-optical hydrogen sensor based on gold-coated optical fiber functionalized with metal-organic framework layer. ACS Sensors 4:3133–3140. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b01074
Klantsataya E, Jia P, Ebendorff-Heidepriem H et al (2016) Plasmonic fiber optic refractometric sensors: From conventional architectures to recent design trends. Sensors 17:12. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010012
Qian Y, Zhao Y, Wulu Q, Yang Y (2018) Review of salinity measurement technology based on optical fiber sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 260:86–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.077
Velázquez-González JS, Monzón-Hernández D, Moreno-Hernández D et al (2017) Simultaneous measurement of refractive index and temperature using a SPR-based fiber optic sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 242:912–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.164
Wei Y, Wu P, Zhang Y et al (2019) A new application of optical fiber surface plasmon resonance for micro-displacement measurement. Sensors Actuators A Phys 285:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2018.11.007
Wang J, Geng Y, Shen Y et al (2019) SERS-active fiber tip for intracellular and extracellular pH sensing in living single cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem 290:527–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.03.149
Zhang JZ, Noguez C (2008) Plasmonic optical properties and applications of metal nanostructures. Plasmonics 3:127–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-008-9066-y
Zhang Y, Wang G, Yang L et al (2018) Recent advances in gold nanostructures based biosensing and bioimaging. Coord Chem Rev 370:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2018.05.005
Masson J-F (2020) Portable and field-deployed surface plasmon resonance and plasmonic sensors. Analyst 145:3776–3800. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AN00316F
Christopher C, Subrahmanyam A, Sai VVR (2018) Gold sputtered U-bent plastic optical fiber probes as SPR- and LSPR-based compact plasmonic sensors. Plasmonics 13:493–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0535-z
Antohe I, Schouteden K, Goos P et al (2016) Thermal annealing of gold coated fiber optic surfaces for improved plasmonic biosensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 229:678–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.02.034
Cheng S, Chau L (2003) Colloidal gold-modified optical fiber for chemical. Anal Chem 75:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac020310v
Aouani H, Wenger J, Gérard D et al (2009) Crucial role of the adhesion layer on the plasmonic fluorescence enhancement. ACS Nano 3:2043–2048. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900460t
Hoey ML, Carlson JB, Osgood RM et al (2010) rf plasma oxidation of Ni thin films sputter deposited to generate thin nickel oxide layers. Appl Phys Lett 97:153104. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3499661
Sexton BA, Feltis BN, Davis TJ (2008) Characterisation of gold surface plasmon resonance sensor substrates. Sensors Actuators A Phys 141:471–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2007.10.020
Zhu M, Lerum MZ, Chen W (2012) How to prepare reproducible, homogeneous, and hydrolytically stable aminosilane-derived layers on silica. Langmuir 28:416–423. https://doi.org/10.1021/la203638g
Scarpettini AF, Bragas AV (2010) Coverage and aggregation of gold nanoparticles on silanized glasses. Langmuir 26:15948–15953. https://doi.org/10.1021/la102937b
Manoharan H, KC D, Sai VVR, (2020) controlled in situ seed-mediated growth of gold and silver nanoparticles on an optical fiber platform for plasmonic sensing applications. Plasmonics 15:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-01008-6
Gong Y, Zhang S, Gao H et al (2020) Recent advances and comprehensive insights of nickel oxide in emerging optoelectronic devices. Sustainable Energy Fuels 17–33. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SE00621A
Kate RS, Khalate SA, Deokate RJ (2018) Overview of nanostructured metal oxides and pure nickel oxide (NiO) electrodes for supercapacitors: a review. J Alloys Compd 734:89–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.10.262
Hajakbari F (2020) Characterization of nanocrystalline nickel oxide thin films prepared at different thermal oxidation temperatures. J Nanostructure Chem 10:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-020-00332-2
Aydin E, Troughton J, De Bastiani M et al (2018) Room-temperature-sputtered nanocrystalline nickel oxide as hole transport layer for p-i-n perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl Energy Mater 1:6227–6233. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.8b01263
Yang F, Zhou X, Plymale NT et al (2020) Evaluation of sputtered nickel oxide, cobalt oxide and nickel–cobalt oxide on n-type silicon photoanodes for solar-driven O 2 (g) evolution from water. J Mater Chem A 8:13955–13963. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA03725G
Turgut E, Çoban Ö, Sarıtaş S et al (2018) Oxygen partial pressure effects on the RF sputtered p-type NiO hydrogen gas sensors. Appl Surf Sci 435:880–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.133
Oh MH, Yu T, Yu S-H et al (2013) galvanic replacement reactions in metal oxide nanocrystals. Science (80- ) 340:964 LP – 968. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1234751
Sai VVR, Kundu T, Mukherji S (2009) Novel U-bent fiber optic probe for localized surface plasmon resonance based biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2804–2809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.02.007
Gowri A, Sai VVR (2016) Development of LSPR based U-bent plastic optical fiber sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 230:536–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.02.074
Jana NR, Gearheart L, Murphy CJ (2001) Wet chemical synthesis of high aspect ratio cylindrical gold nanorods. J Phys Chem B 105:4065–4067. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0107964
