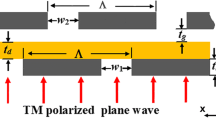
Abstract
We present a theoretical analysis of the effects of short range surface plasmon polariton excitation on subwavelength bridges in metal gratings. We show that localized resonances in thin metal bridges placed within the slit of a free-standing silver grating dramatically modify transmission spectra and boost absorption regardless of the periodicity of the grating. Additionally, the interference of multiple localized resonances makes it possible to tailor the absorption properties of ultrathin gratings, regardless of the apertures’ geometrical size. This tunable, narrow band, enhanced–absorption mechanism triggered by resonant, short-range surface plasmon polaritons may also enhance nonlinear optical processes like harmonic generation, in view of the large third-order susceptibility of metals.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wood RW (1902) On a remarkable case of uneven distribution of light in a diffraction grating spectrum. Proc Phys Soc Lond 18(1):269
Wood RW (1912) XXVII. Diffraction gratings with controlled groove form and abnormal distribution of intensity. Philosophical Magazine Series 6 23(134):310–317
Hessel A, Oliner AA (1965) A new theory of Wood’s Anomalies on optical gratings. Appl Opt 4(10):1275–1297
Ebbesen TW, Lezec HJ, Ghaemi HF, Thio T, Wolff PA (1998) Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 391(6668):667–669
Garcia-Vidal FJ, Martin-Moreno L, Ebbesen TW, Kuipers L (2010) Light passing through subwavelength apertures. Rev Mod Phys 82(1):729–787
Thio T, Ghaemi HF, Lezec HJ, Wolff PA, Ebbesen TW (1999) Surface-plasmon-enhanced transmission through hole arrays in Cr films. J Opt Soc Am B 16(10):1743–1748
Porto JA, García-Vidal FJ, Pendry JB (1999) Transmission resonances on metallic gratings with very narrow slits. Phys Rev Lett 83(14):2845–2848
Ghaemi HF, Thio T, Grupp DE, Ebbesen TW, Lezec HJ (1998) Surface plasmons enhance optical transmission through subwavelength holes. Physical Review B 58(11):6779–6782
Vincenti M, de Ceglia D, Buncick M, Akozbek N, Bloemer M, Scalora M (2010) Extraordinary transmission in the ultraviolet range from subwavelength slits on semiconductors. J Appl Phys 107(5):053101–053106
de Ceglia D, Vincenti MA, Scalora M, Akozbek N, Bloemer MJ (2011) Plasmonic band edge effects on the transmission properties of metal gratings. AIP Adv 1(3):032151–032115
Aközbek N, Mattiucci N, de Ceglia D, Trimm R, Alù A, D’Aguanno G, Vincenti M, Scalora M, Bloemer M (2012) Experimental demonstration of plasmonic Brewster angle extraordinary transmission through extreme subwavelength slit arrays in the microwave. Physical Review B 85(20):205430
Gómez Rivas J, Schotsch C, Haring Bolivar P, Kurz H (2003) Enhanced transmission of THz radiation through subwavelength holes. Physical Review B 68(20):201306
Janke C, Rivas JG, Schotsch C, Beckmann L, Bolivar PH, Kurz H (2004) Optimization of enhanced terahertz transmission through arrays of subwavelength apertures. Physical Review B 69(20):205314
Yang F, Sambles JR (2002) Resonant transmission of microwaves through a narrow metallic slit. Phys Rev Lett 89(6):063901
Xie Y, Zakharian A, Moloney J, Mansuripur M (2004) Transmission of light through slit apertures in metallic films. Opt Express 12(25):6106–6121
Grande M, Vincenti MA, Stomeo T, Morea G, Marani R, Marrocco V, Petruzzelli V, D’Orazio A, Cingolani R, De Vittorio M, de Ceglia D, Scalora M (2011) Experimental demonstration of a novel bio-sensing platform via plasmonic band gap formation in gold nano-patch arrays. Opt Express 19(22):21385–21395
Vincenti MA, Petruzzelli V, D’Orazio A, Prudenzano F, Bloemer MJ, Akozbek N, Scalora M (2008) Second harmonic generation from nanoslits in metal substrates: applications to palladium-based H2 sensor. Journal of Nanophotonics 2(1):021851–021851
Min C, Wang P, Chen C, Deng Y, Lu Y, Ming H, Ning T, Zhou Y, Yang G (2008) All-optical switching in subwavelength metallic grating structure containing nonlinear optical materials. Opt Lett 33(8):869–871
Provine J, Skinner J, Horsley DA (2006) Subwavelength metal grating tunable filter. In: Micro electro mechanical systems. 19th IEEE International Conference on MEMS 2006. Istanbul, Turkey, January 22–26, 2006. pp 854–857.