Murphy CJ, Sau TK, Gole AM et al (2005) Anisotropic metal nanoparticles: synthesis, assembly, and optical applications. J Phys Chem B 109:13857–13870. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0516846
Gupta BD, Verma RK (2009) Surface plasmon resonance-based fiber optic sensors: Principle, probe designs, and some applications. J Sensors. 2009:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/979761
Danny CG, Danny Raj M, Sai VVR (2020) Investigating the refractive index sensitivity of u-bent fiber optic sensors using ray optics. J Light Technol 38:1580–1588. https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2019.2958044
Riedl H, Koller CM, Munnik F et al (2016) Influence of oxygen impurities on growth morphology, structure and mechanical properties of Ti-Al-N thin films. Thin Solid Films 603:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2016.01.039
Payne BP, Biesinger MC, McIntyre NS (2012) Use of oxygen/nickel ratios in the XPS characterisation of oxide phases on nickel metal and nickel alloy surfaces. J Electron Spectros Relat Phenomena 185:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elspec.2012.06.008
Fominykh K, Feckl JM, Sicklinger J et al (2014) Ultrasmall dispersible crystalline nickel oxide nanoparticles as high-performance catalysts for electrochemical water splitting. Adv Funct Mater 24:3123–3129. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201303600
Nama Manjunatha K, Paul S (2015) Investigation of optical properties of nickel oxide thin films deposited on different substrates. Appl Surf Sci 352:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.092
Samal AK, Sreeprasad TS, Pradeep T (2010) Investigation of the role of NaBH4 in the chemical synthesis of gold nanorods. J Nanoparticle Res 12:1777–1786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-009-9733-8
Kang S, Kang K, Huh H et al (2017) Reducing agent-assisted excessive galvanic replacement mediated seed-mediated synthesis of porous gold nanoplates and highly efficient gene-thermo cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:35268–35278. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b13028
R. Daniel J, McCarthy LA, Ringe E, Boudreau D, (2019) Enhanced control of plasmonic properties of silver-gold hollow nanoparticles via a reduction-assisted galvanic replacement approach. RSC Adv 9:389–396. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA09364D
Huang J, Han X, Wang D et al (2013) Facile synthesis of dendritic gold nanostructures with hyperbranched architectures and their electrocatalytic activity toward ethanol oxidation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:9148–9154. https://doi.org/10.1021/am402546p
Gilroy KD, Farzinpour P, Sundar A et al (2014) Sacrificial templates for galvanic replacement reactions: design criteria for the synthesis of pure pt nanoshells with a smooth surface morphology. Chem Mater 26:3340–3347. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm501418d
Cetin AE, Coskun AF, Galarreta BC et al (2014) Handheld high-throughput plasmonic biosensor using computational on-chip imaging. Light Sci Appl 3:e122–e122. https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2014.3
Luo Z, Wang Y, Xu Y et al (2019) Ultrasensitive U-shaped fiber optic LSPR cytosensing for label-free and in situ evaluation of cell surface N-glycan expression. Sensors Actuators B Chem 284:582–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.015
Bin ZL, Yin J, Zheng YM et al (2014) Self-assembly of Au nanoparticles on PMMA template as flexible, transparent, and highly active SERS substrates. Anal Chem 86:6262–6267. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac404224f
Qiu H, Wang M, Jiang S et al (2017) Reliable molecular trace-detection based on flexible SERS substrate of graphene/Ag-nanoflowers/PMMA. Sensors Actuators B Chem 249:439–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.118
Fang C, Agarwal A, Buddharaju KD et al (2008) DNA detection using nanostructured SERS substrates with Rhodamine B as Raman label. Biosens Bioelectron 24:216–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2008.03.032
Ran Y, Strobbia P, Cupil-Garcia V, Vo-Dinh T (2019) Fiber-optrode SERS probes using plasmonic silver-coated gold nanostars. Sensors Actuators B Chem 287:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.167
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from Indo-German Science & Technology Centre (IGSTC) and Indo-UK water quality research program funded by Department of Science and Technology (DST), India. The authors thank Prof. A. Subrahmanyam (Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Madras) for giving access to UV-visible and Raman spectrometer facility. We also acknowledge HR-SEM and sputtering facility in Chemical Engineering, IIT Madras funded by FIST grant from DST, India. Hariharan Manoharan acknowledges the PhD scholarship from Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India. We thank Mr. S. Allwyn (research scholar, IITM) and Mr. Lakshmana Swamy (Project officer, IITM) for designing the customized white LED light source.
Funding
The authors received financial support from Indo-German Science & Technology Centre (IGSTC) and Indo-UK water quality research program funded by Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hariharan Manoharan: conception/design of the work; data acquisition, analysis, interpretation, and manuscript writing.
Dharanibalaji K C: conception/design of the work, data acquisition, and analysis.
V. V. R. Sai: conception/design of the work, data analysis, interpretation, manuscript editing, and project management.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manoharan, H., KC, D. & Sai, V.V.R. Highly Stable Plasmonic Nanostructures on a Nickel-Sputtered Glass and Polymeric Optical Fiber Sensors. Plasmonics 16, 1307–1318 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01400-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01400-1