Vincenti M, Grande M, de Ceglia D, Stomeo T, Petruzzelli V, De Vittorio M, Scalora M, D’Orazio A (2012) Color control through plasmonic metal gratings. Appl Phys Lett 100(20):201107
Lee H-S, Yoon Y-T, S-s L, Kim S-H, Lee K-D (2007) Color filter based on a subwavelength patterned metal grating. Opt Express 15(23):15457–15463
Grande M, Bianco GV, Vincenti MA, Stomeo T, de Ceglia D, De Vittorio M, Petruzzelli V, Scalora M, Bruno G, D’Orazio A (2012) Experimental surface-enhanced Raman scattering response of two-dimensional finite arrays of gold nanopatches. Appl Phys Lett 101(11):111606–111604
Lesuffleur A, Kumar LKS, Brolo AG, Kavanagh KL, Gordon R (2007) Apex-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using double-hole arrays in a gold film. J Phys Chem C 111(6):2347–2350
Chan CY, Xu JB, Waye MY, Ong HC (2010) Angle resolved surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) on two-dimensional metallic arrays with different hole sizes. Appl Phys Lett 96(3):033104–033103
Hao Q, Wang B, Bossard JA, Kiraly B, Zeng Y, Chiang IK, Jensen L, Werner DH, Huang TJ (2012) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering study on graphene-coated metallic nanostructure substrates. J Phys Chem C 116(13):7249–7254
Scalora M, Vincenti M, De Ceglia D, Roppo V, Centini M, Akozbek N, Bloemer M (2010) Second- and third-harmonic generation in metal-based structures. Physical Review A 82(4):043828
Vincenti M, de Ceglia D, Roppo V, Scalora M (2011) Harmonic generation in metallic, GaAs-filled nanocavities in the enhanced transmission regime at visible and UV wavelengths. Opt Express 19(3):2064–2078
Vincenti MA, de Ceglia D, Scalora M (2011) Nonlinear response of GaAs gratings in the extraordinary transmission regime. Opt Lett 36(23):4674–4676
van Nieuwstadt JAH, Sandtke M, Harmsen RH, Segerink FB, Prangsma JC, Enoch S, Kuipers L (2006) Strong modification of the nonlinear optical response of metallic subwavelength hole arrays. Phys Rev Lett 97(14):146102
Fan W, Zhang S, Malloy KJ, Brueck SRJ, Panoiu NC, Osgood RM (2006) Second harmonic generation from patterned GaAs inside a subwavelength metallic hole array. Opt Express 14(21):9570–9575
Barakat EH, Bernal MP, Baida FI (2010) Second harmonic generation enhancement by use of annular aperture arrays embedded into silver and filled by lithium niobate. Opt Express 18(7):6530–6536
Liu N, Mesch M, Weiss T, Hentschel M, Giessen H (2010) Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Letters 10(7):2342–2348
Konstantatos G, Sargent EH (2010) Nanostructured materials for photon detection. Nat Nano 5(6):391–400
Diem M, Koschny T, Soukoulis CM (2009) Wide-angle perfect absorber/thermal emitter in the terahertz regime. Physical Review B 79(3):033101
Atwater HA, Polman A (2010) Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat Mater 9(3):205–213
Le Perchec J, Quémerais P, Barbara A, López-Ríos T (2008) Why metallic surfaces with grooves a few nanometers deep and wide may strongly absorb visible light. Phys Rev Lett 100(6):066408
Popov EK, Bonod N, Enoch S (2007) Comparison of plasmon surface waves on shallow and deep metallic 1D and 2D gratings. Opt Express 15(7):4224–4237
Gan Q, Gao Y, Wagner K, Vezenov D, Ding YJ, Bartoli FJ (2011) Experimental verification of the rainbow trapping effect in adiabatic plasmonic gratings. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Miyazaki HT, Kurokawa Y (2006) Controlled plasmon resonance in closed metal/insulator/metal nanocavities. Appl Phys Lett 89(21):211126–211123
Sobnack MB, Tan WC, Wanstall NP, Preist TW, Sambles JR (1998) Stationary surface plasmons on a zero-order metal grating. Phys Rev Lett 80(25):5667–5670
Kuttge M, García de Abajo FJ, Polman A (2009) How grooves reflect and confine surface plasmon polaritons. Opt Express 17(12):10385–10392
Bozhevolnyi SI, Volkov VS, Devaux E, Ebbesen TW (2005) Channel plasmon-polariton guiding by subwavelength metal grooves. Phys Rev Lett 95(4):046802
Vengurlekar AS (2008) Optical properties of metallo-dielectric deep trench gratings: role of surface plasmons and Wood-Rayleigh anomaly. Opt Lett 33(15):1669–1671
Bonod N, Tayeb G, Maystre D, Enoch S, Popov E (2008) Total absorption of light by lamellar metallic gratings. Opt Express 16(20):15431–15438
Hooper IR, Sambles JR (2003) Surface plasmon polaritons on thin-slab metal gratings. Physical Review B 67(23):235404
Tan WC, Preist TW, Sambles RJ (2000) Resonant tunneling of light through thin metal films via strongly localized surface plasmons. Physical Review B 62(16):11134–11138
Raether H (1988) Surface plasmons on smooth and rough surfaces and on gratings, vol 111. Springer, New York
Economou EN (1969) Surface plasmons in thin films. Physical Review 182(2):539–554
Dionne JA, Sweatlock LA, Atwater HA, Polman A (2006) Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization. Physical Review B 73(3):035407
Novotny L (2007) Effective wavelength scaling for optical antennas. Phys Rev Lett 98(26):266802
Søndergaard T, Bozhevolnyi SI (2008) Strip and gap plasmon polariton optical resonators. Physica Status Solidi (B) 245(1):9–19
Ritchie RH (1957) Plasma losses by fast electrons in thin films. Physical Review 106(5):874–881
Nelder JA, Mead R (1965) A Simplex method for function minimization. Comput J 7(4):308–313
Barnard ES, White JS, Chandran A, Brongersma ML (2008) Spectral properties of plasmonic resonator antennas. Opt Express 16(21):16529–16537
Palik ED, Ghosh G (1998) Handbook of optical constants of solids, vol 3. Academic, New York
Moharam MG, Gaylord TK (1981) Rigorous coupled-wave analysis of planar-grating diffraction. J Opt Soc Am 71(7):811–818
Dorfmüller J, Vogelgesang R, Khunsin W, Rockstuhl C, Etrich C, Kern K (2010) Plasmonic nanowire antennas: experiment, simulation, and theory. Nano Letters 10(9):3596–3603
Coronado EA, Schatz GC (2003) Surface plasmon broadening for arbitrary shape nanoparticles: a geometrical probability approach. J Chem Phys 119(7):3926–3934
Hesketh PJ, Zemel JN, Gebhart B (1986) Organ pipe radiant modes of periodic micromachined silicon surfaces. Nature 324(6097):549–551
Rechberger W, Hohenau A, Leitner A, Krenn JR, Lamprecht B, Aussenegg FR (2003) Optical properties of two interacting gold nanoparticles. Opt Commun 220(1–3):137–141
Su KH, Wei QH, Zhang X, Mock JJ, Smith DR, Schultz S (2003) Interparticle coupling effects on plasmon resonances of nanogold particles. Nano Letters 3(8):1087–1090
Braun J, Gompf B, Kobiela G, Dressel M (2009) How holes can obscure the view: suppressed transmission through an ultrathin metal film by a subwavelength hole array. Phys Rev Lett 103(20):203901
Spevak IS, Nikitin AY, Bezuglyi EV, Levchenko A, Kats AV (2009) Resonantly suppressed transmission and anomalously enhanced light absorption in periodically modulated ultrathin metal films. Physical Review B 79(16):161406
D’Aguanno G, Mattiucci N, Alù A, Bloemer MJ (2011) Quenched optical transmission in ultrathin subwavelength plasmonic gratings. Physical Review B 83(3):035426
Ghoshal A, Kik PG (2008) Theory and simulation of surface plasmon excitation using resonant metal nanoparticle arrays. J Appl Phys 103(11):113111–113118
Jouy P, Todorov Y, Vasanelli A, Colombelli R, Sagnes I, Sirtori C (2011) Coupling of a surface plasmon with localized subwavelength microcavity modes. Appl Phys Lett 98(2):021105–021103
He M-D, Gong Z-Q, Li S, Luo Y-F, Liu J-Q, Chen X (2010) Light transmission through metallic slit with a bar. Solid State Communications 150(29–30):1283–1286
Lee K-L, Lee C-W, Wei P-K (2007) Sensitive detection of nanoparticles using metallic nanoslit arrays. Appl Phys Lett 90(23):233119–233113
Acknowledgments
This research was performed while the authors M. A. Vincenti and D. de Ceglia held a National Research Council Research Associateship award at the U.S. Army Aviation and Missile Research Development and Engineering Center. M. Grande thanks the U.S. Army International Technology Center Atlantic for financial support (contract no. W911NF-12-1-0292). The authors also thank F. Dioguardi for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vincenti, M.A., de Ceglia, D., Grande, M. et al. Tailoring Absorption in Metal Gratings with Resonant Ultrathin Bridges. Plasmonics 8, 1445–1456 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9558-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9558-2